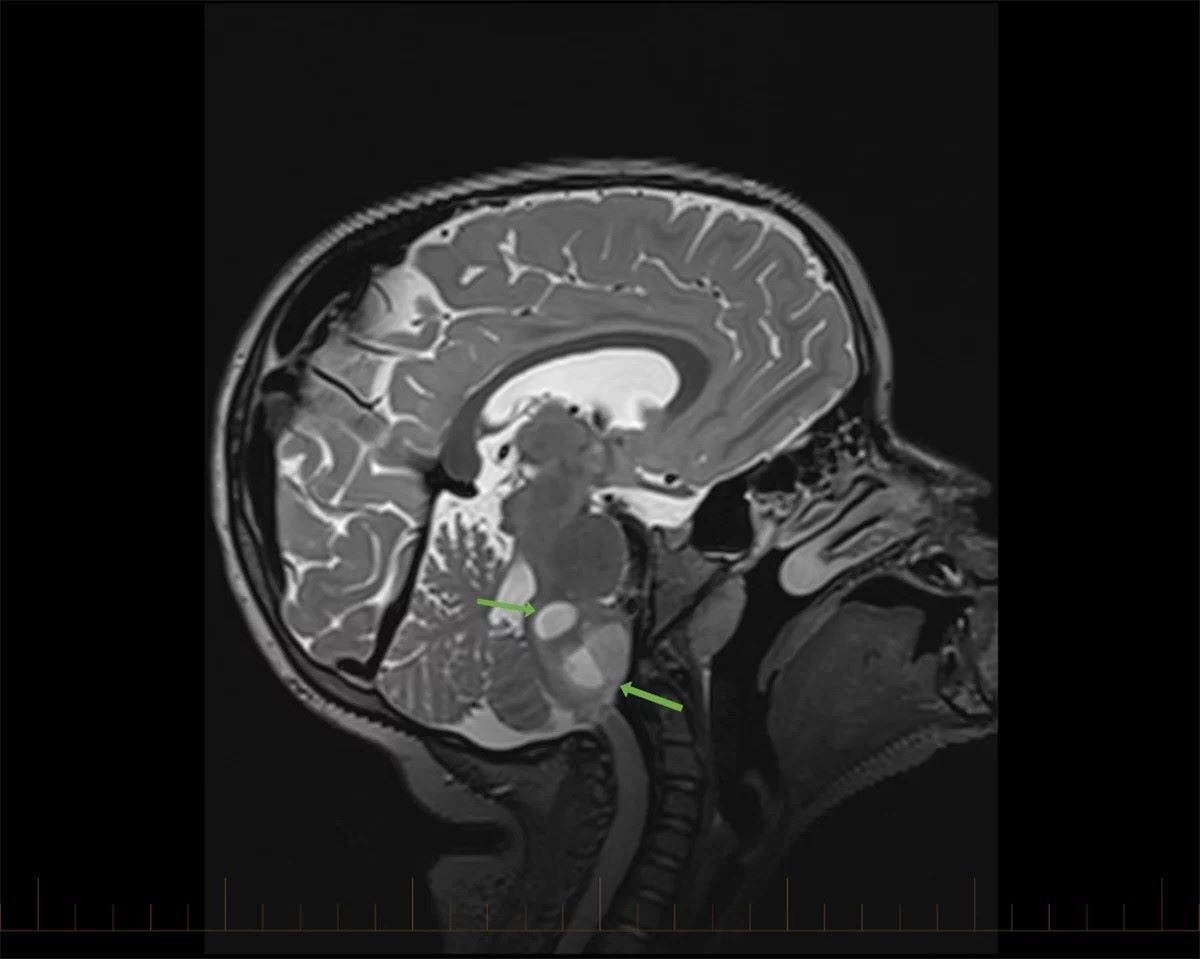
Cerebral astrocytoma might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it is crucial. What exactly is cerebral astrocytoma? It's a type of brain tumor that starts in star-shaped brain cells called astrocytes, which are part of the supportive tissue of the brain. These tumors can vary in their behavior, from slow-growing to aggressive. Knowing the facts about this condition can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment. Symptoms might include headaches, seizures, or changes in behavior, depending on the tumor's location. Treatments often involve surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, tailored to the tumor's grade and size. Awareness and early detection can make a significant difference in managing this condition. Understanding cerebral astrocytoma is not just for medical professionals; it's important for everyone to be informed.
Key Takeaways:
- Cerebral astrocytoma, a type of brain tumor, varies in severity. Surgery, radiation, and targeted therapy are common treatments. Support and lifestyle adjustments are important for patients' well-being.
- Understanding the risks and prevention of cerebral astrocytoma is crucial. Genetic factors, radiation exposure, and family history play a role. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle may reduce overall cancer risk.
Understanding Cerebral Astrocytoma
Cerebral astrocytoma is a type of brain tumor that originates from astrocytes, star-shaped cells in the brain. These tumors can vary greatly in their behavior and prognosis. Let's explore some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Astrocytes' Role: Astrocytes are crucial for maintaining the blood-brain barrier and providing nutrients to nervous tissue. They also play a role in repairing the brain and spinal cord after injuries.
-
Tumor Grades: Cerebral astrocytomas are classified into four grades. Grades I and II are low-grade, while III and IV are high-grade, with grade IV being the most aggressive, known as glioblastoma.
-
Common in Adults: These tumors are more common in adults than children, with the majority occurring in individuals aged 45 to 70.
-
Symptoms Vary: Symptoms depend on the tumor's location and size. Common signs include headaches, seizures, and changes in personality or memory.
-
Diagnosis Tools: MRI and CT scans are primary tools for diagnosing cerebral astrocytomas. They help determine the tumor's size and location.
Treatment Options
Treatment for cerebral astrocytoma can be complex and depends on several factors. Here are some key points about the available treatments.
-
Surgery First: Surgery is often the first line of treatment to remove as much of the tumor as possible.
-
Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells and is often used after surgery to target remaining tumor cells.
-
Chemotherapy Use: Chemotherapy involves drugs that kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It's more commonly used for high-grade astrocytomas.
-
Targeted Therapy: This newer treatment targets specific genes or proteins that contribute to cancer growth, offering a more personalized approach.
-
Clinical Trials: Patients may have the option to participate in clinical trials, which test new treatments or drugs.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Understanding the prognosis and survival rates for cerebral astrocytoma is crucial for patients and their families. Here are some insights.
-
Varied Prognosis: Prognosis varies widely depending on the tumor's grade. Low-grade astrocytomas have a better outlook than high-grade ones.
-
Survival Rates: The five-year survival rate for low-grade astrocytomas is around 60-80%, while for glioblastomas, it's about 5-10%.
-
Age Factor: Younger patients generally have a better prognosis compared to older individuals.
-
Complete Resection: Complete surgical removal of the tumor can significantly improve survival rates.
-
Recurrence Risk: High-grade astrocytomas have a higher risk of recurrence even after treatment.
Research and Advancements
Ongoing research is crucial for improving treatment and outcomes for cerebral astrocytoma patients. Here are some recent advancements.
-
Genetic Research: Scientists are studying genetic mutations that may contribute to astrocytoma development, which could lead to targeted therapies.
-
Immunotherapy Potential: Immunotherapy, which uses the body's immune system to fight cancer, is being explored as a treatment option.
-
Biomarker Discovery: Researchers are identifying biomarkers that could help in early detection and treatment planning.
-
Artificial Intelligence: AI is being used to analyze medical images and predict tumor behavior, aiding in more accurate diagnoses.
-
Personalized Medicine: Advances in personalized medicine are allowing treatments to be tailored to individual patients based on their genetic makeup.
Living with Cerebral Astrocytoma
Living with a cerebral astrocytoma can be challenging, but understanding and support can make a difference. Here are some aspects of life with this condition.
-
Support Systems: Having a strong support system, including family, friends, and support groups, is vital for patients.
-
Rehabilitation Needs: Rehabilitation therapies, such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy, can help patients regain lost skills.
-
Cognitive Challenges: Patients may face cognitive challenges, requiring strategies to manage memory and concentration issues.
-
Emotional Impact: The emotional toll of a brain tumor diagnosis can be significant, making mental health support important.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments: Patients may need to make lifestyle adjustments, including changes in diet and exercise, to improve their quality of life.
Prevention and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of cerebral astrocytoma is unknown, certain risk factors have been identified. Here are some facts about prevention and risks.
-
Genetic Factors: Some genetic conditions, like neurofibromatosis, can increase the risk of developing astrocytomas.
-
Radiation Exposure: Previous exposure to radiation, especially to the head, can increase the risk of brain tumors.
-
Family History: A family history of brain tumors may slightly increase the risk.
-
Environmental Factors: Research is ongoing into environmental factors that may contribute to brain tumor development.
-
Healthy Lifestyle: While not a guarantee, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise may reduce overall cancer risk.
Final Thoughts on Cerebral Astrocytoma
Cerebral astrocytoma is a complex condition that affects many lives. Understanding its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can make a big difference for those impacted. Early detection is crucial, as it often leads to better outcomes. Symptoms like headaches, seizures, or changes in behavior shouldn't be ignored. Diagnosis usually involves imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, and sometimes a biopsy. Treatment varies depending on the tumor's grade and location, but it often includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Research is ongoing, offering hope for improved therapies and outcomes. Staying informed and seeking medical advice when needed can empower patients and their families. Knowledge is power, and being aware of the facts surrounding cerebral astrocytoma can lead to better decisions and support. Stay proactive, and don't hesitate to reach out to healthcare professionals for guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
