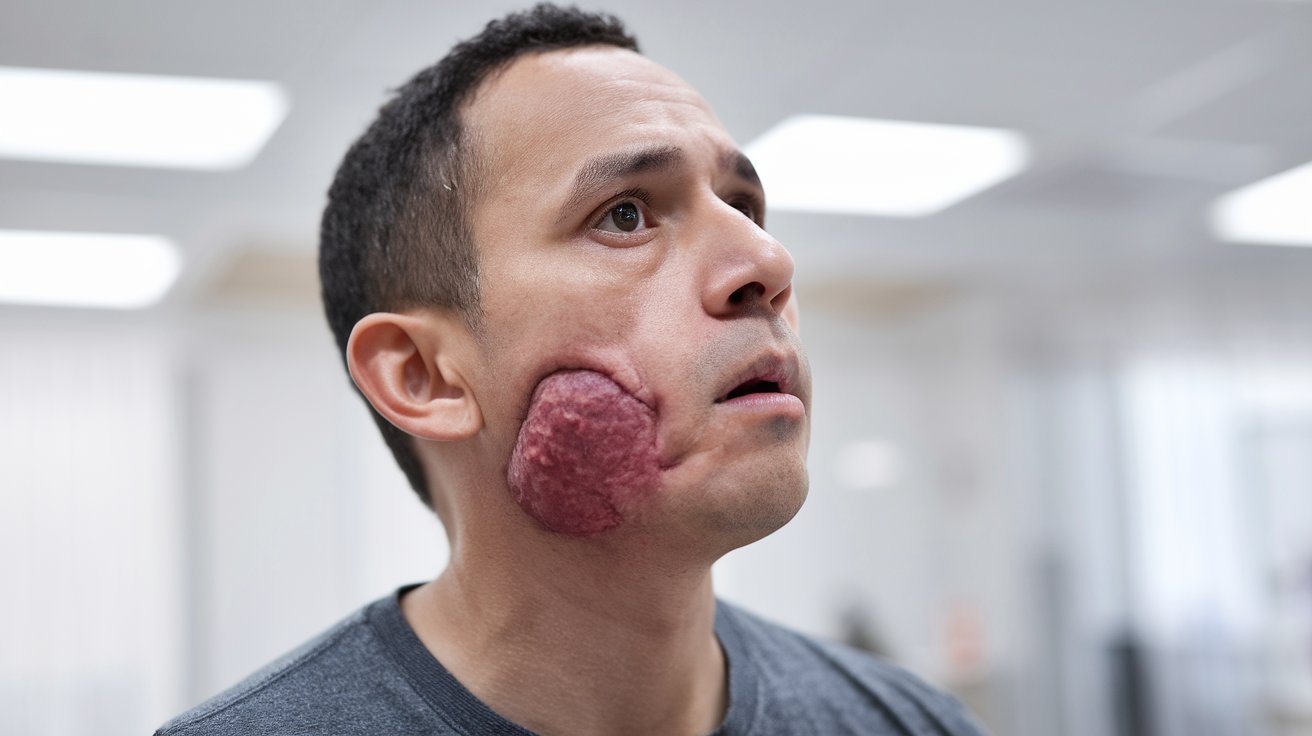
What is salivary gland cancer? Salivary gland cancer is a rare type of cancer that begins in the salivary glands, which are responsible for producing saliva. These glands are located in and around the mouth and throat. While there are several types of salivary glands, cancer can develop in any of them, affecting how saliva is produced and secreted. This cancer can manifest as a lump or swelling in the mouth, cheek, jaw, or neck area. Symptoms might include difficulty swallowing, facial numbness, or persistent pain. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes. Treatment options often involve surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the cancer's stage and location. Understanding the symptoms and seeking medical advice promptly can make a significant difference in managing this condition effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Salivary gland cancer is rare, affecting less than 1% of all cancers. It can occur in any salivary gland and has various types, symptoms, and treatment options.
- Understanding the causes, risk factors, and treatment options for salivary gland cancer is crucial for early detection and effective management. Support and ongoing research are essential for patients and their families.
Understanding Salivary Gland Cancer
Salivary gland cancer is a rare type of cancer that starts in the salivary glands, which are responsible for producing saliva. This cancer can occur in any of the salivary glands located in the mouth, neck, or throat. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Rare Occurrence
Salivary gland cancer is uncommon, accounting for less than 1% of all cancers in the United States. Due to its rarity, it often requires specialized medical attention. -
Multiple Types
There are several types of salivary gland cancer, including mucoepidermoid carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, and acinic cell carcinoma. Each type has its own characteristics and treatment approaches. -
Location Matters
This cancer can develop in any of the major or minor salivary glands. The major ones include the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands, while the minor glands are scattered throughout the mouth and throat. -
Symptoms Vary
Symptoms can include a lump or swelling in the mouth, neck, or jaw, difficulty swallowing, and facial numbness or weakness. These symptoms can vary greatly depending on the tumor's location and size. -
Age Factor
While it can occur at any age, salivary gland cancer is more commonly diagnosed in older adults, typically between the ages of 50 and 70.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes salivary gland cancer and the risk factors involved can help in early detection and prevention.
-
Unknown Causes
The exact cause of salivary gland cancer is not well understood. However, genetic mutations in the cells of the salivary glands are believed to play a role. -
Radiation Exposure
Exposure to radiation, particularly in the head and neck area, is a known risk factor for developing this type of cancer. -
Family History
A family history of salivary gland cancer or other cancers can increase the risk, though this is less common compared to other cancers. -
Workplace Hazards
Certain occupations, such as those involving rubber manufacturing or asbestos exposure, may increase the risk due to exposure to carcinogenic substances. -
Viral Infections
Some studies suggest a link between viral infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus, and an increased risk of salivary gland cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing salivary gland cancer effectively.
-
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnosis often involves imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, as well as a biopsy to examine the cells under a microscope. -
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is the most common treatment, aiming to remove the tumor and some surrounding tissue. The extent of surgery depends on the tumor's size and location. -
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy may be used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells or as a primary treatment if surgery isn't possible. -
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is less commonly used but may be recommended for advanced cases or when cancer has spread to other parts of the body. -
Targeted Therapy
Newer treatments, like targeted therapy, focus on specific molecules involved in cancer growth and may offer options for patients with advanced disease.
Living with Salivary Gland Cancer
Coping with a cancer diagnosis and treatment can be challenging, but understanding the journey can help.
-
Rehabilitation Needs
Post-surgery, patients may require physical therapy, speech therapy, or occupational therapy to regain function and improve quality of life. -
Follow-Up Care
Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor for any signs of recurrence and manage any long-term side effects of treatment. -
Emotional Support
Emotional and psychological support is vital. Support groups and counseling can help patients and their families cope with the emotional impact of cancer. -
Nutritional Considerations
Nutrition plays a key role in recovery. A dietitian can help create a plan that meets the nutritional needs of someone undergoing cancer treatment. -
Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption, can improve overall health and potentially reduce the risk of cancer recurrence.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for improving the understanding and treatment of salivary gland cancer.
-
Genetic Research
Scientists are studying genetic mutations associated with salivary gland cancer to develop more effective treatments and diagnostic tools. -
Immunotherapy Advances
Immunotherapy, which harnesses the body's immune system to fight cancer, is being explored as a potential treatment for salivary gland cancer. -
Clinical Trials
Participation in clinical trials can provide access to new treatments and contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge. -
Biomarker Studies
Research into biomarkers aims to identify specific indicators in the body that can help diagnose salivary gland cancer earlier and more accurately. -
Patient Advocacy
Patient advocacy groups play a vital role in raising awareness, supporting research, and providing resources for those affected by salivary gland cancer.
Understanding Salivary Gland Cancer
Salivary gland cancer might not be the most common type, but knowing about it is crucial. This cancer affects the glands that produce saliva, which helps with digestion and keeps your mouth moist. Symptoms can include a lump or swelling in your mouth, cheek, jaw, or neck, and sometimes pain. Early detection is key, so if you notice any unusual changes, it's important to see a doctor. Treatments often involve surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, depending on the stage and location of the cancer. Research is ongoing, and new treatments are being developed to improve outcomes. Staying informed and aware of your health can make a big difference. Remember, knowledge is power, and understanding the facts about salivary gland cancer can help you or someone you know navigate this challenging journey with more confidence and hope.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
