Preaxial deficiency postaxial polydactyly hypospadias might sound like a mouthful, but it's a fascinating topic worth understanding. This condition involves a combination of limb and genital anomalies. Preaxial deficiency refers to the underdevelopment or absence of the thumb or big toe. Postaxial polydactyly means having extra fingers or toes on the side of the pinky or little toe. Hypospadias is a condition where the opening of the urethra is not located at the tip of the penis. These conditions can occur together due to genetic factors. Understanding these can help in recognizing and managing them effectively. Let's dive into 25 intriguing facts about this unique combination of conditions.
Key Takeaways:
- Rare limb and genital conditions like preaxial deficiency, postaxial polydactyly, and hypospadias can affect mobility and function. Early diagnosis and multidisciplinary treatment are crucial for improving outcomes and quality of life.
- Genetic and environmental factors play a role in the development of these conditions. Research and advancements in medical technology continue to improve treatment options and outcomes for those affected.
Understanding Preaxial Deficiency
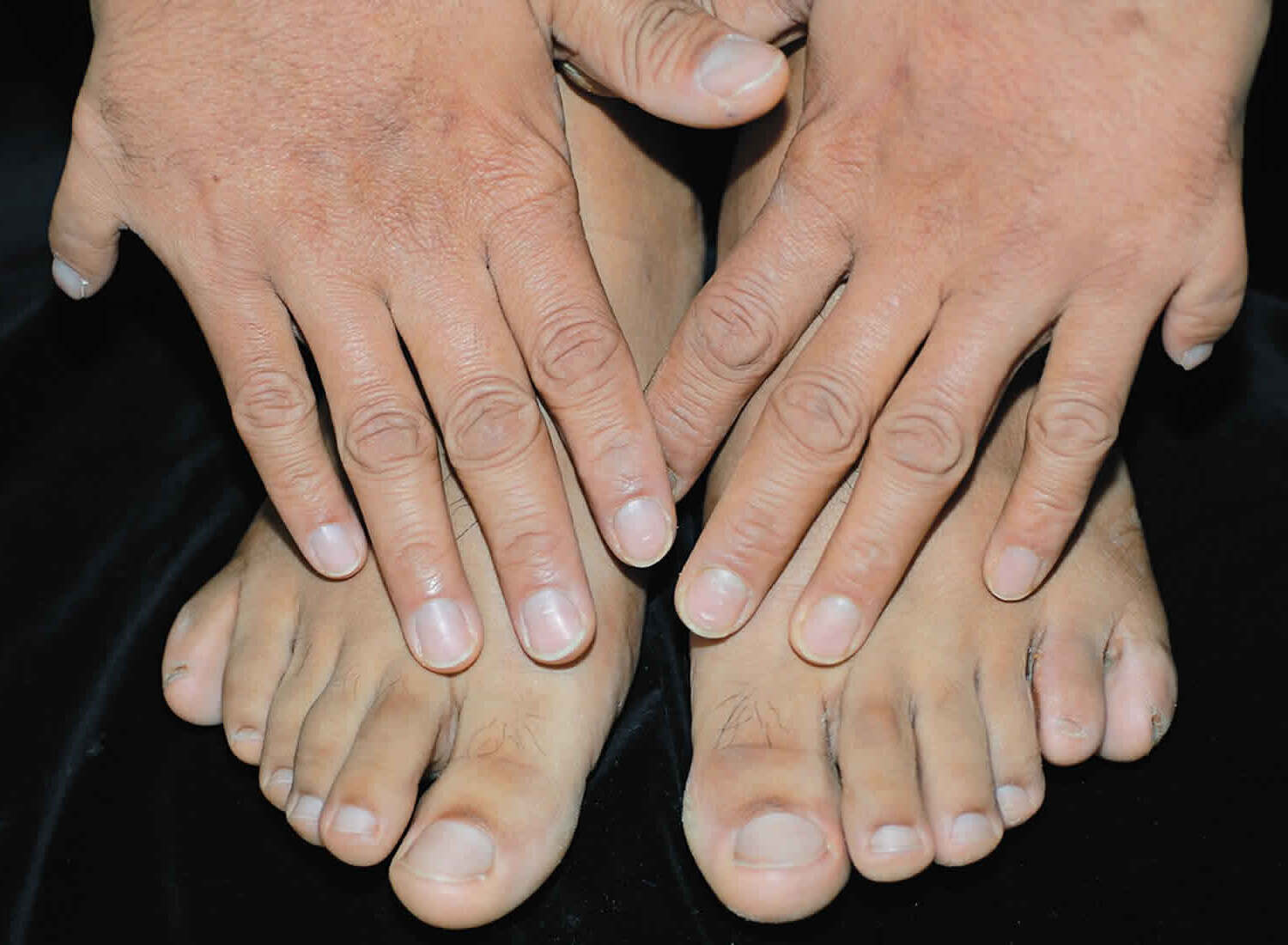
Preaxial deficiency is a rare congenital condition affecting the development of limbs. It often involves the absence or malformation of bones on the thumb side of the hand or foot.
- Preaxial deficiency primarily affects the radial side of the limb, which includes the thumb and radius bone.
- This condition can range from mild, where only the thumb is affected, to severe, where the entire limb is underdeveloped.
- Preaxial deficiency is often diagnosed at birth through physical examination and imaging studies like X-rays.
- The exact cause of preaxial deficiency is unknown, but it is believed to involve genetic and environmental factors.
- Treatment options vary based on severity and may include surgical correction, physical therapy, or prosthetics.
Exploring Postaxial Polydactyly
Postaxial polydactyly is a condition where extra digits form on the ulnar side of the hand or the fibular side of the foot. This can lead to functional and cosmetic concerns.
- Postaxial polydactyly is more common than preaxial deficiency, occurring in about 1 in 500 to 1,000 live births.
- The extra digit in postaxial polydactyly is often smaller and less functional than the other fingers or toes.
- This condition can be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning only one copy of the altered gene is needed to cause the disorder.
- Surgical removal of the extra digit is a common treatment, usually performed in early childhood to improve hand or foot function.
- Postaxial polydactyly can occur as an isolated condition or as part of a syndrome involving other abnormalities.
Hypospadias: A Closer Look
Hypospadias is a birth defect in males where the urethral opening is not located at the tip of the penis. This can affect urination and, later in life, sexual function.
- Hypospadias affects approximately 1 in every 200 to 300 male births.
- The severity of hypospadias can vary, with the urethral opening located anywhere along the underside of the penis, scrotum, or perineum.
- The exact cause of hypospadias is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Early surgical correction, typically between 6 and 18 months of age, is the standard treatment for hypospadias.
- Untreated hypospadias can lead to difficulties with urination, increased risk of urinary tract infections, and issues with sexual function.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
The development of preaxial deficiency, postaxial polydactyly, and hypospadias can be influenced by both genetic and environmental factors.
- Genetic mutations or alterations in specific genes can lead to these congenital conditions.
- Environmental factors, such as maternal exposure to certain drugs or chemicals during pregnancy, can also play a role.
- Family history of congenital limb or genital abnormalities increases the risk of these conditions in offspring.
- Prenatal screening and genetic counseling can help identify potential risks and prepare for early intervention.
- Research is ongoing to better understand the genetic and environmental contributions to these conditions.
Treatment and Management
Managing these congenital conditions often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including surgical, medical, and therapeutic interventions.
- Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for improving outcomes and quality of life.
- Surgical correction is often necessary to address functional and cosmetic concerns.
- Physical and occupational therapy can help improve mobility and function in affected limbs.
- Psychological support and counseling may be beneficial for individuals and families coping with these conditions.
- Ongoing research and advancements in medical technology continue to improve treatment options and outcomes for those affected by preaxial deficiency, postaxial polydactyly, and hypospadias.
Final Thoughts on Preaxial Deficiency Postaxial Polydactyly Hypospadias
Preaxial deficiency, postaxial polydactyly, and hypospadias are rare but fascinating conditions. Each one affects individuals differently, often requiring specialized medical care. Understanding these conditions helps in recognizing their impact on those who live with them.
Preaxial deficiency involves missing or underdeveloped thumbs, while postaxial polydactyly means extra fingers or toes. Hypospadias affects the urethra in males, causing it to open on the underside of the penis. These conditions can occur alone or together, making diagnosis and treatment complex.
Awareness and education about these conditions are crucial. They help reduce stigma and improve support for affected individuals. Medical advancements continue to offer better treatment options, enhancing quality of life. By learning about these conditions, we foster empathy and support for those who face these unique challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
