Poikilodermia Alopecia Retrognathism Cleft Palate is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple parts of the body. This condition combines skin abnormalities, hair loss, a receding jaw, and a cleft palate. Understanding this complex syndrome can be challenging, but knowing key facts can help. Poikilodermia refers to changes in skin color and texture, while alopecia means hair loss. Retrognathism is a condition where the jaw is set back from the facial plane, and a cleft palate is an opening in the roof of the mouth. These symptoms can vary in severity and impact daily life. This article will provide 25 essential facts to help you better understand Poikilodermia Alopecia Retrognathism Cleft Palate.
Key Takeaways:
- Poikilodermia Alopecia Retrognathism Cleft Palate (PARC) is a rare genetic disorder that causes skin changes, hair loss, jaw issues, and cleft palate. It requires ongoing medical care and support from family and healthcare providers.
- Understanding PARC can help manage its symptoms with treatments like skin and hair care, surgical interventions, speech therapy, and nutritional support. Regular check-ups, support groups, and educational accommodations are essential for those affected.
What is Poikilodermia Alopecia Retrognathism Cleft Palate?
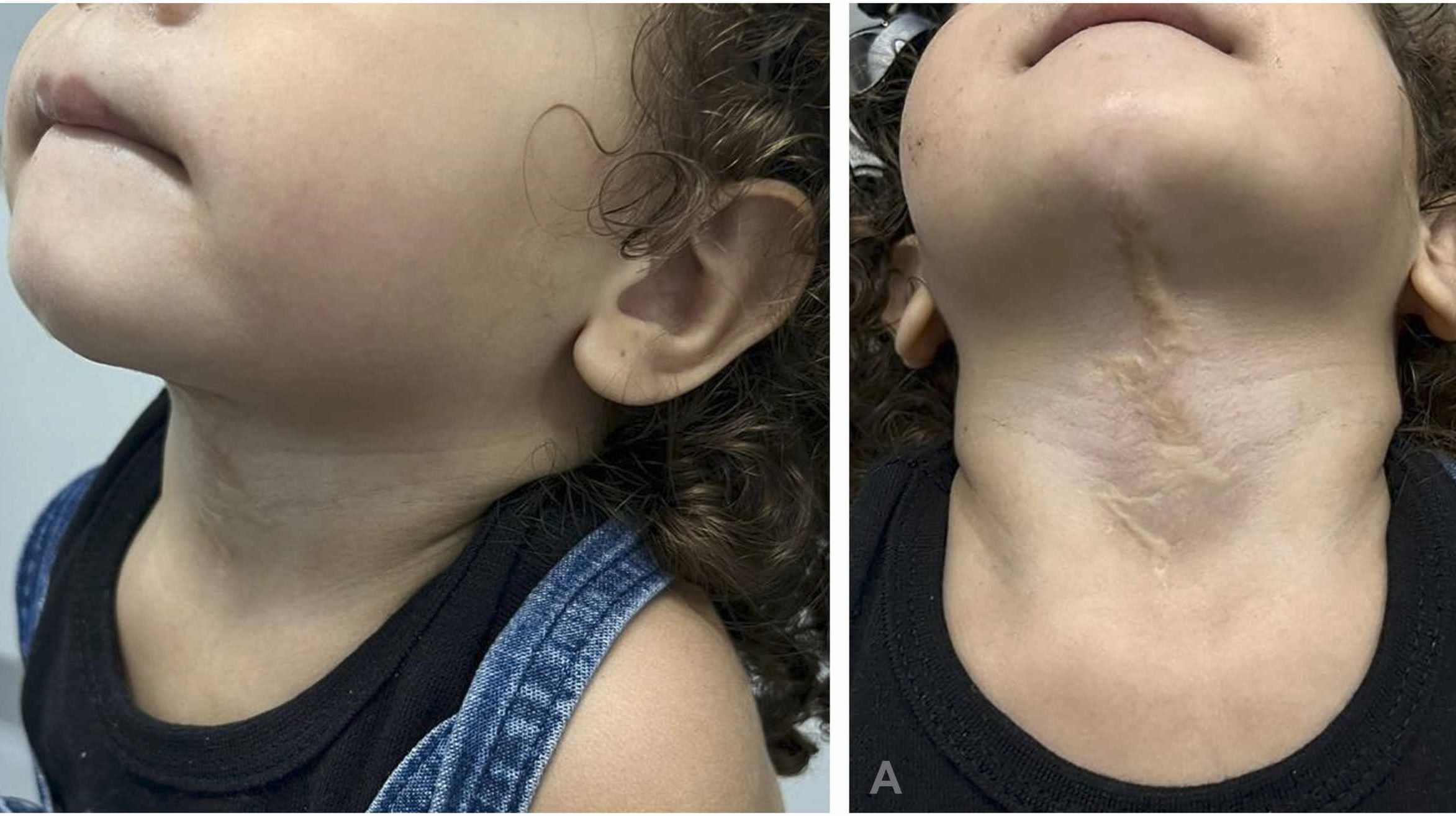
Poikilodermia Alopecia Retrognathism Cleft Palate (PARC) is a rare genetic disorder. It affects multiple parts of the body, leading to a variety of symptoms. Understanding this condition can help those affected and their families manage it better.
- Poikilodermia refers to a group of skin conditions that cause changes in skin color and texture.
- Alopecia is the medical term for hair loss, which can be partial or complete.
- Retrognathism means a receding jaw, where the lower jaw is set back from the upper jaw.
- Cleft Palate is a condition where there is an opening or split in the roof of the mouth.
Genetic Causes of PARC
PARC is primarily caused by genetic mutations. These mutations can be inherited or occur spontaneously.
- Mutations in the TP63 gene are often linked to PARC.
- The condition follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, meaning only one copy of the mutated gene is needed to cause the disorder.
- Spontaneous mutations can also lead to PARC, even if there is no family history of the condition.
Symptoms of PARC
The symptoms of PARC can vary widely among individuals. However, some common symptoms are often observed.
- Skin changes include redness, scaling, and areas of increased or decreased pigmentation.
- Hair loss can affect the scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes.
- Dental issues are common due to the receding jaw and cleft palate.
- Difficulty eating and speaking can result from the cleft palate.
- Growth delays may occur, affecting overall development.
Diagnosis of PARC
Diagnosing PARC involves a combination of clinical evaluations and genetic testing.
- Physical examination by a dermatologist can identify skin changes.
- Dental assessments help in identifying jaw and palate issues.
- Genetic testing confirms the presence of mutations in the TP63 gene.
- Family history is reviewed to identify any inherited patterns.
Treatment Options for PARC
While there is no cure for PARC, various treatments can help manage the symptoms.
- Skin treatments include topical creams and ointments to manage skin changes.
- Hair loss treatments like minoxidil may help in some cases.
- Surgical interventions can correct cleft palate and jaw issues.
- Speech therapy assists with communication difficulties.
- Nutritional support ensures proper growth and development.
Living with PARC
Living with PARC requires ongoing medical care and support from family and healthcare providers.
- Regular check-ups with a dermatologist and dentist are essential.
- Support groups provide emotional and social support for affected individuals and their families.
- Educational accommodations may be necessary for children with PARC.
- Awareness and advocacy can help improve understanding and support for those with PARC.
Final Thoughts on Poikilodermia Alopecia Retrognathism Cleft Palate
Understanding Poikilodermia Alopecia Retrognathism Cleft Palate can be challenging, but knowing the facts helps. This rare genetic disorder affects skin, hair, jaw, and palate, making early diagnosis crucial. Symptoms vary widely, so staying informed is key.
Treatment focuses on managing symptoms. Dermatologists, orthodontists, and other specialists often work together to provide comprehensive care. Genetic counseling can also offer valuable insights for affected families.
Raising awareness about this condition is important. Sharing knowledge helps reduce stigma and supports those living with it. If you or someone you know is affected, seek medical advice and connect with support groups.
Remember, every bit of information counts. Stay curious, stay informed, and support those navigating this rare condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
