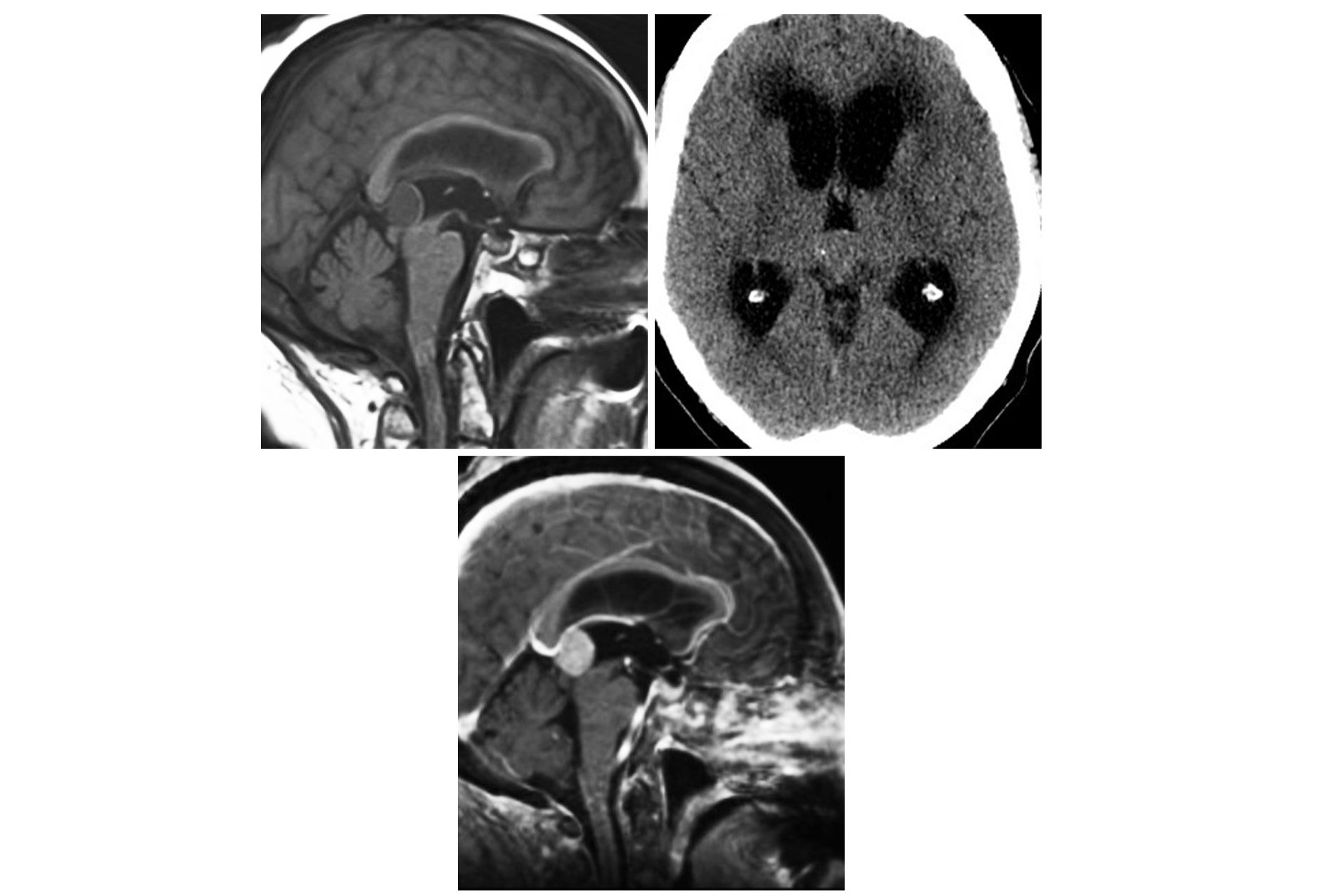
What is a Pineal Astrocytoma? It's a rare type of brain tumor that forms in the pineal gland, a small organ deep within the brain responsible for producing melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep patterns. These tumors arise from astrocytes, the star-shaped cells that support and nourish neurons. While they can occur at any age, they are more common in children and young adults. Symptoms might include headaches, nausea, vision problems, or sleep disturbances due to increased pressure in the brain. Diagnosis often involves imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, and treatment may include surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy depending on the tumor's size and location. Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Key Takeaways:
- Pineal astrocytoma is a rare brain tumor that affects the pineal gland. It can cause symptoms like headaches and vision problems, but early detection and treatment can improve outcomes.
- Treatment options for pineal astrocytoma include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Support groups and rehabilitation services can help patients and their families cope with the challenges of living with this condition.
Understanding Pineal Astrocytoma
Pineal astrocytoma is a rare type of brain tumor that occurs in the pineal gland, a small endocrine gland located deep within the brain. This tumor arises from astrocytes, which are star-shaped glial cells that support and protect neurons. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Rare Occurrence: Pineal astrocytomas are quite rare, accounting for a small percentage of brain tumors. They are more commonly found in children and young adults.
-
Location Matters: The pineal gland, where these tumors develop, is responsible for producing melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles.
-
Symptoms Vary: Symptoms can include headaches, nausea, vision problems, and difficulty with balance. These occur due to the tumor pressing on surrounding brain structures.
-
Diagnosis Tools: MRI and CT scans are commonly used to diagnose pineal astrocytomas. These imaging techniques help visualize the tumor's size and location.
-
Biopsy for Confirmation: A biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. This involves taking a small sample of the tumor tissue for examination under a microscope.
Treatment Options
Treatment for pineal astrocytoma depends on the tumor's size, location, and the patient's overall health. Various approaches are used to manage this condition.
-
Surgical Removal: Surgery is often the first line of treatment. The goal is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without damaging surrounding brain tissue.
-
Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It may be used after surgery to eliminate any remaining tumor cells.
-
Chemotherapy: In some cases, chemotherapy may be recommended. This involves using drugs to destroy cancer cells or stop them from growing.
-
Observation: For small, slow-growing tumors, doctors may recommend regular monitoring with MRI scans instead of immediate treatment.
Prognosis and Outcomes
The prognosis for pineal astrocytoma varies based on several factors, including the tumor's grade and the patient's age and overall health.
-
Grade Matters: Pineal astrocytomas are graded based on how abnormal the cells look under a microscope. Lower-grade tumors tend to have a better prognosis.
-
Age Factor: Younger patients often have a better outcome compared to older individuals, as their bodies may respond more favorably to treatment.
-
Survival Rates: Survival rates vary widely. Early detection and treatment can improve the chances of a positive outcome.
-
Recurrence Risk: There is a risk of recurrence, especially with higher-grade tumors. Regular follow-up appointments are crucial for monitoring.
Research and Advances
Ongoing research is crucial for improving the understanding and treatment of pineal astrocytomas. Scientists are exploring new therapies and diagnostic tools.
-
Genetic Studies: Researchers are studying the genetic mutations associated with pineal astrocytomas to develop targeted therapies.
-
Immunotherapy Potential: Immunotherapy, which harnesses the body's immune system to fight cancer, is being investigated as a potential treatment option.
-
Clinical Trials: Patients may have the opportunity to participate in clinical trials, which test new treatments and approaches.
-
Improved Imaging: Advances in imaging technology are helping doctors better visualize these tumors, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
Living with Pineal Astrocytoma
Living with a pineal astrocytoma can be challenging, but support and resources are available to help patients and their families cope.
-
Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who understand the journey.
-
Rehabilitation Services: Physical and occupational therapy can help patients regain strength and improve their quality of life after treatment.
-
Mental Health Care: Counseling and therapy can be beneficial for managing the emotional impact of a brain tumor diagnosis.
-
Educational Resources: Educational materials and resources can help patients and families better understand the condition and treatment options.
Prevention and Awareness
While there is no known way to prevent pineal astrocytoma, awareness and early detection are key to improving outcomes.
-
Regular Check-Ups: Regular medical check-ups can help detect any unusual symptoms early, leading to prompt diagnosis and treatment.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Awareness campaigns can educate the public about the signs and symptoms of brain tumors, encouraging early medical attention.
-
Research Funding: Supporting research funding can lead to breakthroughs in understanding and treating this rare condition.
-
Advocacy Efforts: Advocacy efforts can help raise awareness and support for those affected by pineal astrocytoma, promoting better care and resources.
Final Thoughts on Pineal Astrocytoma
Pineal astrocytoma is a rare brain tumor that affects the pineal gland, a tiny organ deep within the brain. Understanding its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for those affected. Symptoms can include headaches, nausea, and vision problems, often leading to a challenging diagnosis. MRI and CT scans are typically used to identify the tumor, while a biopsy confirms its nature. Treatment often involves surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the tumor's size and location. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes. It's essential for patients and their families to work closely with healthcare professionals to navigate this complex condition. Staying informed and seeking support from medical experts and support groups can make a significant difference in managing pineal astrocytoma. Knowledge empowers patients to make informed decisions about their health and treatment journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
