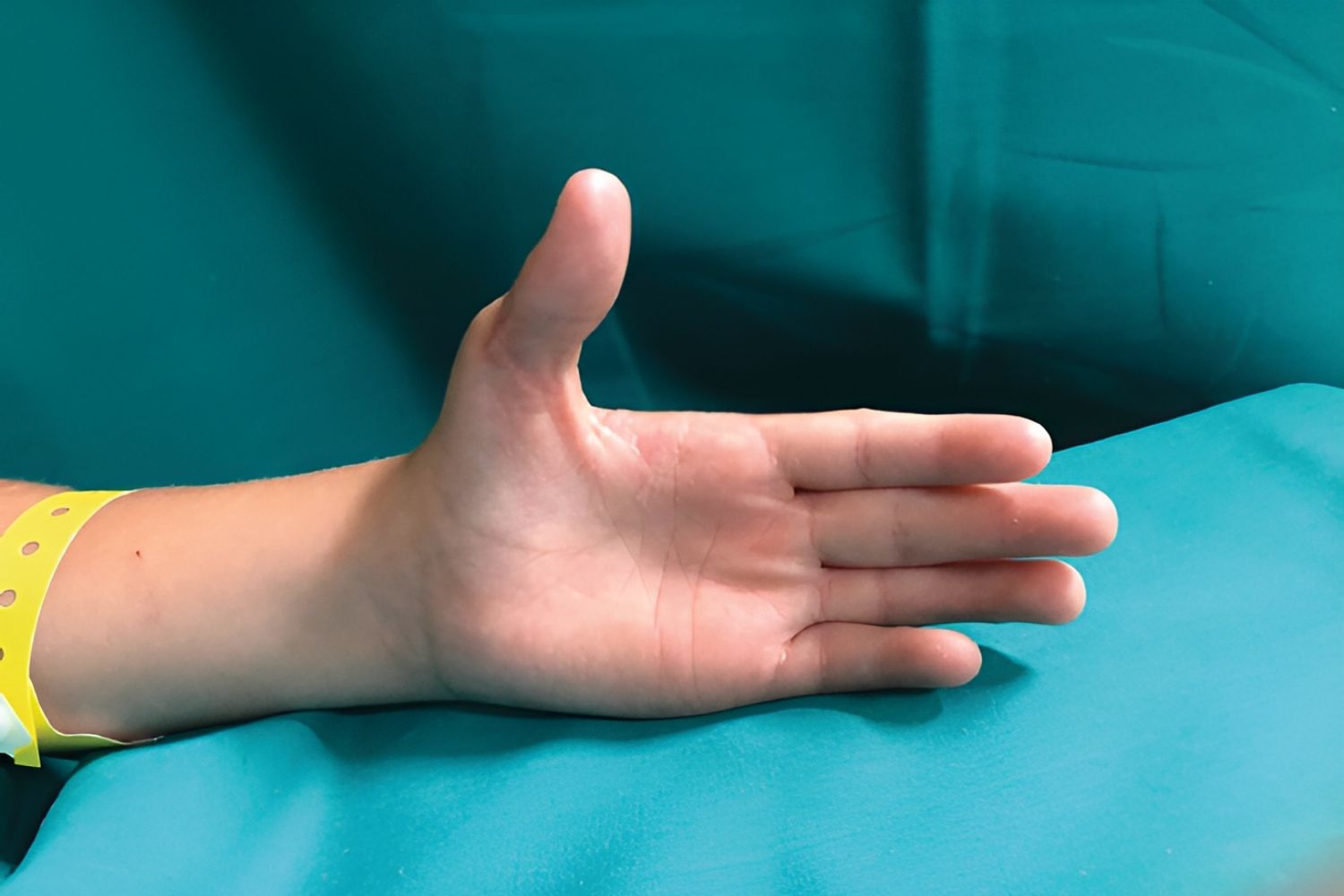
Meningoencephalocele-Arthrogryposis-Hypoplastic Thumb syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple parts of the body. Meningoencephalocele refers to a condition where brain tissue protrudes through a defect in the skull. Arthrogryposis involves joint contractures, meaning joints are stuck in one position. Hypoplastic thumb means the thumb is underdeveloped or absent. This syndrome can lead to various complications, including developmental delays, physical disabilities, and challenges with daily activities. Understanding this condition can help in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Here are 25 facts to give you a comprehensive overview of this complex syndrome.
Key Takeaways:
- Meningoencephalocele-Arthrogryposis-Hypoplastic Thumb is a rare genetic disorder affecting the brain, muscles, and skeleton, leading to various symptoms and challenges in daily life.
- While there is no cure, treatments like surgery, therapy, and medication can improve quality of life. Support groups, educational services, and adaptive devices are available to help those affected.
Understanding Meningoencephalocele-Arthrogryposis-Hypoplastic Thumb
Meningoencephalocele-Arthrogryposis-Hypoplastic Thumb is a rare genetic disorder. It affects multiple systems in the body, leading to a combination of neurological, muscular, and skeletal abnormalities. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Meningoencephalocele is a neural tube defect where brain tissue and membranes protrude through an opening in the skull.
-
Arthrogryposis refers to joint contractures that limit movement, often present at birth.
-
Hypoplastic Thumb means the thumb is underdeveloped or absent, impacting hand function.
Causes and Genetics
Understanding the root causes and genetic factors of this condition can help in diagnosis and management.
-
Genetic Mutation: The disorder is often caused by mutations in specific genes, such as the ZIC2 gene.
-
Inheritance Pattern: It can be inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry the mutated gene.
-
Prenatal Diagnosis: Advanced imaging techniques like ultrasound and MRI can detect abnormalities before birth.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better management and care.
-
Neurological Symptoms: These can include seizures, developmental delays, and intellectual disabilities.
-
Physical Symptoms: Joint stiffness, muscle weakness, and abnormal limb positioning are common.
-
Craniofacial Abnormalities: Some children may have facial asymmetry or other skull deformities.
-
Diagnostic Tests: Genetic testing, imaging studies, and physical exams are crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure, various treatments can improve quality of life.
-
Surgical Interventions: Surgery may be needed to correct skull defects or joint contractures.
-
Physical Therapy: Regular therapy helps maintain joint mobility and muscle strength.
-
Occupational Therapy: This can assist in improving hand function and daily living skills.
-
Medication: Anti-seizure medications may be prescribed for neurological symptoms.
Living with the Condition
Daily life can be challenging, but support and resources are available.
-
Support Groups: Connecting with others who have the condition can provide emotional support.
-
Educational Support: Special education services can help children reach their full potential.
-
Adaptive Devices: Tools like braces or custom-made utensils can aid in daily activities.
-
Regular Monitoring: Ongoing medical check-ups are essential to manage symptoms and complications.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment options.
-
Genetic Research: Scientists are studying the specific genes involved to develop targeted therapies.
-
Stem Cell Therapy: Experimental treatments using stem cells show promise for repairing damaged tissues.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in trials can provide access to new treatments and contribute to scientific knowledge.
Raising Awareness
Increasing awareness can lead to better support and resources for affected families.
-
Advocacy Groups: Organizations work to raise awareness and fund research for rare genetic disorders.
-
Public Education: Informing the public about the condition can reduce stigma and promote understanding.
-
Healthcare Training: Educating healthcare providers about the condition ensures better care for patients.
-
Policy Changes: Advocating for policy changes can improve access to medical care and support services.
Final Thoughts on Meningoencephalocele-Arthrogryposis-Hypoplastic Thumb
Meningoencephalocele-Arthrogryposis-Hypoplastic Thumb is a rare condition that combines several complex medical issues. Understanding its intricacies can help in managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life for those affected. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for better outcomes. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for families dealing with this condition. While research is ongoing, advancements in medical science offer hope for more effective treatments in the future. Awareness and education about this condition can lead to better support systems and resources for patients and their families. By staying informed and proactive, we can make a significant difference in the lives of those impacted by Meningoencephalocele-Arthrogryposis-Hypoplastic Thumb.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
