Magnesium wasting renal is a condition where the kidneys fail to retain magnesium, leading to its excessive loss in urine. This can result in low magnesium levels in the blood, causing symptoms like muscle cramps, fatigue, and irregular heartbeats. Understanding this condition is crucial because magnesium plays a vital role in many bodily functions, including nerve function, muscle contraction, and bone health. Magnesium wasting renal can be caused by genetic disorders, certain medications, or other underlying health issues. Knowing the facts about this condition can help in managing it effectively and improving overall health. Let's dive into 25 essential facts about magnesium wasting renal to better understand its impact and management.
Key Takeaways:
- Magnesium wasting renal occurs when the kidneys don't reabsorb magnesium properly, leading to deficiency. It can cause muscle cramps, fatigue, and heart irregularities, but can be diagnosed through blood and urine tests.
- Treatment involves oral supplements, dietary changes, and monitoring. Untreated magnesium wasting renal can lead to cardiovascular, bone, neurological, and muscle issues, so prevention through hydration, exercise, and stress management is crucial.
What is Magnesium Wasting Renal?
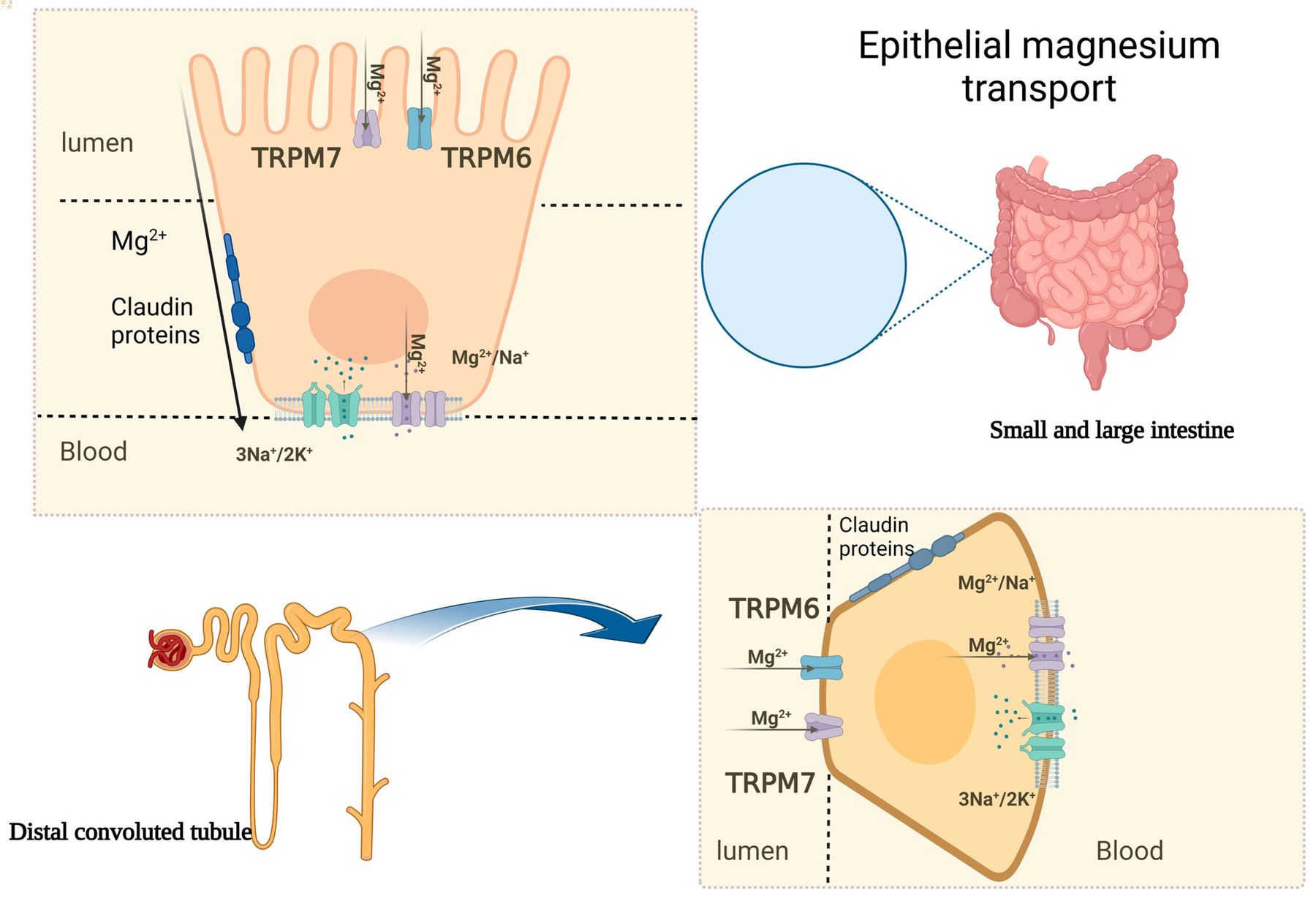
Magnesium wasting renal, also known as renal magnesium loss, is a condition where the kidneys fail to reabsorb magnesium efficiently. This leads to excessive magnesium being excreted in the urine, causing a deficiency in the body. Understanding this condition is crucial for maintaining overall health.
-
Magnesium is essential for over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, including muscle and nerve function, blood glucose control, and protein synthesis.
-
The kidneys play a vital role in regulating magnesium levels by filtering and reabsorbing it. When this process is disrupted, magnesium wasting occurs.
-
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency include muscle cramps, fatigue, weakness, and irregular heartbeats.
-
Magnesium wasting renal can be caused by genetic disorders, such as Gitelman syndrome and Bartter syndrome, which affect kidney function.
-
Certain medications, like diuretics and antibiotics, can lead to increased magnesium excretion and contribute to magnesium wasting renal.
How is Magnesium Wasting Renal Diagnosed?
Diagnosing magnesium wasting renal involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. These tests help determine the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
-
Blood tests measure serum magnesium levels to identify deficiencies. Low levels indicate a potential issue with magnesium absorption or retention.
-
Urine tests assess magnesium excretion. High levels of magnesium in the urine suggest that the kidneys are not reabsorbing it properly.
-
Genetic testing can identify inherited disorders that cause magnesium wasting renal, such as mutations in specific genes related to kidney function.
-
Electrolyte panels check for imbalances in other minerals, like calcium and potassium, which often accompany magnesium deficiency.
-
Renal function tests evaluate overall kidney health and help rule out other potential causes of magnesium loss.
Treatment Options for Magnesium Wasting Renal
Managing magnesium wasting renal involves addressing the underlying cause and replenishing magnesium levels. Treatment plans are tailored to each individual's needs.
-
Oral magnesium supplements are commonly prescribed to increase magnesium intake and correct deficiencies.
-
Intravenous magnesium may be necessary for severe cases or when oral supplements are not effective.
-
Dietary changes can help boost magnesium levels. Foods rich in magnesium include leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
-
Medications that cause magnesium loss may need to be adjusted or replaced with alternatives that have less impact on magnesium levels.
-
Monitoring and regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider ensure that treatment is effective and magnesium levels remain stable.
Complications of Untreated Magnesium Wasting Renal
If left untreated, magnesium wasting renal can lead to serious health complications. Recognizing and addressing these risks is essential for preventing long-term damage.
-
Chronic magnesium deficiency can cause cardiovascular problems, such as arrhythmias and hypertension.
-
Bone health may be compromised, leading to conditions like osteoporosis and increased fracture risk.
-
Neurological issues, including seizures and mood disorders, can arise from prolonged magnesium deficiency.
-
Muscle function is affected, resulting in persistent cramps, spasms, and weakness.
-
Electrolyte imbalances can disrupt overall bodily functions, making it harder to maintain homeostasis.
Preventing Magnesium Wasting Renal
Prevention strategies focus on maintaining healthy magnesium levels and supporting kidney function. Simple lifestyle changes can make a significant difference.
-
Staying hydrated supports kidney health and helps prevent excessive magnesium loss through urine.
-
Regular exercise promotes overall well-being and can improve kidney function.
-
Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption reduces the risk of magnesium depletion, as alcohol can interfere with magnesium absorption.
-
Managing stress levels is important, as chronic stress can impact magnesium levels and kidney function.
-
Routine medical check-ups help detect early signs of magnesium deficiency and kidney issues, allowing for timely intervention.
Final Thoughts on Magnesium Wasting Renal
Magnesium wasting renal is a condition that affects the kidneys' ability to retain magnesium, leading to various health issues. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatments can help manage this condition effectively. Common symptoms include muscle cramps, fatigue, and irregular heartbeats. Causes range from genetic disorders to certain medications. Treatment often involves magnesium supplements and dietary changes.
Staying informed about magnesium levels and kidney health is crucial. Regular check-ups and blood tests can help detect any imbalances early. If you experience symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Remember, managing magnesium wasting renal is a continuous process that requires attention and care.
By staying proactive and informed, you can better manage your health and well-being. Keep these facts in mind and take steps to ensure your kidneys function optimally.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
