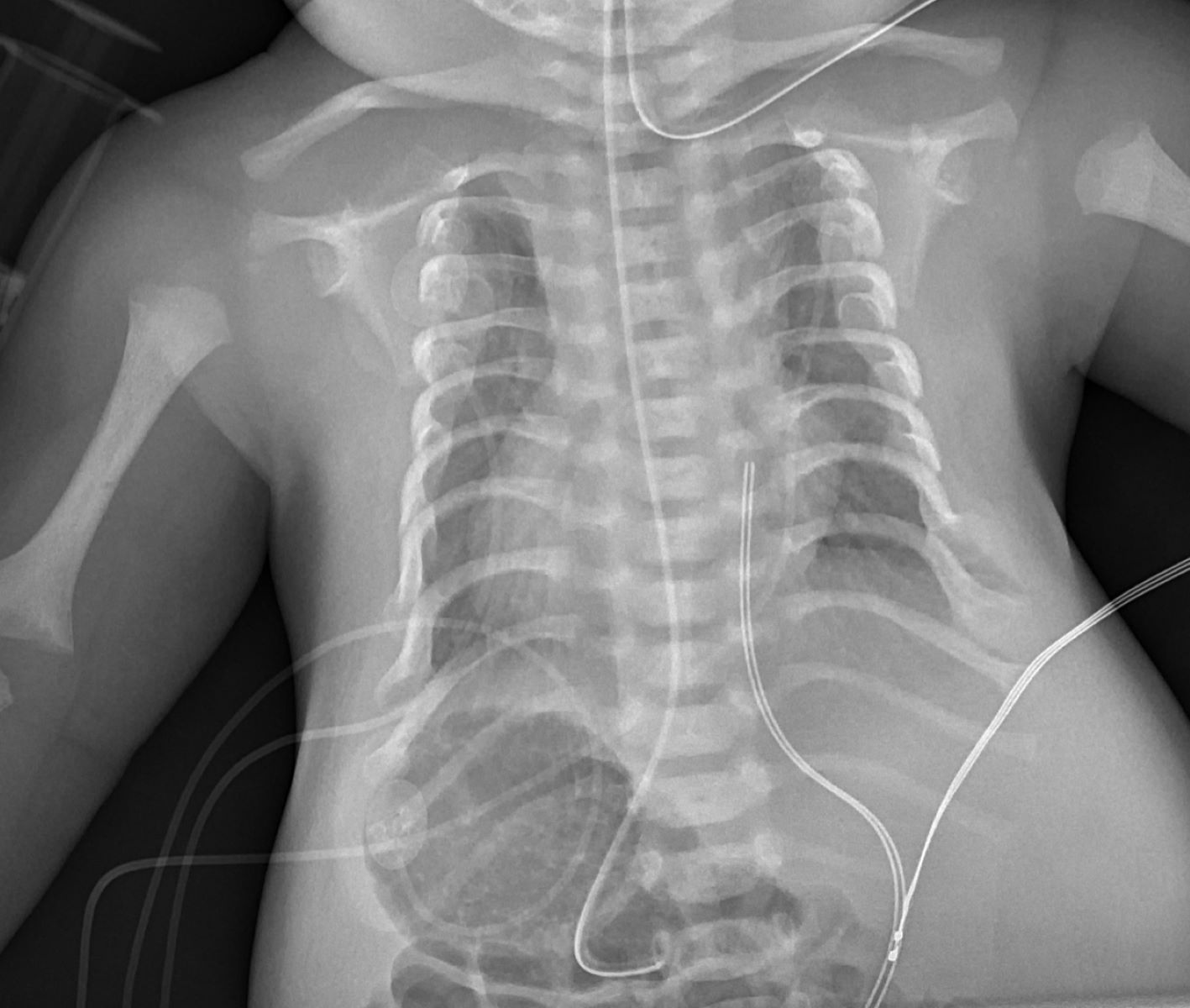
What is Jeune Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy? Jeune Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy, often called Jeune Syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder. It primarily affects the development of the rib cage, leading to a narrow, bell-shaped chest. This condition can cause serious breathing difficulties due to restricted lung growth. Besides the chest, Jeune Syndrome may also impact bones in the arms, legs, and pelvis, leading to short stature and other skeletal abnormalities. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the gene for a child to be affected. Symptoms can vary widely, with some individuals experiencing mild issues while others face life-threatening complications. Early diagnosis and medical intervention are crucial for managing respiratory problems and improving quality of life. Understanding Jeune Syndrome helps in providing better care and support for those affected by this challenging condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Jeune Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy (JATD) is a rare genetic disorder affecting the rib cage and respiratory system, requiring early diagnosis and comprehensive care for improved outcomes.
- Families affected by JATD can find support through resources, advocacy organizations, and medical specialists, offering hope and guidance in navigating the challenges of the condition.
What is Jeune Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy?
Jeune Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy (JATD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the rib cage, limbs, and other parts of the body. It is also known as Jeune Syndrome. This condition can lead to serious respiratory issues due to the small size of the chest, which restricts lung growth and function. Let's explore some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Rare Genetic Disorder
JATD is classified as a rare disease, affecting approximately 1 in 100,000 to 130,000 live births. Its rarity makes it a subject of interest for genetic researchers. -
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry a copy of the mutated gene for their child to be affected. -
Shortened Rib Cage
One of the hallmark features is a shortened rib cage, which can severely impact breathing and lung development. -
Skeletal Abnormalities
Individuals with JATD often have shortened limbs and other skeletal abnormalities, which can affect mobility and growth. -
Respiratory Challenges
Due to the small chest size, many affected individuals experience significant respiratory challenges, requiring medical intervention.
Genetic Causes of Jeune Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy
Understanding the genetic basis of JATD is crucial for diagnosis and potential treatment options. Several genes have been linked to this condition, each playing a role in its development.
-
Mutations in IFT80 Gene
Mutations in the IFT80 gene are one of the known causes of JATD, affecting the function of cilia, which are tiny hair-like structures on cells. -
Role of DYNC2H1 Gene
The DYNC2H1 gene is another gene associated with JATD, involved in the movement of cilia, which is essential for normal skeletal development. -
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing can confirm a diagnosis of JATD by identifying mutations in the associated genes, aiding in early intervention and management.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Jeune Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better management of the condition. Diagnosis often involves a combination of clinical evaluation and genetic testing.
-
Respiratory Distress in Infants
Infants with JATD often present with respiratory distress shortly after birth due to the restricted chest cavity. -
Distinctive Facial Features
Some individuals may have distinctive facial features, such as a small chin or a flat nasal bridge. -
Radiographic Findings
X-rays and other imaging techniques can reveal the characteristic skeletal abnormalities, aiding in diagnosis. -
Growth Delays
Growth delays are common, with affected individuals often being shorter than their peers.
Treatment and Management of Jeune Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy
While there is no cure for JATD, various treatments and management strategies can improve quality of life and address specific symptoms.
-
Surgical Interventions
Surgery may be necessary to expand the chest cavity, improving respiratory function. -
Respiratory Support
Many individuals require respiratory support, such as oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation, especially during infancy. -
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help improve mobility and strength, addressing some of the skeletal challenges. -
Nutritional Support
Nutritional support is important to ensure proper growth and development, as feeding difficulties can occur.
Prognosis and Life Expectancy
The prognosis for individuals with JATD can vary widely, depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of interventions.
-
Varied Prognosis
Prognosis varies; some individuals may have a normal lifespan with appropriate medical care, while others may face life-threatening complications. -
Early Intervention
Early intervention and comprehensive care can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life. -
Ongoing Research
Research is ongoing to better understand JATD and develop new treatments, offering hope for affected individuals and their families.
Support and Resources for Families
Families affected by JATD can benefit from various resources and support networks to help navigate the challenges associated with the condition.
-
Support Groups
Support groups provide a platform for families to connect, share experiences, and offer emotional support. -
Educational Resources
Educational resources can help families understand the condition and advocate for their loved ones. -
Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling is recommended for families to understand the inheritance pattern and assess risks for future pregnancies. -
Medical Specialists
A team of medical specialists, including geneticists, pulmonologists, and orthopedic surgeons, is often involved in the care of individuals with JATD. -
Advocacy Organizations
Advocacy organizations work to raise awareness, fund research, and support affected individuals and their families. -
Community Involvement
Community involvement can help raise awareness and support for those living with JATD, fostering a sense of belonging and understanding.
Understanding Jeune Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy
Jeune Asphyxiating Thoracic Dystrophy, also known as Jeune Syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the rib cage, leading to respiratory issues. This condition is caused by mutations in specific genes, such as IFT80 and DYNC2H1, which play a role in the development of the skeletal system. Symptoms can vary widely, but they often include a narrow chest, short ribs, and sometimes limb abnormalities. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing the condition effectively, as it can lead to severe breathing problems. Treatment typically involves supportive care, and in some cases, surgical interventions to expand the chest cavity. While Jeune Syndrome presents significant challenges, advancements in medical research continue to improve the quality of life for those affected. Raising awareness and understanding of this condition can help support individuals and families navigating its complexities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
