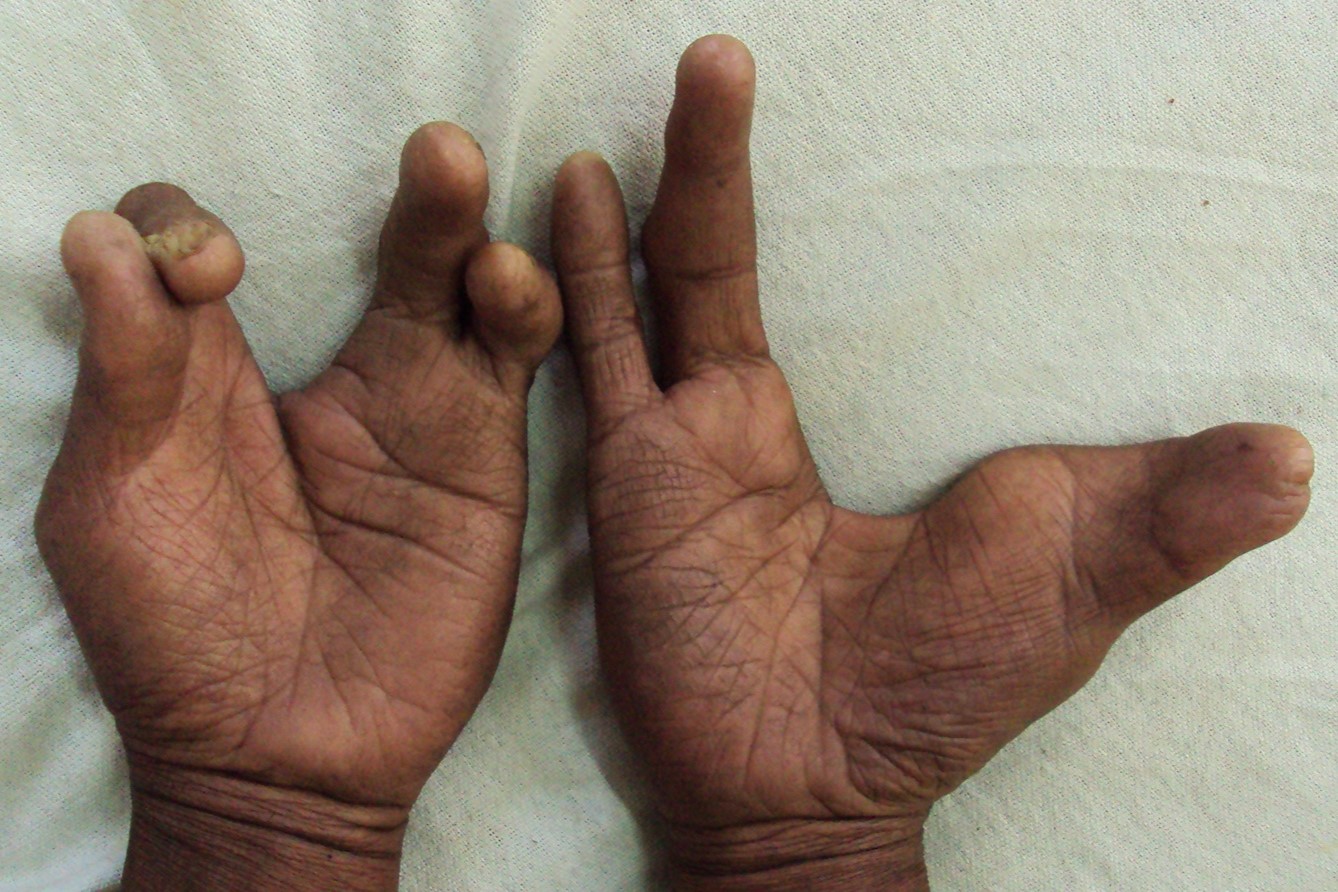
What is Hydrops Ectrodactyly Syndactyly (HES)? It's a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of limbs and other parts of the body. Imagine having fewer fingers or toes, or even webbed ones. That's part of what HES can do. This condition is caused by changes in specific genes, which can be passed down from parents or occur spontaneously. People with HES might also experience fluid buildup in tissues, known as hydrops, which can lead to swelling. While it's not very common, understanding HES helps in providing better care and support for those affected. Scientists and doctors continue to study this condition to find more effective treatments and improve the quality of life for individuals with HES.
Key Takeaways:
- HES is a rare genetic disorder that affects limb development, causing physical anomalies. Early diagnosis and treatments like surgery and therapy can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Research and awareness are crucial for understanding HES better and developing new treatments. Gene therapy, stem cell research, and clinical trials offer hope for the future.
Understanding Hydrops Ectrodactyly Syndactyly
Hydrops Ectrodactyly Syndactyly (HES) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of limbs and other parts of the body. This condition can lead to various physical anomalies, and understanding it can help in managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life for those affected.
-
Genetic Origins: HES is caused by mutations in specific genes that are responsible for limb development. These mutations can be inherited from parents or occur spontaneously.
-
Limb Malformations: Individuals with HES often have limb malformations, such as missing fingers or toes (ectrodactyly) and webbed fingers or toes (syndactyly).
-
Hydrops Fetalis: A severe form of the condition, hydrops fetalis, involves abnormal fluid accumulation in the fetus, which can be life-threatening.
-
Variable Symptoms: The symptoms of HES can vary widely among individuals, even within the same family, making diagnosis and treatment challenging.
-
Rare Occurrence: HES is extremely rare, with only a few cases reported worldwide, which makes research and awareness crucial.
Diagnosing HES
Diagnosing HES involves a combination of genetic testing, physical examinations, and imaging studies. Early diagnosis can lead to better management of the condition.
-
Genetic Testing: Genetic testing can confirm the presence of mutations associated with HES, helping in accurate diagnosis.
-
Ultrasound Imaging: Prenatal ultrasound can sometimes detect limb abnormalities or hydrops fetalis, indicating the possibility of HES.
-
Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination by a specialist can identify characteristic features of HES.
-
Family History: A detailed family history can provide clues, as HES can be inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for HES, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Surgical Interventions: Surgery may be necessary to correct limb deformities and improve function.
-
Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy can help maintain mobility and strength in affected limbs.
-
Supportive Care: Supportive care, including respiratory support for those with hydrops fetalis, is essential for managing severe cases.
-
Genetic Counseling: Genetic counseling can provide families with information about the risks of passing HES to future generations.
Living with HES
Living with HES requires adapting to physical challenges and finding ways to lead a fulfilling life.
-
Adaptive Devices: Use of adaptive devices can assist with daily activities and enhance independence.
-
Community Support: Connecting with support groups and communities can provide emotional support and practical advice.
-
Educational Support: Tailored educational support can help children with HES succeed academically.
-
Psychological Support: Access to psychological support can help individuals and families cope with the emotional aspects of living with HES.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for understanding HES better and developing new treatments.
-
Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for correcting genetic mutations in HES.
-
Stem Cell Research: Stem cell research holds promise for regenerating damaged tissues and improving limb function.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide access to new therapies and contribute to scientific knowledge.
-
Awareness Campaigns: Raising awareness about HES can lead to increased funding for research and support for affected families.
Interesting Facts about HES
Here are some intriguing facts about HES that highlight its complexity and the ongoing efforts to understand it.
-
Historical Cases: Some historical figures are believed to have had conditions similar to HES, based on descriptions of their physical anomalies.
-
Artistic Representations: HES and similar conditions have been depicted in art and literature, reflecting society's fascination with rare disorders.
-
Genetic Diversity: The genetic mutations causing HES can vary greatly, contributing to the wide range of symptoms observed.
-
Hope for the Future: Advances in genetic research and technology offer hope for better treatments and outcomes for those with HES.
Understanding HES: A Glimpse into a Rare Condition
Hydrops Ectrodactyly Syndactyly (HES) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of limbs and other body parts. This condition can lead to limb malformations, such as missing fingers or toes, and sometimes fluid accumulation in the body. While HES is uncommon, understanding its characteristics helps in early diagnosis and management.
Genetic mutations are the primary cause, and they can be inherited or occur spontaneously. Early intervention and supportive care can improve quality of life for those affected. Genetic counseling is crucial for families with a history of HES, providing insights into potential risks and options.
Raising awareness about HES can lead to better support systems and research opportunities. Though rare, every bit of knowledge contributes to a broader understanding of genetic disorders, paving the way for future advancements in treatment and care.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
