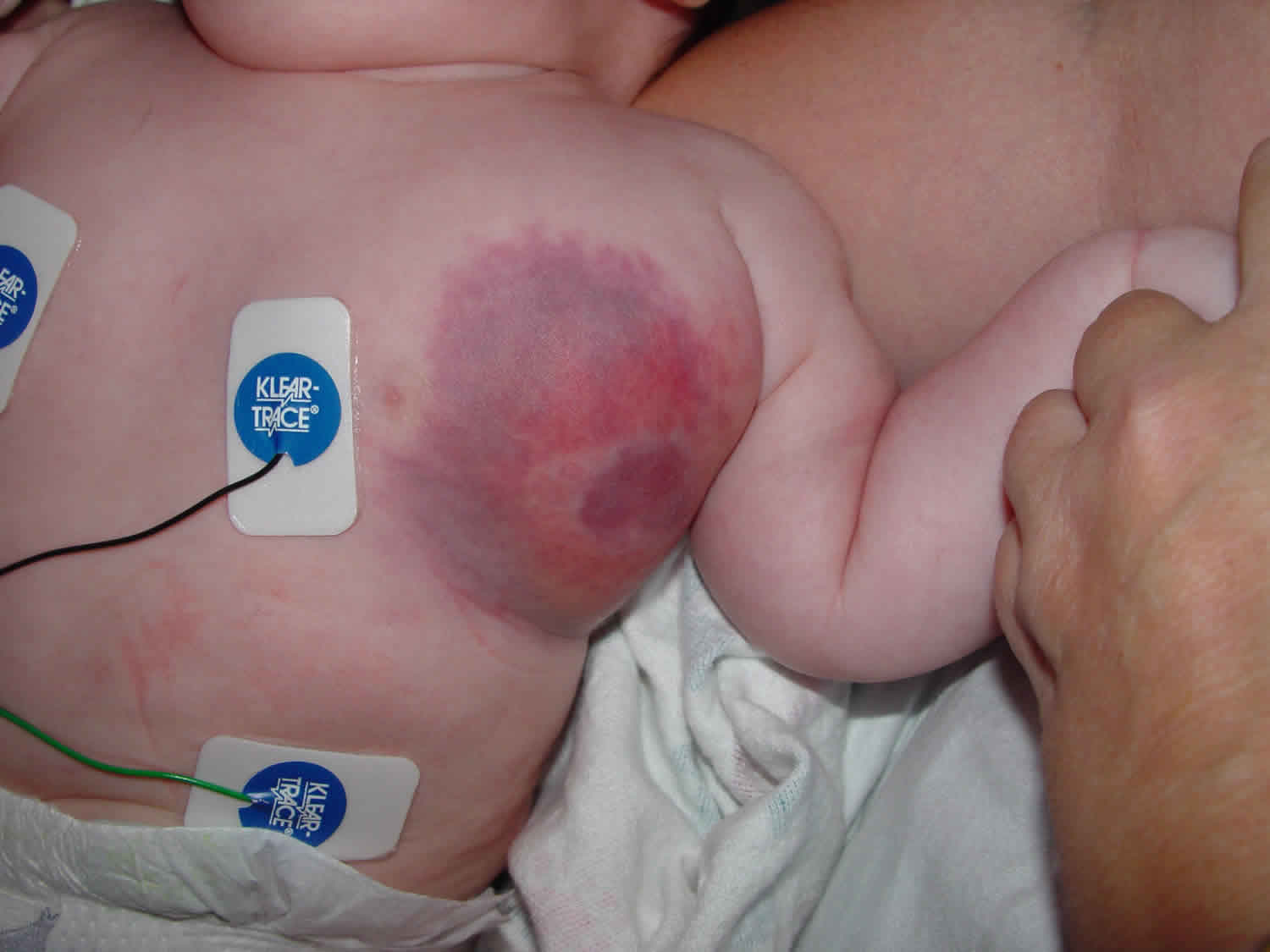
Hemangioma thrombocytopenia is a rare condition that combines two distinct medical issues: hemangiomas and thrombocytopenia. Hemangiomas are benign tumors made up of blood vessels, often appearing as red or purple marks on the skin. Thrombocytopenia refers to a low platelet count in the blood, which can lead to excessive bleeding and bruising. When these two conditions occur together, it can create a complex medical scenario requiring careful management. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for anyone affected by this condition. This article will provide 25 essential facts to help you grasp the intricacies of hemangioma thrombocytopenia.
Key Takeaways:
- Hemangioma thrombocytopenia is a rare condition causing low platelet count due to vascular tumors. It can lead to bruising, bleeding, and serious complications, requiring careful medical attention.
- Early diagnosis and effective treatment can lead to good outcomes for patients with hemangioma thrombocytopenia. Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential, and research is ongoing to improve treatments.
What is Hemangioma Thrombocytopenia?
Hemangioma thrombocytopenia, also known as Kasabach-Merritt syndrome, is a rare condition involving a vascular tumor and low platelet count. This disorder can lead to serious complications and requires careful medical attention.
- Hemangioma thrombocytopenia is named after Dr. Haig Kasabach and Dr. Katharine K. Merritt, who first described it in 1940.
- This condition typically affects infants and young children, though it can occur at any age.
- Hemangiomas involved in this syndrome are usually large and can be found on the skin, liver, or other organs.
- The low platelet count, or thrombocytopenia, results from platelets being trapped and destroyed within the hemangioma.
- Symptoms often include bruising, bleeding, and petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin).
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes hemangioma thrombocytopenia can help in managing and treating the condition. Here are some key points about its causes and risk factors.
- The exact cause of hemangioma thrombocytopenia is unknown, but it is believed to involve abnormal blood vessel growth.
- Genetic factors may play a role, although no specific genes have been identified.
- Premature infants are at a higher risk of developing this condition.
- There is no known way to prevent hemangioma thrombocytopenia, as it is not linked to any lifestyle factors.
- Some studies suggest that maternal health conditions during pregnancy might influence the development of hemangiomas in infants.
Diagnosis and Symptoms
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some facts about how hemangioma thrombocytopenia is diagnosed and its symptoms.
- Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI.
- A biopsy of the hemangioma may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
- Common symptoms include visible hemangiomas, easy bruising, and frequent nosebleeds.
- Severe cases can lead to internal bleeding and organ damage.
- Some patients may experience anemia due to chronic blood loss.
Treatment Options
Treatment for hemangioma thrombocytopenia aims to reduce the size of the hemangioma and manage symptoms. Here are some treatment options.
- Corticosteroids are often the first line of treatment to reduce inflammation and shrink the hemangioma.
- Vincristine, a chemotherapy drug, may be used if corticosteroids are ineffective.
- Interferon-alpha, another medication, can help in shrinking the hemangioma but has significant side effects.
- Surgical removal of the hemangioma may be necessary in severe cases.
- Supportive care, including blood transfusions, may be required to manage thrombocytopenia and anemia.
Prognosis and Long-term Outlook
The long-term outlook for patients with hemangioma thrombocytopenia varies. Here are some important facts about the prognosis and long-term outlook.
- With early and effective treatment, many patients can achieve good outcomes.
- Some children may outgrow the condition as the hemangioma naturally regresses over time.
- Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is essential to monitor for potential complications.
- In rare cases, the condition can be life-threatening if not properly managed.
- Research is ongoing to find more effective treatments and improve the prognosis for patients with hemangioma thrombocytopenia.
Final Thoughts on Hemangioma Thrombocytopenia
Hemangioma thrombocytopenia, also known as Kasabach-Merritt syndrome, is a rare yet serious condition. It involves a vascular tumor that traps platelets, leading to thrombocytopenia and potential bleeding issues. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications. Treatments range from steroids and vincristine to surgical removal of the tumor in severe cases.
Understanding the symptoms, such as bruising, petechiae, and anemia, can help in seeking timely medical advice. Though rare, awareness about this condition can make a significant difference in outcomes. If you suspect any signs, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Knowledge and prompt action are your best defenses against this complex condition. Stay informed, stay proactive, and always prioritize your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
