What is Dyserythropoietic Anemia? It's a rare blood disorder where the bone marrow produces abnormal red blood cells. These cells often don't function properly, leading to anemia. Imagine trying to build a house with bricks that crumble easily—it's a bit like that. This condition can cause fatigue, weakness, and pale skin. It's not just about feeling tired; it can affect daily life significantly. Understanding this disorder is crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. While it might sound complex, breaking it down helps in grasping its impact. Let's explore some intriguing facts about this condition, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and potential treatments. Whether you're affected by it or just curious, these insights can be eye-opening.
Key Takeaways:
- Dyserythropoietic anemia is a rare genetic blood disorder causing symptoms like fatigue and pale skin. There's no cure yet, but treatments like blood transfusions and gene therapy research offer hope for the future.
- Families with a history of dyserythropoietic anemia can benefit from prenatal genetic testing. Joining support groups and staying informed about the condition can help manage expectations and reduce stigma.
Understanding Dyserythropoietic Anemia
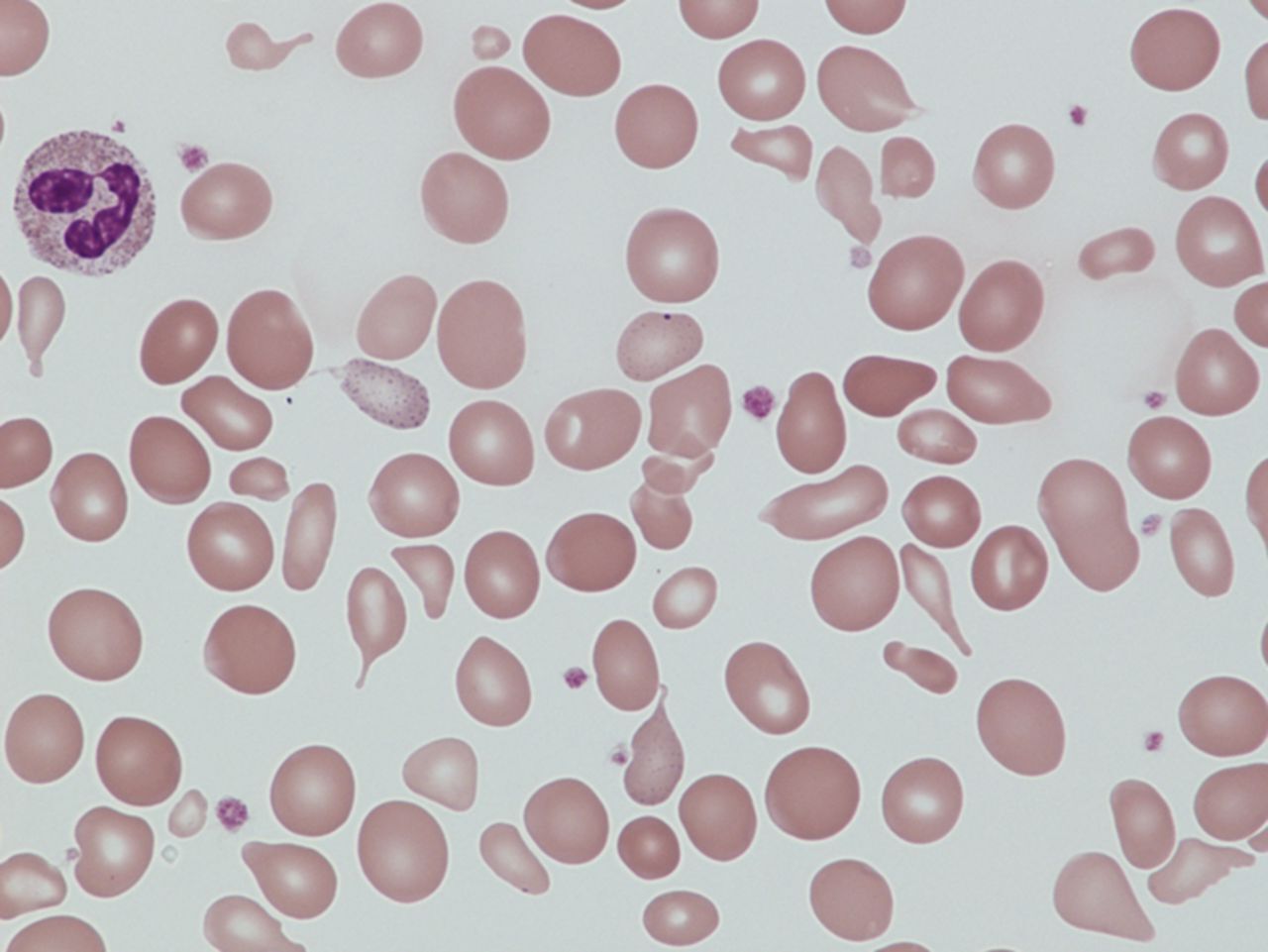
Dyserythropoietic anemia is a rare blood disorder that affects the production of red blood cells. This condition can lead to various health issues due to the body's inability to produce enough healthy red blood cells. Let's explore some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Rare Genetic Disorder: Dyserythropoietic anemia is primarily a genetic disorder. It is often inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry the gene for a child to be affected.
-
Types of Dyserythropoietic Anemia: There are three main types: Type I, Type II, and Type III. Each type has distinct characteristics and varying severity levels.
-
Bone Marrow Abnormalities: This condition is characterized by abnormal development of red blood cells in the bone marrow, leading to ineffective erythropoiesis.
-
Symptoms Vary: Common symptoms include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and jaundice. Severity can differ greatly from person to person.
-
Diagnosis Through Blood Tests: Blood tests, including a complete blood count (CBC), are crucial for diagnosing dyserythropoietic anemia. They help identify abnormal red blood cell shapes and sizes.
Causes and Genetic Factors
Understanding the causes and genetic factors behind dyserythropoietic anemia can help in managing the condition better.
-
Gene Mutations: Mutations in specific genes, such as CDAN1 for Type I and SEC23B for Type II, are known to cause this condition.
-
Family History Matters: A family history of dyserythropoietic anemia increases the likelihood of inheriting the disorder.
-
Not Linked to Lifestyle: Unlike some other forms of anemia, dyserythropoietic anemia is not caused by diet or lifestyle choices.
-
Prenatal Testing Available: For families with a history of the disorder, prenatal genetic testing can determine if a fetus is affected.
Treatment and Management
Managing dyserythropoietic anemia involves addressing symptoms and improving quality of life.
-
No Cure Yet: Currently, there is no cure for dyserythropoietic anemia, but treatments can help manage symptoms.
-
Blood Transfusions: Regular blood transfusions may be necessary to maintain adequate red blood cell levels.
-
Iron Chelation Therapy: This therapy helps remove excess iron from the body, a common issue due to frequent blood transfusions.
-
Bone Marrow Transplant: In severe cases, a bone marrow transplant might be considered as a potential treatment option.
-
Monitoring and Support: Regular monitoring by healthcare professionals is essential to manage the condition effectively.
Living with Dyserythropoietic Anemia
Living with this condition requires adjustments and support from family and healthcare providers.
-
Diet and Nutrition: While not a cause, maintaining a balanced diet can support overall health and well-being.
-
Regular Check-Ups: Frequent medical check-ups are crucial to monitor the condition and adjust treatments as needed.
-
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from others with similar experiences.
-
Education and Awareness: Educating oneself and others about the condition can help in managing expectations and reducing stigma.
-
Exercise with Caution: Physical activity is beneficial, but individuals should consult with healthcare providers to tailor exercise plans to their needs.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of dyserythropoietic anemia.
-
Gene Therapy Potential: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential future treatment option.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide access to new treatments and contribute to scientific knowledge.
-
Advancements in Genetic Testing: Improved genetic testing techniques are helping in early diagnosis and better management strategies.
-
International Collaboration: Global research collaborations are crucial for advancing knowledge and treatment options for rare disorders like dyserythropoietic anemia.
-
Patient Advocacy: Advocacy groups play a vital role in raising awareness and funding for research into rare diseases.
-
Hope for the Future: With ongoing research and advancements in medical science, there is hope for better treatments and possibly a cure in the future.
Final Thoughts on Dyserythropoietic Anemia
Dyserythropoietic anemia, a rare blood disorder, affects the body's ability to produce healthy red blood cells. Understanding its symptoms, like fatigue and pale skin, can lead to early diagnosis and better management. Genetic mutations often cause this condition, making family history a key factor in assessing risk. While treatments vary, they might include blood transfusions or medications to boost red blood cell production. Research continues to explore new therapies, offering hope for those affected. Awareness and education about this condition can help patients and families navigate the challenges it presents. Staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers ensures the best possible outcomes. Though rare, dyserythropoietic anemia reminds us of the complexities of the human body and the importance of ongoing medical research. Knowledge empowers individuals to take charge of their health and seek the support they need.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


