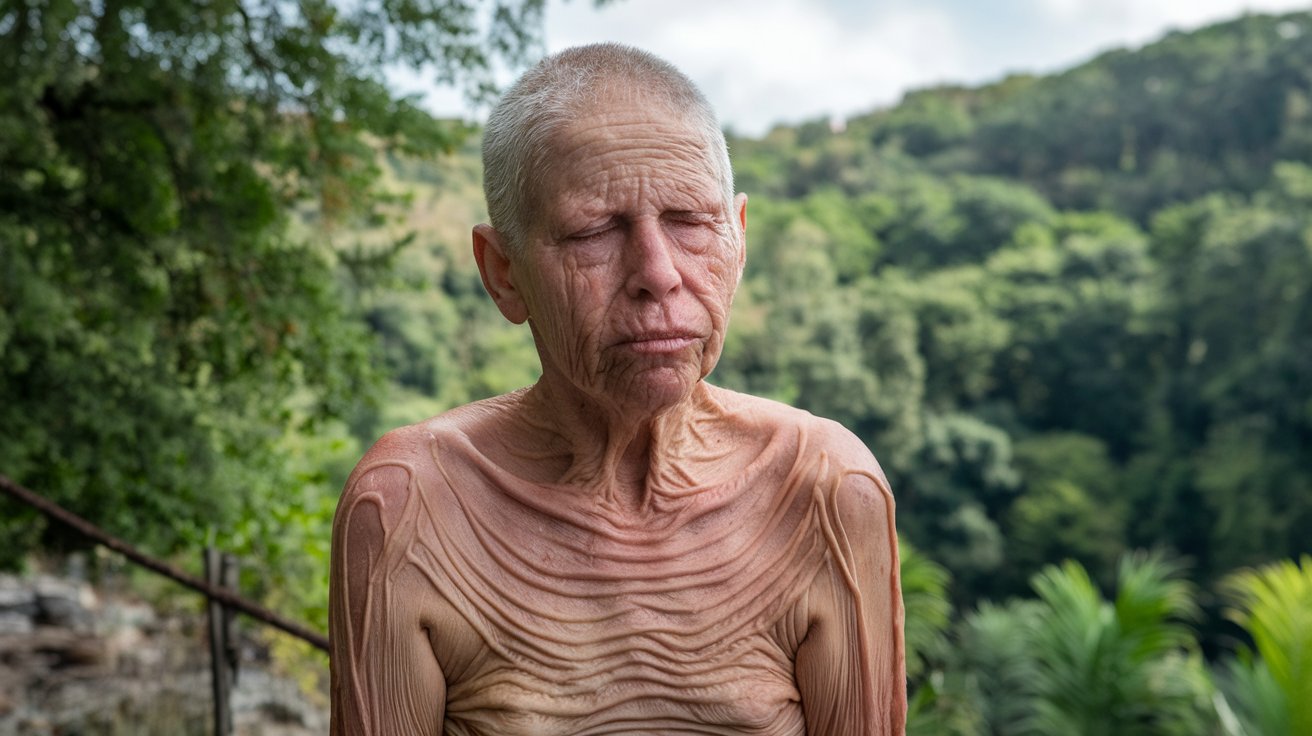
Gerodermia Osteodysplastica is a rare genetic disorder that affects connective tissue, leading to symptoms like loose, wrinkled skin and brittle bones. Caused by mutations in the GORAB gene, this condition often presents itself in early childhood. Individuals with this disorder may experience frequent bone fractures and joint dislocations due to weakened skeletal structures. Despite its rarity, understanding Gerodermia Osteodysplastica is crucial for early diagnosis and management. This article will provide 20 essential facts about this condition, covering its symptoms, genetic basis, and potential treatments. Stay informed and learn how this disorder impacts those who live with it daily.
Key Takeaways:
- Gerodermia Osteodysplastica is a rare genetic disorder affecting skin, bones, and joints. It causes loose, wrinkled skin, bone fragility, and joint pain, impacting daily life. Medical management focuses on orthopedic care, skin care, nutritional support, pain management, and genetic counseling.
- Ongoing research for Gerodermia Osteodysplastica includes gene therapy, stem cell research, animal models, patient registries, and support networks. These efforts aim to understand the condition better, develop new treatments, and provide valuable resources and emotional support for affected individuals and families.
What is Gerodermia Osteodysplastica?
Gerodermia Osteodysplastica (GO) is a rare genetic disorder affecting connective tissues. It primarily impacts the skin, bones, and joints, leading to various symptoms and complications. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Rare Genetic Disorder: GO is extremely rare, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide. This rarity makes it challenging to study and understand fully.
-
Inheritance Pattern: GO follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. This means both parents must carry the defective gene for a child to be affected.
-
Gene Mutation: The disorder is caused by mutations in the GORAB gene. This gene plays a crucial role in the function of the Golgi apparatus, which is essential for processing and transporting proteins within cells.
-
Skin Symptoms: Individuals with GO often have loose, wrinkled skin, especially noticeable on the face, hands, and feet. This symptom is due to the abnormal structure of connective tissues.
-
Bone Fragility: People with GO are prone to fractures due to brittle bones. This fragility can lead to frequent breaks and long-term complications.
How Does Gerodermia Osteodysplastica Affect Daily Life?
Living with GO can be challenging due to its impact on various bodily functions. Understanding these effects can help in managing the condition better.
-
Joint Laxity: GO often causes hypermobility in joints, leading to frequent dislocations and joint pain. This can limit physical activities and mobility.
-
Growth Retardation: Children with GO may experience delayed growth and shorter stature compared to their peers. This can affect their physical development and self-esteem.
-
Dental Issues: Dental anomalies, such as delayed tooth eruption and misalignment, are common in GO patients. Regular dental care is essential to manage these issues.
-
Vision Problems: Some individuals with GO may develop vision problems, including myopia and strabismus. Regular eye check-ups are crucial for early detection and treatment.
-
Hearing Loss: Hearing impairment can occur in GO patients due to abnormalities in the middle ear bones. Hearing aids and regular audiological evaluations can help manage this symptom.
Medical Management and Treatment Options
While there is no cure for GO, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Here are some key points about medical management.
-
Orthopedic Care: Regular monitoring by an orthopedic specialist is vital for managing bone fragility and joint issues. This may include physical therapy and surgical interventions.
-
Skin Care: Specialized skin care routines can help manage the loose, wrinkled skin associated with GO. Moisturizers and protective measures can prevent skin damage.
-
Nutritional Support: A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is essential for bone health. Nutritional supplements may be recommended to support overall health.
-
Pain Management: Pain relief strategies, including medications and physical therapy, can help manage joint and bone pain. Regular exercise can also improve mobility and reduce discomfort.
-
Genetic Counseling: Families affected by GO can benefit from genetic counseling to understand the inheritance pattern and risks for future pregnancies. This can help in making informed decisions.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand GO and develop new treatments. Here are some exciting developments in this field.
-
Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for GO. This approach aims to correct the defective GORAB gene and restore normal function.
-
Stem Cell Research: Stem cell therapy holds promise for regenerating damaged tissues and improving symptoms in GO patients. Clinical trials are underway to test its efficacy.
-
Animal Models: Scientists are developing animal models to study GO and test new treatments. These models can provide valuable insights into the disease mechanisms and potential therapies.
-
Patient Registries: Establishing patient registries can help collect data on GO cases worldwide. This information is crucial for understanding the disease's prevalence and developing targeted treatments.
-
Support Networks: Patient support groups and online communities provide valuable resources and emotional support for individuals and families affected by GO. Connecting with others facing similar challenges can be empowering.
Final Thoughts on Gerodermia Osteodysplastica
Gerodermia Osteodysplastica, a rare genetic disorder, affects connective tissues, leading to fragile bones and sagging skin. Understanding this condition helps in early diagnosis and better management. Genetic mutations in the GORAB gene cause this disorder, impacting collagen production. Symptoms often appear in childhood, with bone fractures and joint dislocations being common. While no cure exists, treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Physical therapy, orthopedic interventions, and regular monitoring play crucial roles. Raising awareness about Gerodermia Osteodysplastica can lead to more research and support for affected individuals. Knowledge empowers families and caregivers to provide better care and advocate for those living with this challenging condition. Stay informed, support research, and foster a community of understanding around Gerodermia Osteodysplastica.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
