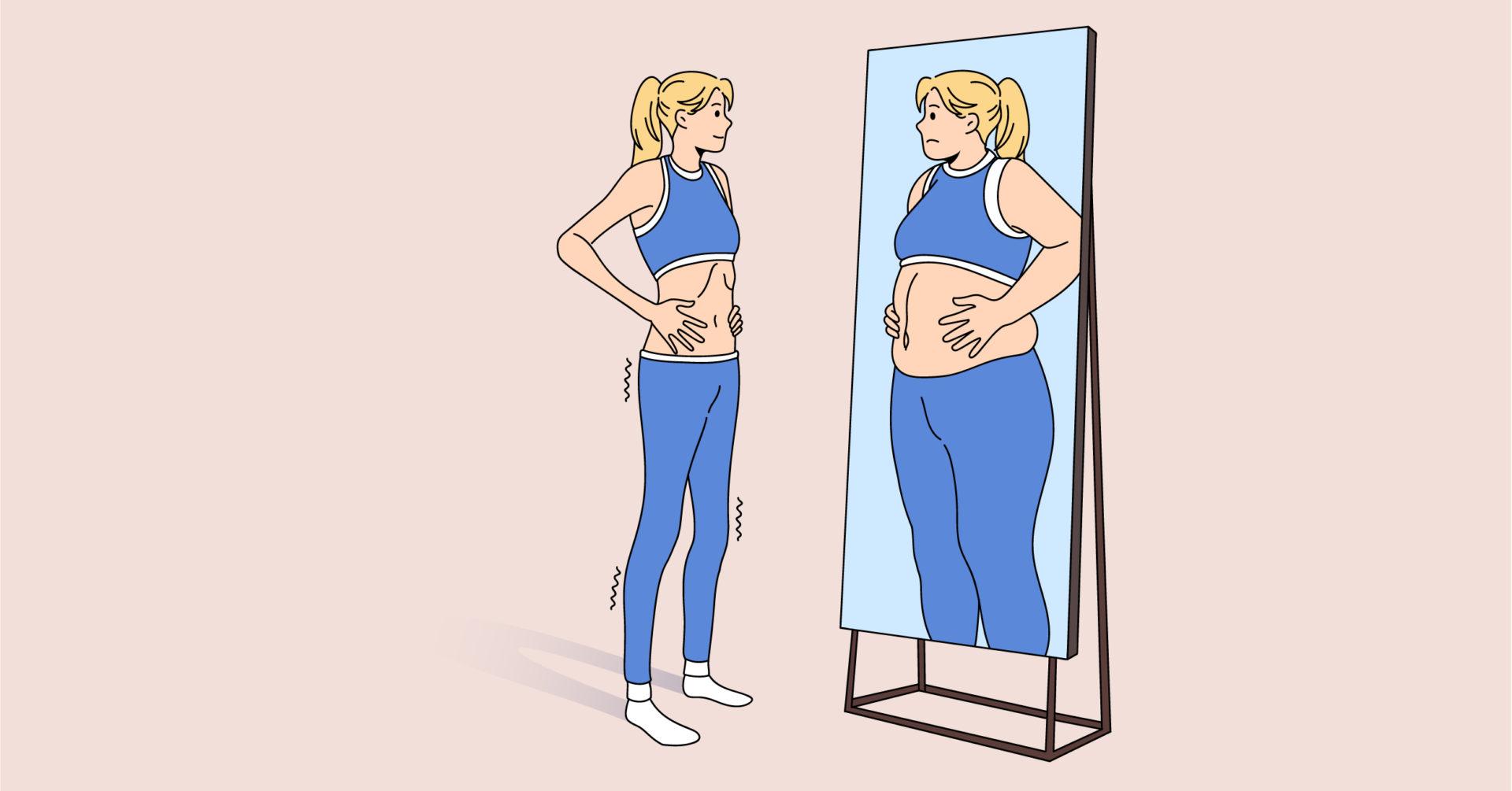
Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD) is a complex and often misunderstood mental health condition that affects individuals of all ages, genders, and backgrounds. It is characterized by obsessive preoccupation with perceived flaws in physical appearance, leading to significant distress and impairment in daily functioning. People with BDD may spend hours scrutinizing their appearance, engaging in repetitive behaviors such as excessive grooming or seeking reassurance, and avoiding social situations due to feelings of shame and inadequacy. Understanding the intricacies of BDD is crucial in promoting empathy and providing effective support for those grappling with this challenging disorder. In this article, we’ll delve into 15 enlightening facts about Body Dysmorphic Disorder, shedding light on its impact, prevalence, and potential avenues for healing and recovery.
Key Takeaways:
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD) affects both men and women equally and can lead to severe emotional distress, impacting daily life. Early recognition and intervention are crucial for addressing this mental health condition.
- Individuals with BDD may engage in repetitive behaviors or mental acts, such as constantly checking their appearance in mirrors, seeking reassurance about their looks, or grooming excessively. These behaviors are driven by the distressing belief that their perceived flaws are highly noticeable to others.
Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD) affects both men and women.
Body Dysmorphic Disorder, commonly known as BDD, is a mental health condition that involves a preoccupation with perceived flaws in appearance. While it is often associated with women, BDD affects both men and women equally. The disorder can lead to severe emotional distress and can significantly impact daily functioning.
Onset of BDD typically occurs during adolescence.
BDD often develops during adolescence, with the average age of onset being around 16-17 years old. During this vulnerable stage of life, individuals may become excessively concerned about their physical appearance, leading to the development of BDD. Early recognition and intervention are crucial in addressing this disorder and preventing long-term negative effects.
Individuals with BDD may engage in repetitive behaviors or mental acts.
People with BDD may engage in repetitive behaviors or mental acts, such as constantly checking their appearance in mirrors, seeking reassurance about their looks, or grooming excessively. These behaviors are driven by the distressing belief that their perceived flaws are highly noticeable to others, causing significant impairment in their daily lives.
BDD can co-occur with other mental health conditions.
It is not uncommon for individuals with BDD to experience other mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety disorders, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). The presence of these co-occurring conditions can further exacerbate the distress and impairment caused by BDD, making comprehensive treatment essential.
Social and occupational functioning may be significantly impaired in individuals with BDD.
Due to the distress and preoccupation with their appearance, individuals with BDD may experience significant impairment in their social and occupational functioning. This can manifest as avoidance of social situations, difficulty maintaining relationships, and challenges in pursuing educational or career goals.
BDD is not the same as vanity or low self-esteem.
It is important to distinguish BDD from normal concerns about appearance, vanity, or low self-esteem. BDD involves a distorted perception of one’s appearance, leading to obsessive thoughts and behaviors that can have a debilitating impact on an individual’s life.
Individuals with BDD may seek unnecessary cosmetic procedures.
Driven by their preoccupation with perceived flaws, individuals with BDD may seek out multiple cosmetic procedures in an attempt to correct their appearance. However, these procedures rarely provide the relief they seek, as the distress is rooted in the individual’s perception rather than actual physical imperfections.
BDD can lead to severe emotional distress and functional impairment.
The distress caused by BDD can be intense, leading to significant emotional suffering and impairment in various areas of life. This can include difficulty concentrating, disruptions in daily routines, and a diminished quality of life.
Media and societal influences can exacerbate BDD symptoms.
The portrayal of idealized beauty standards in the media and societal pressures regarding appearance can exacerbate BDD symptoms. Constant exposure to unrealistic beauty ideals and societal judgment can intensify the distress experienced by individuals with BDD.
Effective treatments for BDD include therapy and medication.
Therapeutic interventions, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), have been found to be effective in treating BDD. Additionally, certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), may be prescribed to help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Support from loved ones is crucial for individuals with BDD.
Having a strong support system can make a significant difference in the lives of individuals with BDD. Understanding, empathy, and encouragement from family and friends can contribute to the individual’s recovery journey and overall mental well-being.
Early intervention is key in addressing BDD.
Early recognition and intervention are crucial in addressing BDD and preventing the exacerbation of symptoms. By seeking help as soon as symptoms arise, individuals with BDD can receive the necessary support and treatment to manage the disorder effectively.
Self-help strategies can complement professional treatment for BDD.
Engaging in self-help strategies, such as mindfulness practices, stress-reduction techniques, and self-care activities, can complement professional treatment for BDD. These strategies can empower individuals to actively participate in their own healing and well-being.
Increased awareness and understanding of BDD are essential.
Enhanced awareness and understanding of BDD within the community and healthcare settings are essential for promoting early detection, reducing stigma, and ensuring that individuals receive appropriate support and treatment. Education and advocacy play a vital role in addressing the challenges associated with BDD.
Recovery from BDD is possible with comprehensive treatment and support.
With access to effective treatment, ongoing support, and a commitment to the recovery process, individuals with BDD can experience significant improvement in their symptoms and overall quality of life. Recovery is a journey that is achievable with the right resources and encouragement.
Conclusion
Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD) is a complex and often misunderstood mental health condition that can have a profound impact on an individual’s life. It is crucial to raise awareness about BDD and to provide support and understanding to those who are affected by it. By educating ourselves and others about the facts and realities of BDD, we can work towards reducing stigma and promoting empathy and effective treatment. Remember, seeking professional help and support is essential for individuals living with BDD. With the right resources and understanding, those affected by BDD can find hope and healing.
FAQs
What is Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD)?
Body Dysmorphic Disorder (BDD) is a mental health condition characterized by obsessive preoccupation with perceived flaws or defects in one’s physical appearance.
How common is Body Dysmorphic Disorder?
BDD affects approximately 1-2% of the population, but the actual prevalence may be higher due to underreporting and misdiagnosis.
What are the common signs and symptoms of Body Dysmorphic Disorder?
Common signs and symptoms of BDD include excessive grooming or seeking reassurance about one’s appearance, avoiding social situations, and engaging in repetitive behaviors such as checking mirrors or seeking cosmetic procedures.
What are the treatment options for Body Dysmorphic Disorder?
Treatment for BDD may include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), medication, and support groups. Seeking help from mental health professionals is crucial for managing BDD.
Can Body Dysmorphic Disorder be effectively managed?
With proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals with BDD can experience improvement in their symptoms and quality of life. However, ongoing support and management are often necessary.
How can I support someone with Body Dysmorphic Disorder?
Supporting someone with BDD involves offering empathy, understanding, and encouragement to seek professional help. It is important to avoid judgment and criticism while being a source of comfort and support.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
