Stranger Things has captured the hearts of millions since its debut. But did you know there are some mind-blowing facts about this hit series? Stranger Things isn't just a show; it's a phenomenon filled with hidden gems and behind-the-scenes secrets. From the inspiration behind the Upside Down to the real-life locations used for filming, there's so much more to this series than meets the eye. Ever wondered how the Duffer Brothers came up with Eleven's character or why the show is set in the '80s? Stranger Things fans, get ready to dive into a world of fascinating trivia that will make you appreciate the series even more. Buckle up, because these 31 facts are about to turn your world upside down!
Key Takeaways:
- Strain is a way to measure how much an object is stretched or compressed. It helps engineers and scientists understand how materials react to different forces, like stretching a rubber band or squeezing a stress ball.
- Measuring strain is important for making sure structures and materials are safe and reliable. It's used in building bridges, designing airplanes, and even in everyday activities like twisting a wet towel or bending a plastic ruler.
What is Strain?
Strain is a measure of deformation representing the displacement between particles in a material body. It quantifies how much an object is stretched or compressed. Understanding strain helps in fields like engineering, physics, and materials science.
-
Strain is dimensionless, meaning it has no units. It’s a ratio of change in length to the original length.
-
There are two main types of strain: normal strain and shear strain. Normal strain measures changes in length, while shear strain measures changes in shape.
-
Strain can be positive or negative. Positive strain indicates stretching, while negative strain indicates compression.
-
Strain is often represented by the Greek letter epsilon (ε) for normal strain and gamma (γ) for shear strain.
-
Engineers use strain gauges to measure strain in structures. These devices can detect tiny changes in length.
Types of Strain
Different types of strain help us understand how materials react under various forces. Each type provides unique insights into material behavior.
-
Tensile strain occurs when a material is stretched. It’s common in materials like rubber bands and metal wires.
-
Compressive strain happens when a material is compressed. It’s seen in materials like concrete and foam.
-
Shear strain occurs when a material is subjected to forces that cause it to twist or change shape without changing volume.
-
Volumetric strain measures the change in volume of a material. It’s important in fluid mechanics and material science.
-
Thermal strain results from changes in temperature. Materials expand or contract when heated or cooled.
Measuring Strain
Accurate measurement of strain is crucial for ensuring the safety and performance of structures and materials. Various tools and techniques are used for this purpose.
-
Strain gauges are the most common tools for measuring strain. They consist of a thin wire or foil that deforms with the material.
-
Optical methods, like digital image correlation, use cameras to measure strain by tracking changes in a material’s surface.
-
Extensometers measure strain by directly measuring the change in length between two points on a material.
-
Piezoelectric sensors generate an electric charge in response to strain, providing another method for measurement.
-
Fiber optic sensors use changes in light transmission to measure strain, offering high sensitivity and resistance to electromagnetic interference.
Applications of Strain
Understanding and measuring strain has numerous practical applications across various industries. It helps in designing safer and more efficient structures and materials.
-
In civil engineering, strain measurements ensure the safety of bridges, buildings, and dams by monitoring structural integrity.
-
Aerospace engineers use strain data to design aircraft that can withstand extreme forces during flight.
-
Automotive engineers rely on strain measurements to improve vehicle safety and performance by testing components under stress.
-
In biomechanics, strain analysis helps in designing prosthetics and understanding how bones and tissues respond to forces.
-
Strain measurements in manufacturing ensure the quality and reliability of products by detecting defects and weaknesses.
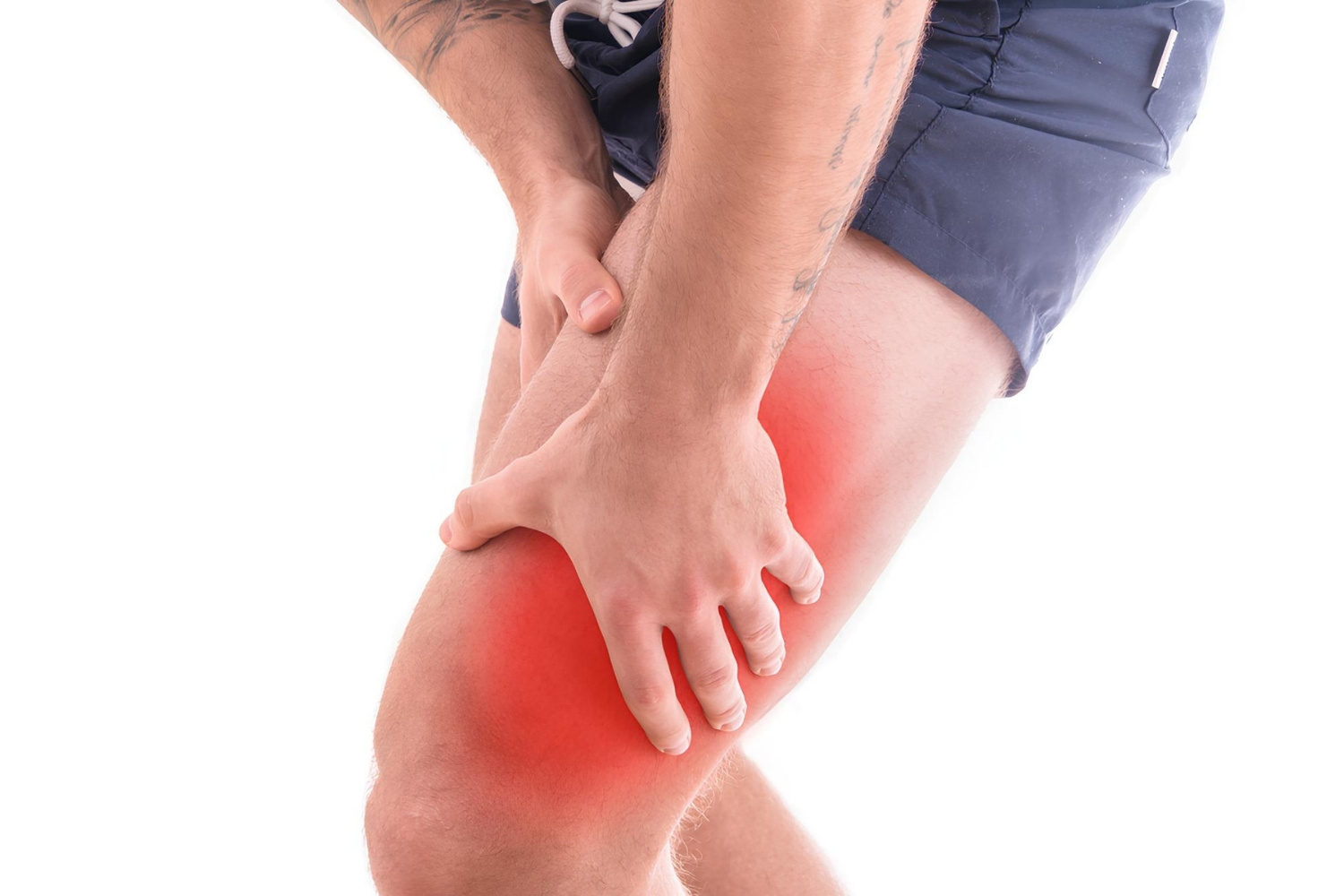
Strain in Everyday Life
Strain isn’t just a concept for scientists and engineers. It’s something we encounter in everyday life, often without realizing it.
-
When you stretch a rubber band, you’re applying tensile strain.
-
Squeezing a stress ball involves compressive strain.
-
Twisting a wet towel to wring out water applies shear strain.
-
The expansion of metal in a hot car engine is an example of thermal strain.
-
The bending of a plastic ruler when you apply force demonstrates both tensile and compressive strain.
Interesting Facts about Strain
Here are some fascinating tidbits about strain that highlight its importance and versatility.
-
The first strain gauge was invented in 1938 by Edward E. Simmons and Arthur C. Ruge.
-
Strain gauges can measure deformations as small as a few micrometers.
-
Strain energy is the energy stored in a material due to deformation. It’s a key concept in material science.
-
The study of strain helps in earthquake engineering by understanding how buildings and structures respond to seismic forces.
-
Strain analysis is crucial in the development of new materials, such as composites and smart materials, which have unique properties.
-
Strain can also be used in medical diagnostics, such as measuring the strain in blood vessels to detect cardiovascular diseases.
Final Thoughts on Strain
Strain, a concept often overlooked, plays a crucial role in various fields. From engineering to biology, understanding strain helps in predicting how materials and organisms respond to stress. It’s fascinating how strain can affect everything from bridges to human muscles. Knowing these facts can give you a new appreciation for the invisible forces at work in our world.
Whether you’re a student, a professional, or just curious, grasping the basics of strain can be incredibly beneficial. It’s not just about numbers and equations; it’s about understanding the world around us. So next time you see a building or even stretch your muscles, remember the science of strain working behind the scenes.
Thanks for sticking around and diving into these intriguing facts. Keep exploring, keep questioning, and always stay curious!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
