What is the Aufbau Principle? The Aufbau Principle is a fundamental concept in chemistry that explains how electrons fill atomic orbitals. According to this principle, electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals first before moving to higher energy levels. This rule helps predict the electron configurations of atoms, which in turn determines their chemical properties. Understanding the Aufbau Principle is crucial for grasping how elements interact in chemical reactions. It’s like a guidebook for placing electrons in their proper "homes" within an atom. Want to know more about this essential principle? Keep reading to uncover 35 fascinating facts about the Aufbau Principle that will deepen your understanding of atomic structure and electron behavior.
The Basics of Aufbau
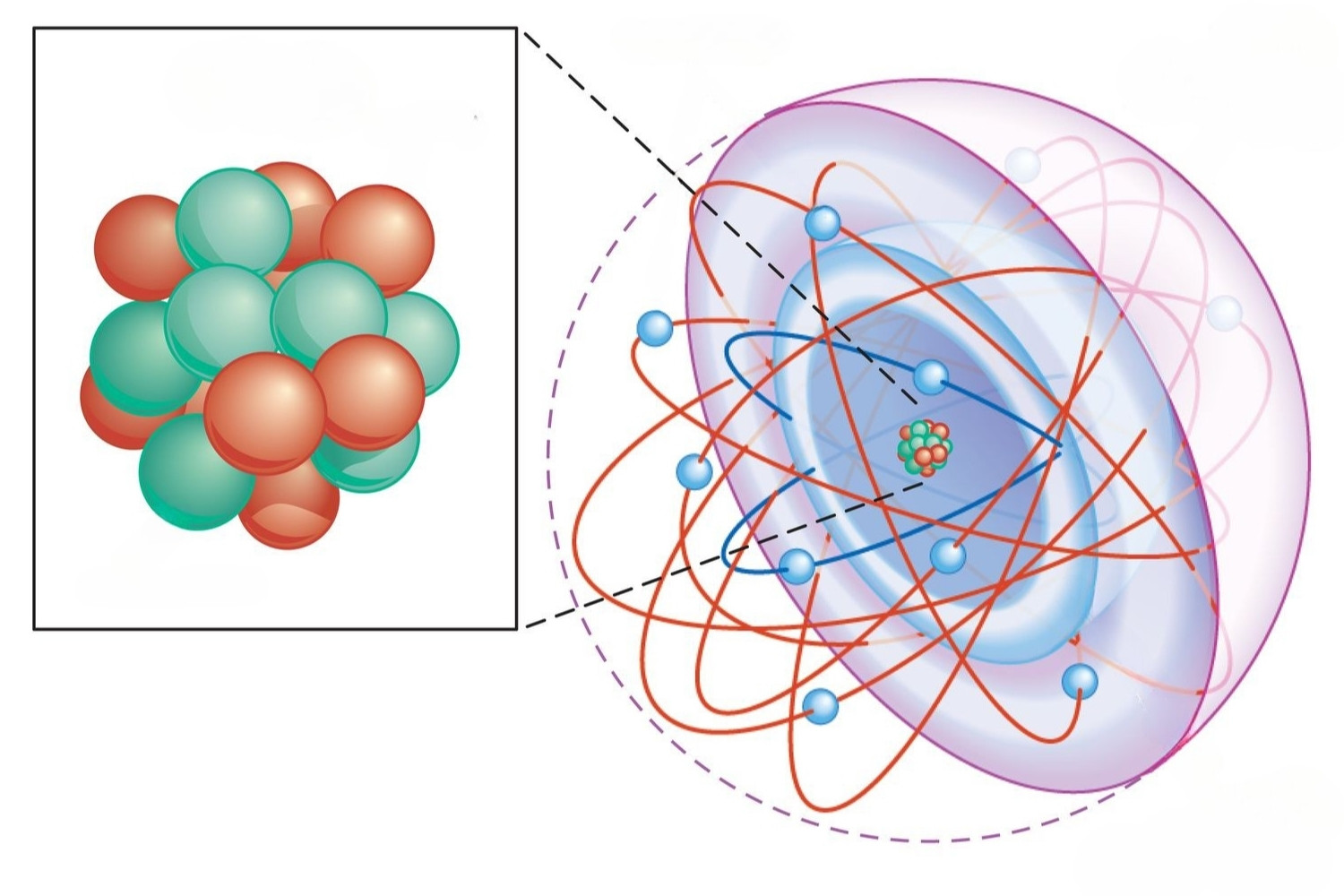
The Aufbau principle is a fundamental concept in chemistry. It helps explain how electrons are arranged in atoms. Let's dive into some interesting facts about this principle.
-
Meaning of Aufbau: The word "Aufbau" comes from German, meaning "building up" or "construction." It reflects how electrons fill up atomic orbitals.
-
Electron Configuration: Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals first before moving to higher ones.
-
Pauli Exclusion Principle: This principle works alongside the Pauli Exclusion Principle, which states that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers.
-
Hund's Rule: Hund's Rule complements Aufbau by stating that electrons will fill degenerate orbitals singly before pairing up.
-
Energy Levels: Electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy levels, starting from 1s, 2s, 2p, and so on.
-
Orbital Types: The types of orbitals filled include s, p, d, and f, each with different shapes and capacities.
Historical Context
Understanding the historical context of the Aufbau principle can provide deeper insights into its development and significance.
-
Niels Bohr: Niels Bohr, a Danish physicist, played a crucial role in developing the concept of electron configurations.
-
Early 20th Century: The Aufbau principle was formulated in the early 20th century, during the development of quantum mechanics.
-
Quantum Mechanics: The principle is rooted in quantum mechanics, which describes the behavior of particles at atomic and subatomic levels.
-
Bohr Model: The Bohr model of the atom laid the groundwork for understanding electron arrangements.
-
Schrödinger Equation: The Schrödinger equation, developed by Erwin Schrödinger, mathematically describes how electrons occupy orbitals.
Practical Applications
The Aufbau principle is not just theoretical; it has practical applications in various fields.
-
Periodic Table: The principle helps explain the structure of the periodic table, showing how elements are organized based on electron configurations.
-
Chemical Reactions: Understanding electron configurations aids in predicting how atoms will interact in chemical reactions.
-
Spectroscopy: Spectroscopy, the study of how matter interacts with electromagnetic radiation, relies on electron configurations to interpret spectra.
-
Material Science: In material science, knowing electron arrangements helps in designing new materials with specific properties.
-
Pharmaceuticals: The principle is used in drug design to understand how molecules will interact at the atomic level.
Exceptions to the Rule
While the Aufbau principle is widely applicable, there are notable exceptions.
-
Transition Metals: Transition metals often have irregular electron configurations due to the close energy levels of their d and s orbitals.
-
Lanthanides and Actinides: These elements also show deviations from the expected order due to their complex electron interactions.
-
Copper and Chromium: Copper and chromium are classic examples where the actual electron configuration differs from the predicted one.
-
Electron-Electron Repulsion: Sometimes, electron-electron repulsion within an atom causes deviations from the Aufbau principle.
Quantum Numbers
Quantum numbers are essential for understanding the Aufbau principle.
-
Principal Quantum Number (n): Indicates the energy level of an electron in an atom.
-
Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l): Determines the shape of the orbital.
-
Magnetic Quantum Number (m_l): Specifies the orientation of the orbital in space.
-
Spin Quantum Number (m_s): Describes the spin of the electron, which can be either +1/2 or -1/2.
Visualizing Aufbau
Visual aids can make the Aufbau principle easier to grasp.
-
Orbital Diagrams: Orbital diagrams visually represent electron configurations using arrows to indicate electron spins.
-
Energy Level Diagrams: These diagrams show the relative energy levels of different orbitals.
-
Electron Configuration Notation: A shorthand notation that uses numbers and letters to describe electron arrangements, like 1s² 2s² 2p⁶.
-
Periodic Table Blocks: The periodic table is divided into blocks (s, p, d, f) that correspond to the filling of different orbitals.
Educational Importance
The Aufbau principle is a cornerstone in chemistry education.
-
High School Chemistry: Students learn about Aufbau in high school chemistry classes to understand atomic structure.
-
College Courses: In college, the principle is explored in more depth, especially in physical chemistry and quantum mechanics courses.
-
Textbooks: Chemistry textbooks often dedicate entire chapters to electron configurations and the Aufbau principle.
-
Online Resources: Numerous online resources, including videos and interactive tools, help students visualize and understand the principle.
Fun Facts
Let's end with some fun and lesser-known facts about the Aufbau principle.
-
Mnemonic Devices: Mnemonic devices like "1s2 2s2 2p6" help students remember the order of orbital filling.
-
Periodic Trends: The Aufbau principle helps explain periodic trends like atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity.
-
Element Discovery: Understanding electron configurations has been crucial in the discovery and classification of new elements.
Final Thoughts on Aufbau
Aufbau is a fascinating principle in chemistry that helps us understand how electrons fill atomic orbitals. It’s like a rulebook for building atoms, guiding us through the process step by step. Knowing these 35 facts about Aufbau can deepen your appreciation for the intricate dance of electrons and how they shape the elements around us. Whether you’re a student, a teacher, or just a curious mind, these insights can make the world of chemistry a bit more approachable. Keep exploring, keep questioning, and remember that every atom has a story to tell. Understanding Aufbau is just one chapter in the grand tale of science. So next time you look at the periodic table, think about the Aufbau principle and the hidden order within the elements. Happy learning!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
