Ampere is a name you might have heard in your science class, but do you know why it's so important? Named after André-Marie Ampère, a French physicist and mathematician, the ampere is the unit of electric current in the International System of Units (SI). Electric current is the flow of electric charge, and it's measured in amperes, often shortened to "amps." This unit is crucial for everything from powering your smartphone to running massive industrial machines. Understanding amperes can help you grasp how electricity works in everyday life. Ready to learn some cool facts about this essential unit? Let's dive in!
What is an Ampere?
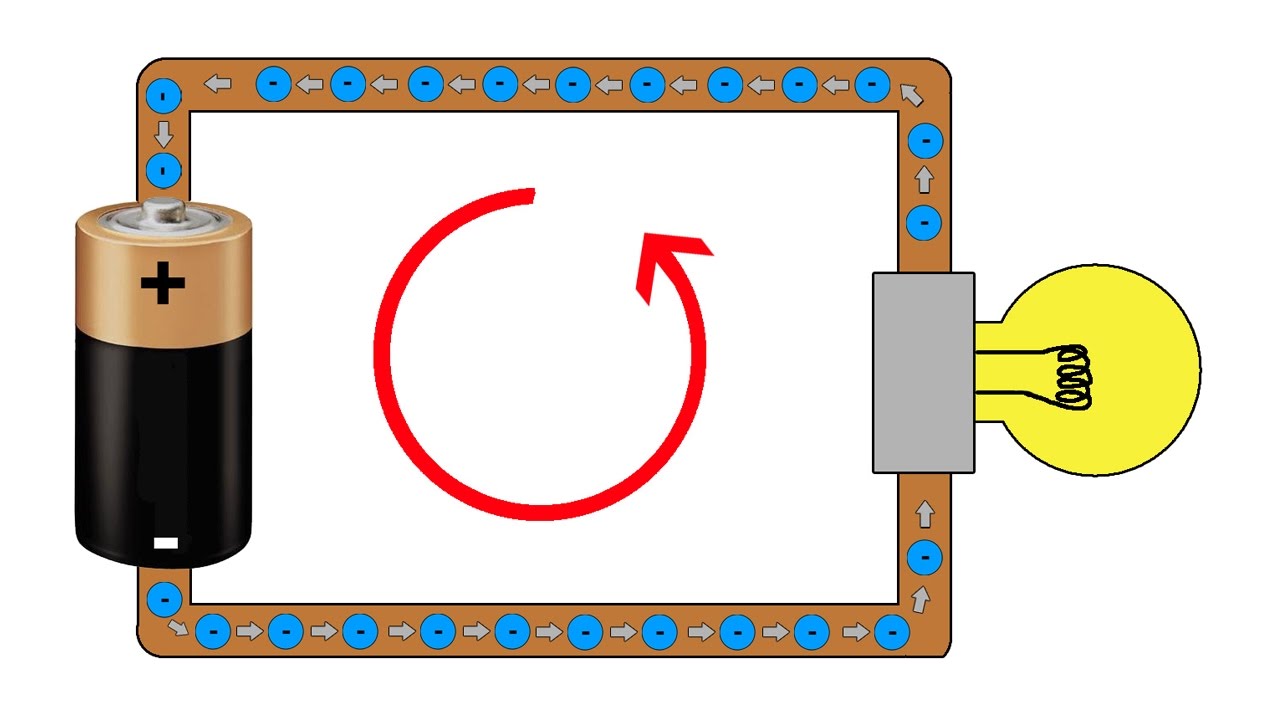
An ampere, often shortened to amp, is a unit of electric current. Named after André-Marie Ampère, a French physicist, it measures the amount of electric charge passing a point in an electric circuit per unit time.
-
The ampere is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). This makes it fundamental in the world of physics and engineering.
-
One ampere equals one coulomb of charge passing through a point in one second. This relationship ties together electric current and charge.
-
The symbol for ampere is 'A'. This simple notation is universally recognized in electrical engineering.
-
André-Marie Ampère, the unit's namesake, was a pioneer in electromagnetism. His work laid the foundation for much of modern electrical science.
Historical Background
Understanding the history of the ampere helps appreciate its significance in science and technology.
-
The ampere was officially defined in 1881. This happened at the International Exposition of Electricity in Paris.
-
Before the ampere, electric current was measured in arbitrary units. Standardizing the ampere helped unify electrical measurements globally.
-
The original definition of the ampere was based on the force between two wires. This method involved measuring the force per meter between two parallel conductors.
-
In 2019, the definition of the ampere was updated. The new definition relies on the elementary charge, making it more precise.
Practical Applications
Amperes are crucial in various practical applications, from household electronics to industrial machinery.
-
Household electrical systems typically use 15-20 amp circuits. This ensures safe and efficient power distribution in homes.
-
Car batteries are rated in ampere-hours (Ah). This rating indicates how long a battery can supply a certain current.
-
Electricians use ammeters to measure current. These devices help diagnose electrical issues and ensure systems operate correctly.
-
High-power industrial machines often require hundreds of amps. This high current enables heavy-duty operations.
Ampere in Everyday Life
Amperes play a significant role in everyday gadgets and appliances.
-
Smartphones charge at rates measured in milliamps (mA). This smaller unit of current is crucial for battery life and charging speed.
-
LED bulbs use fewer amps than traditional incandescent bulbs. This efficiency makes them more energy-saving.
-
Electric vehicles (EVs) use high-current charging systems. These systems can deliver hundreds of amps for fast charging.
-
USB ports supply power in milliamps. This standardization ensures compatibility across various devices.
Scientific Significance
In science, the ampere is essential for experiments and theoretical work.
-
The ampere is used in Ohm's Law. This fundamental law relates current, voltage, and resistance.
-
In physics, amperes help describe electromagnetic fields. These fields are crucial for understanding forces and waves.
-
Amperes are vital in quantum mechanics. They help measure and predict particle behavior.
-
In chemistry, amperes measure the rate of electrochemical reactions. This is important for processes like electrolysis.
Ampere and Safety
Safety in electrical systems often revolves around controlling and measuring current.
-
Circuit breakers are rated in amps. They protect systems by interrupting excessive current flow.
-
Fuses also use amp ratings. These devices melt and break the circuit when current exceeds safe levels.
-
Electrical insulation is tested for ampere capacity. This ensures materials can handle expected currents without failure.
-
Grounding systems are designed to carry fault currents safely. Proper grounding prevents dangerous situations.
Ampere in Technology
Modern technology relies heavily on precise current measurements.
-
Microprocessors operate with currents in microamps (µA). These tiny currents enable complex computations.
-
Solar panels generate current measured in amps. This current is then converted to usable electricity.
-
Medical devices often use low-current circuits. These ensure patient safety while providing necessary functions.
-
Telecommunications equipment requires precise current control. This ensures reliable signal transmission.
Fun Facts About Amperes
Some interesting tidbits about amperes can make learning about them more enjoyable.
-
The ampere is sometimes called the "amp" for short. This nickname is widely used in both professional and casual contexts.
-
A lightning bolt can carry up to 300,000 amps. This immense current is what makes lightning so powerful and dangerous.
-
The human body can feel currents as low as 1 milliamp. Higher currents can cause pain or even be lethal.
-
Superconductors can carry extremely high currents without resistance. This property makes them useful in advanced technologies.
-
The ampere is related to the watt, a unit of power. One watt equals one ampere of current flowing through one volt of potential difference.
The Final Ampere Facts
Ampere's contributions to science are monumental. His work laid the groundwork for electromagnetism, a field that powers much of our modern technology. From the ampere unit of electric current to Ampère's circuital law, his legacy is everywhere. Understanding these facts gives us a glimpse into the mind of a genius who changed the world.
Ampere's life wasn't just about equations and experiments. He faced personal struggles, yet his passion for science never wavered. This resilience adds depth to his story, making his achievements even more inspiring.
By learning about Ampere, we not only honor his memory but also gain a deeper appreciation for the scientific principles that shape our daily lives. So next time you flip a light switch or charge your phone, remember the man who made it all possible. Ampere's legacy is a testament to the power of curiosity and perseverance.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
