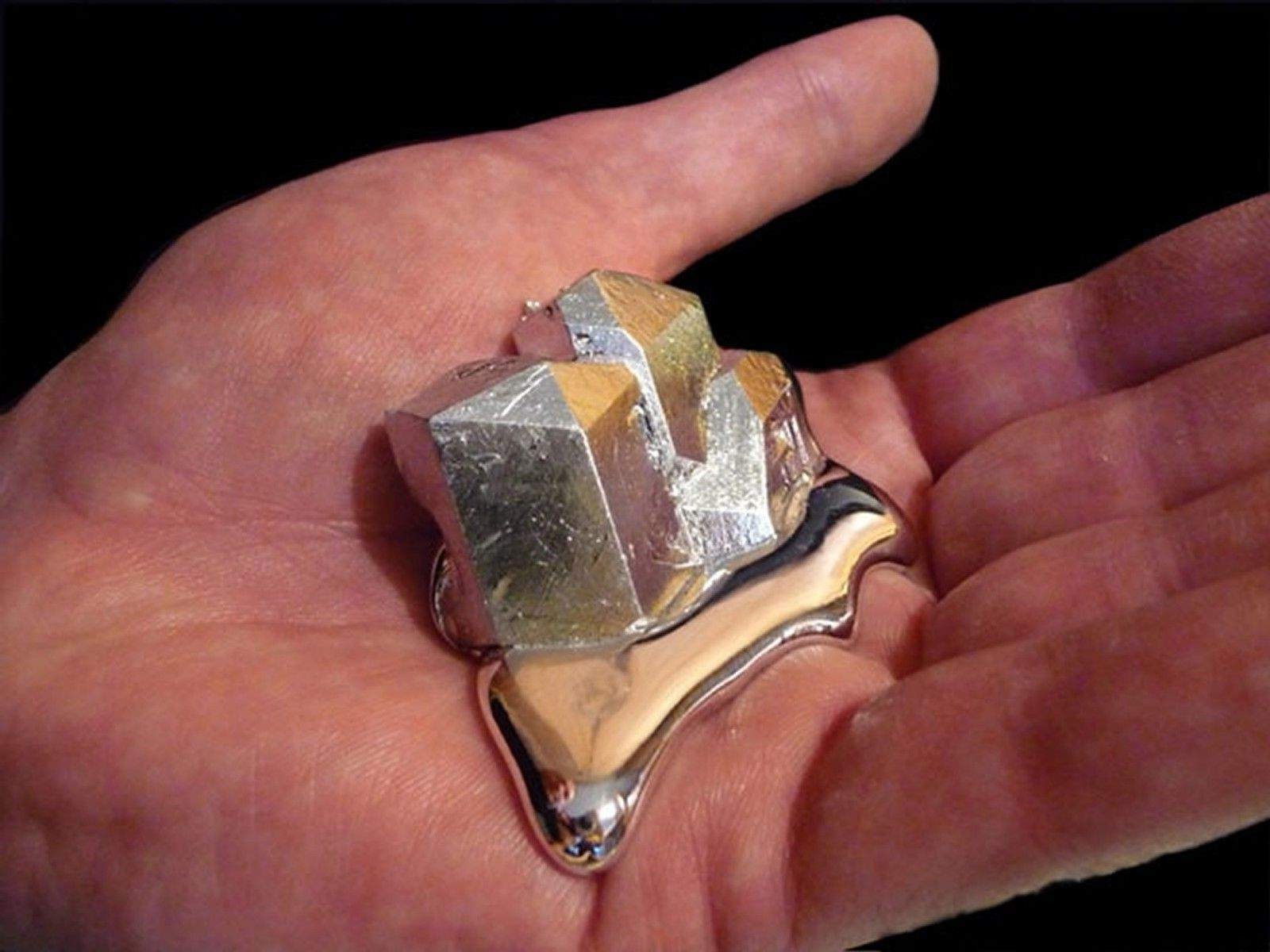
Gallium is a fascinating element that often flies under the radar. Ever wondered what makes this metal so special? Gallium is unique because it can melt in your hand, turning from a solid to a liquid at just above room temperature. This quirky characteristic isn't the only thing that sets it apart. Gallium is also used in electronics, solar panels, and even medical imaging. Its ability to form alloys with other metals makes it incredibly versatile. Ready to dive into more intriguing facts about this amazing element? Let's explore the wonders of Gallium and see why it's more than just a melting metal.
What is Gallium?
Gallium is a fascinating element with unique properties that make it stand out. Found in the periodic table with the symbol Ga and atomic number 31, this metal has some surprising characteristics.
-
Gallium Melts in Your Hand: With a melting point of just 29.76°C (85.57°F), gallium can melt from the warmth of your hand. This makes it a fun and educational tool for science demonstrations.
-
Gallium Expands When Solidifying: Unlike most metals, gallium expands when it solidifies. This can cause containers to break if the metal is allowed to freeze inside them.
Gallium's Role in Technology
Gallium plays a crucial role in modern technology, especially in electronics and semiconductors. Its unique properties make it indispensable in various applications.
-
Gallium Arsenide in Semiconductors: Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a compound used in semiconductors. It has superior electron mobility compared to silicon, making it ideal for high-speed electronics and optoelectronic devices.
-
Gallium Nitride in LEDs: Gallium nitride (GaN) is another compound used in light-emitting diodes (LEDs). It produces bright, energy-efficient light and is used in everything from smartphone screens to streetlights.
Gallium in Medicine
Gallium's properties also make it valuable in the field of medicine. Its compounds are used in various diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
-
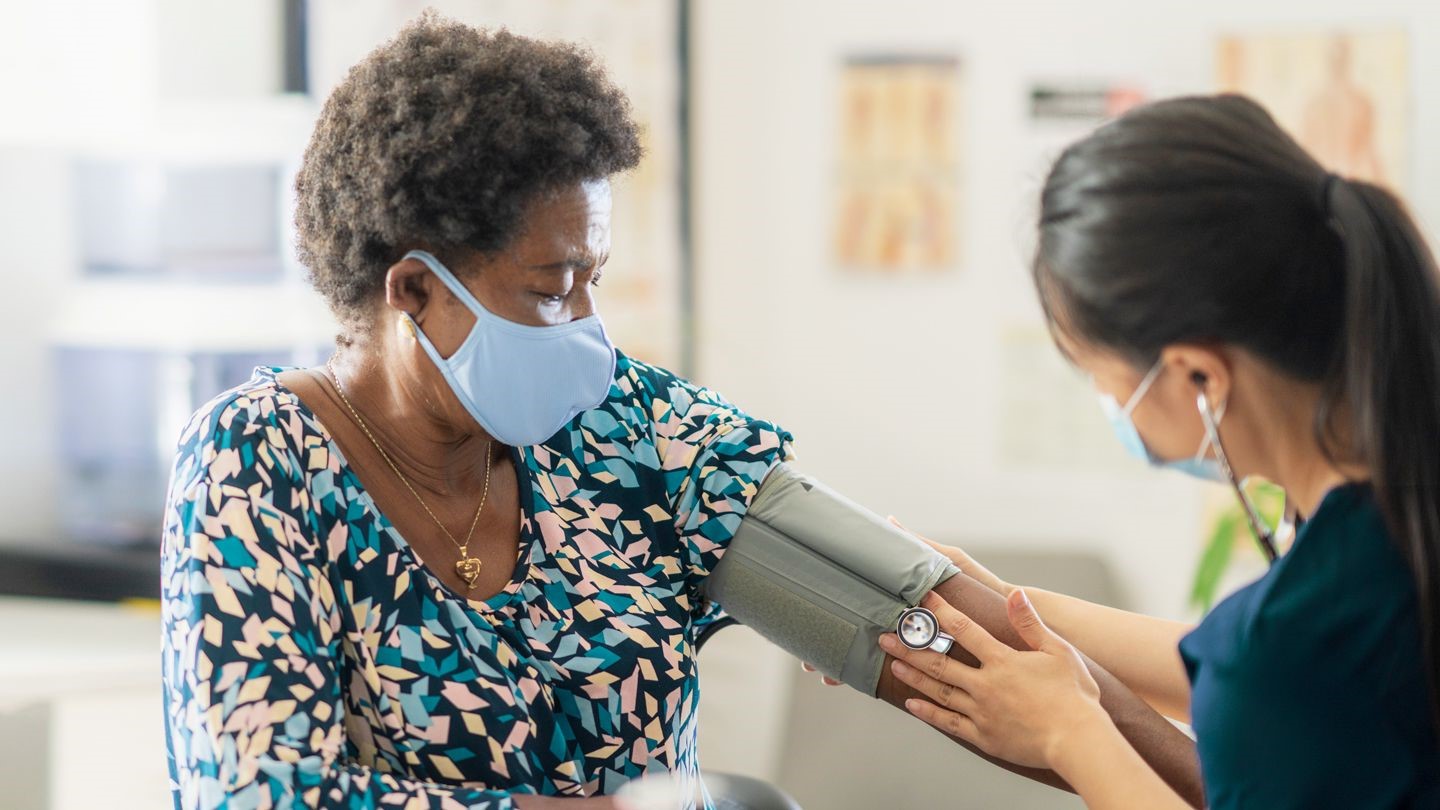
Gallium Scans for Cancer Detection: Gallium-67 is a radioactive isotope used in medical imaging to detect cancerous tumors and inflammation. It helps doctors diagnose and monitor the progression of diseases.
-
Gallium Nitrate for Bone Disease: Gallium nitrate is used to treat hypercalcemia (high calcium levels in the blood) associated with cancer. It helps reduce calcium levels and alleviate symptoms.
Fun and Unusual Facts About Gallium
Gallium has some quirky and lesser-known facts that make it even more interesting. These tidbits highlight its unique nature and versatility.
-
Gallium Mirrors: Gallium can be used to create mirrors. When applied to glass, it forms a reflective surface, making it useful in scientific instruments and telescopes.
-
Gallium in Thermometers: Gallium is sometimes used in thermometers as a non-toxic alternative to mercury. Its low melting point and high boiling point make it suitable for measuring a wide range of temperatures.
-
Gallium's Discovery: Gallium was discovered in 1875 by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran. He named it after "Gallia," the Latin name for France.
-
Gallium's Appearance in Pop Culture: Gallium has made appearances in pop culture, including the TV show "Breaking Bad," where it was used in a science experiment to demonstrate its melting properties.
Environmental Impact of Gallium
Gallium's extraction and use have environmental implications. Understanding these impacts is essential for sustainable practices.
-
Gallium Recycling: Gallium can be recycled from electronic waste, reducing the need for new mining and minimizing environmental impact. Recycling helps conserve resources and reduce pollution.
-
Gallium's Abundance: Gallium is not found in its pure form in nature. It is typically extracted as a byproduct of mining other metals like aluminum and zinc. This makes its extraction more environmentally friendly compared to primary mining.
-
Gallium's Role in Solar Panels: Gallium is used in thin-film solar panels, which are more efficient and less resource-intensive than traditional silicon-based panels. This contributes to the development of sustainable energy solutions.
The Fascinating World of Gallium
Gallium's unique properties make it a standout element. From melting in your hand to its role in electronics, gallium is more than just a curiosity. Its low melting point and ability to form alloys with other metals have practical applications in thermometers, LEDs, and even solar panels. This element's versatility extends to medical imaging and cancer treatment, showcasing its importance in various fields.
Understanding gallium's characteristics helps us appreciate its contributions to technology and science. Whether you're a student, a hobbyist, or just someone who loves learning new things, gallium offers a wealth of interesting facts to explore. So next time you hear about this remarkable element, you'll know there's much more to it than meets the eye. Keep discovering and stay curious about the wonders of the periodic table!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.