
Numbers dictate our lives. From money, to our weight, to the amount of stars in the galaxy. These number facts will prove how amazing life is by the digits.
- Numbers are arithmetic objects used to count and measure.
- Numerals are the symbols that represent numbers.
- Numerals vary with each language.
- The numerals we use now are called “Hindu-Arabic” numbers.
- 1 is not a prime number.
- The earliest form of numbers were tally marks found on prehistoric bones and artifacts.
- The tally system was first observed in the Sumerian and Babylonian civilizations of Mesopotamia and Egypt.
- The Hindu-Arabic number system originated from 6th to 7th century India.
- Zero is the only number without a roman numeral.
- There’s only one even prime number – and that is 2.
- Roman Numerals were invented for trading.
- Zero is an even number because it is an integer multiple of 2 (0 x 2).
- The only prime numbers ending with “2” or “5” are the numbers two and five themselves.
- China has the biggest population: 1,436,207,552.
- The Vatican has the smallest population: 799.
- 13 is the most famous 2-digit number.
- The average person has 100,000 hairs.
- Sudoku is an American game.
- There are more permutations to a deck of cards than all the atoms on the Earth.
- Certain cultures don’t have numbers.
Number Facts Infographics

A rubik’s cube has 43 quintillion different permutations.
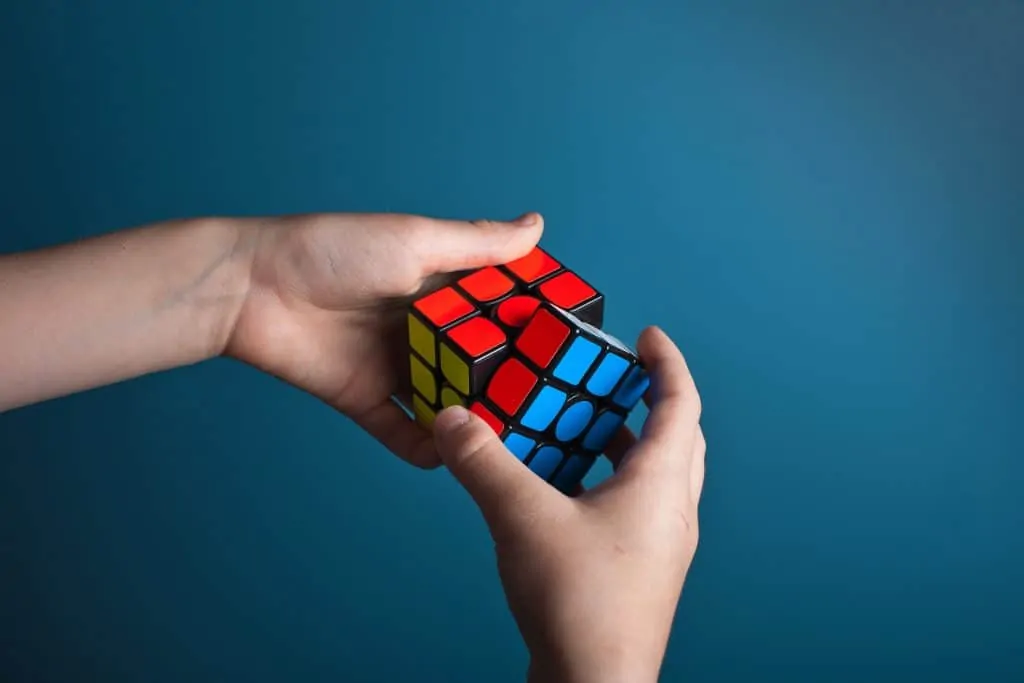

Permutations are the different ways that a set can be arranged. For a 3×3 Rubik’s cube, there are 43,252,003,274,489,856,000 possible combinations. However, each one can be solved in 20 moves or less, according to Google‘s supercomputers.
Friday the 13th? More like Friday the 17th.
Italian superstition warns against Friday the 17th because the Roman numeral “XVII” can be rearranged to create the word “VIXI” which means, “My life is over” in Latin.
A hundred doesn’t actually mean 100.

The word “hundred” is derived from the Old Norse word hundrath, which actually means 120, not 100.
Only one number is spelled with the same amount of letters as its value.
The number 4 has four letters, too. It’s the only number that has this trait. Mind-blowing.
The fastest record for a person counting to 1 million is 89 days.
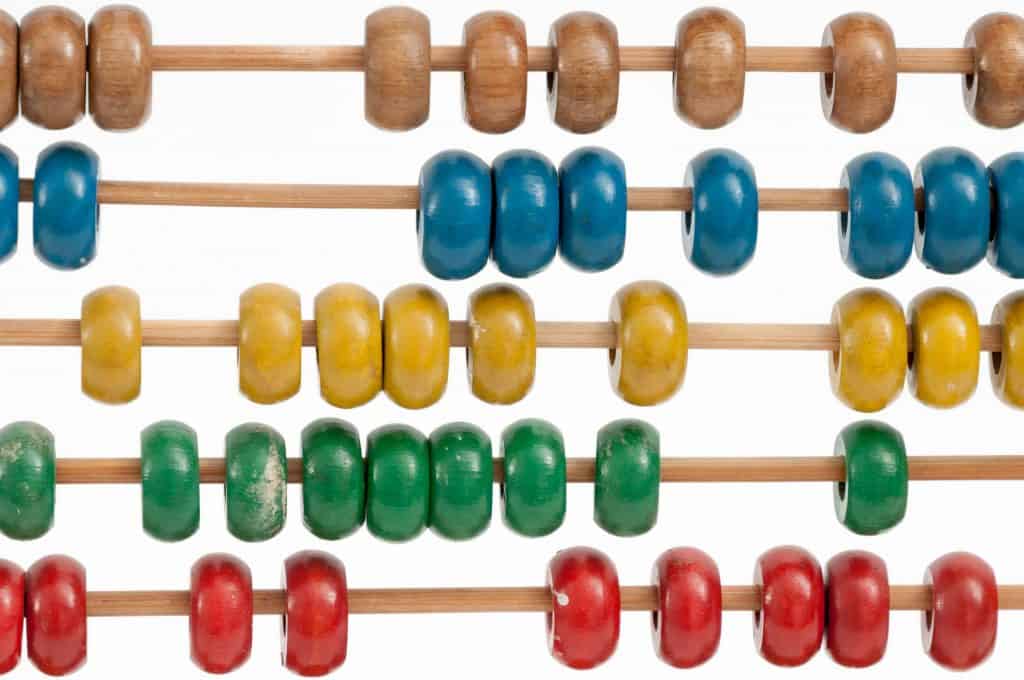

Jeremy Harper of Alabama holds the Guinness World Record for counting to one million. He live-streamed the entire process that took him 89 days. He spent 16 hours per day counting aloud, while 8 hours were for eating and sleeping.
If you multiply a single-digit number by 9 and add all the digits of the product, the sum will always be 9.
For example: 2 x 9 = 18 > 1 + 8 = 9 or 6 x 9 = 54, 5 + 4 = 9.
7 is the most loved number.
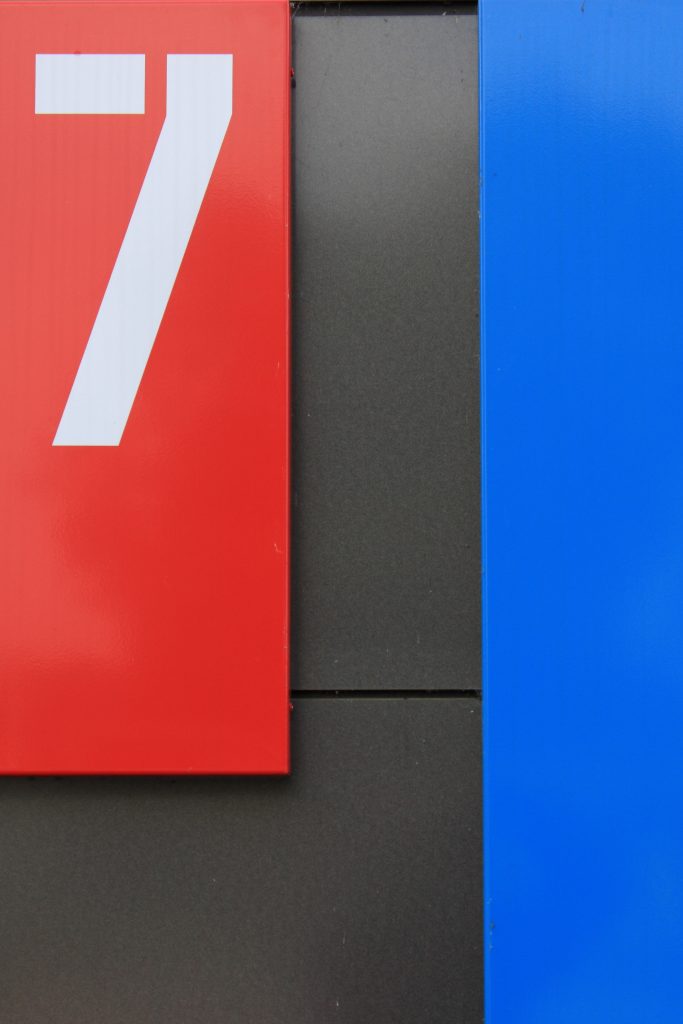

In a study conducted by mathematics author Alex Bellos, 10% of people chose the “Lucky 7” as their favorite number. The number 7 has been used in imagery in the Bible as well as the winning match in slot machines. According to Bellos, 7’s “uniqueness” is why it’s so loved. 7 is the only number not divisible or doubled from the numbers in the 1-10 group.
A written googolplex would weigh more than the whole Earth.
A googolplex is a “1” followed by 100 zeros. The biggest number is so long that if you wrote it out or printed it into physical form, the book would weigh more than the planet itself.
4 is an unlucky number in East Asia.
You won’t find much love for four-leafed clovers in Asia. The word for 4 in many Asian languages sound like the word for “death” which is why it is generally seen as a bad omen. In more intense cases, tetraphobia is the fear of the number four.
Bees can count.
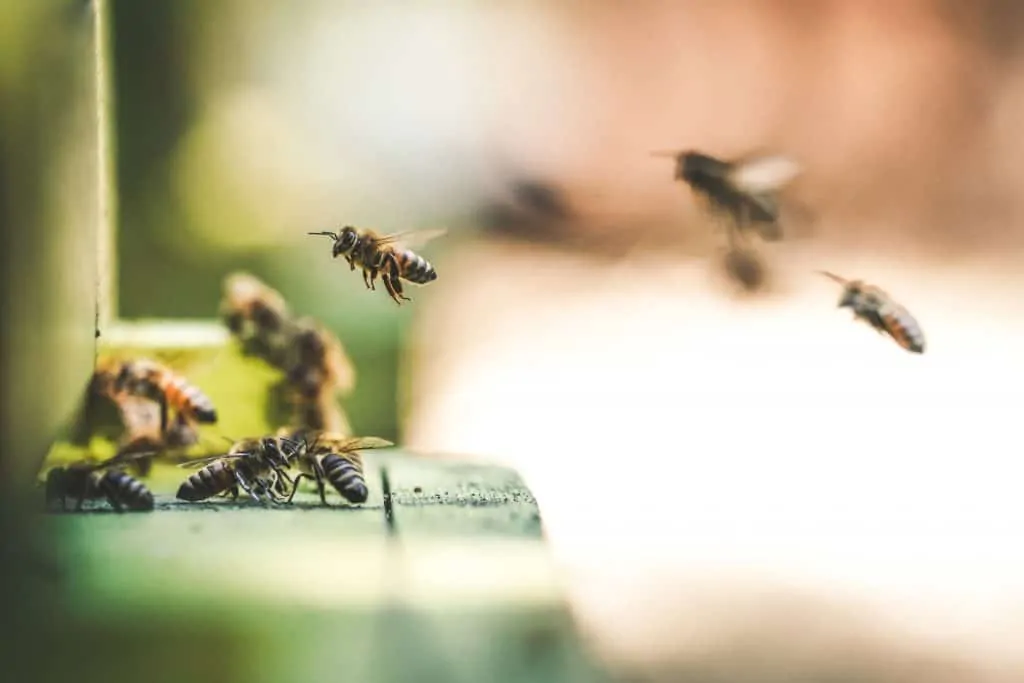

Studies show that bees can identify and count up to four and recognize the concept of zero. Bees were trained to choose which sample has “more” or “less.” Eventually they exhibited an 80% success rate.
Thai people laugh in numbers.
Well, a number. The Thai word for 5 is ha, which explains all the 555’s.
If you shuffle a pack of cards right, there’s a chance the order has never been done before in the history of the universe.
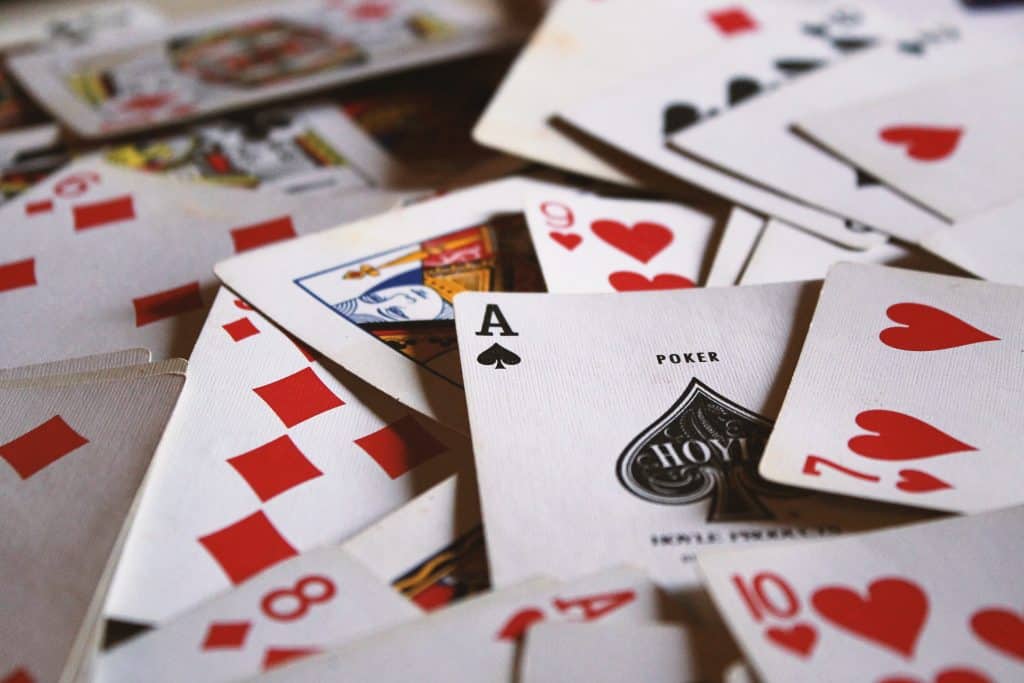

As with Rubik’s cube permutations, the amount of possible combinations in a deck of cards is so varied that you could be making history with each shuffle.
People view odd numbers as male and even numbers as female.
According to a study, people often interpreted baby pictures as male or female depending on numbers placed next to it.
M77232917 is the largest prime number.
This number has 23,249,425 digits. The biggest prime number known as M77232917 was discovered in January 2018 by a computer in Tennessee.
A room full of 70 people would most probably have two people who share a birthday.

In a room full of 70 people, there’s already a 99.9% chance that two people share a birthday.
Numbers could determine your life.
Numerology is the study of significant numbers and how they impact aspects of one’s life, much like astrology.
The word ‘love’ in tennis means a score of zero.

Some point its origins to the gambling expression ‘love or money’ aka playing a game for money (stakes) or love (nothing).
Others claim it’s because the French word l’oeuf means ‘the egg’ and an egg looks like a zero.
Leonardo Da Vinci started the paint by numbers concept.
The popular hobby craft we now know is based on Leonardo Da Vinci’s teaching method. Paint by number sets were created in 1950 by Dan Robbins. Originally a children’s book illustrator, Robbins was tasked to think of a way to sell more paint at his workplace. From there, paint by numbers took off as a timeless craft activity.
5 to 10% of people have Dyscalculia.
Experts estimate that the arithmetic learning disability dyscalculia may be just as common as dyslexia.
Voltaire cracked the lottery system in 18th Century France.

Definitely one for the number facts Hall of Fame is Voltaire’s lottery heist. Famed as a writer of the Enlightenment, Voltaire is iconic for his not-so-illegal lottery heist in 18th century France. Voltaire earned an equivalent of US$121 million through “rigging” the lottery. How did he do it? He and mathematician Charles Marie de la Condamine discovered that the lottery system allowed a way for small bond-holders to buy enough tickets for a sure win. From here, him and de la Condamine devised a plan to exploit the system without technically breaking the law. Voltaire used his winnings to fund his businesses and studies.
Maps have four colors.
According to the four-color theorem, any map can be colored using only four colors so that regions sharing a boundary do not share the same color. You can get the nearest map to check.
Scott Flansburg can solve equations as quickly and accurately as a calculator.
One of the most amazing number facts: The Guinness Book of World Records listed him as “Fastest Human Calculator“ in 2001 and 2003. Flansburg secured the title after he broke the record for adding the same number to itself in 15 seconds. Flansburg beat his time with more equations finished than someone with a calculator would at the same time.
Sudoku’s original name was Number Place.
Modern Sudoku was invented in America as “Number Place” (in 1979). However, it gained popularity as “Sudoku” because of Japanese publisher Nikoli. Sadly, Howard Garns died in 1989, way before the game reached global popularity.
The first recorded mention of a lottery was in the Bible.
Lotteries raise money through selling numbered tickets and awarding cash prizes through a random number draw. Moses was the first recorded participant of a lottery. In the Book of Numbers, it was mentioned that he won plots of land through a lottery draw.
Different cultures discovered the concept of zero at different times.
It is generally accepted that the Indian astronomer and mathematician Brahmagupta first discussed the concept of zero around 600 A.D.
There are more stars in the universe than there are grains of sand in all the beaches on Earth.
We’re talking 1 billion trillion stars. There’s a wishing star for everyone.
9 is feared in Japan.

Although some cultures view 9 as a mystic or sacred number, it is feared in Japan. because it sounds similar to the Japanese word for torture or suffering.
Triskaidekaphobia is the fear of the number 13.
This fear of the number 13 possibly roots from literature and mythology. For example: Judas was the 13th guest on the Last Supper, where he betrayed the son of God.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
