Did you know that ancient China was a pioneer in seismology, developing the world's first seismograph over 1,800 years ago? This remarkable achievement is just one of many fascinating aspects of ancient Chinese seismology. From detailed earthquake records dating back to the Shang Dynasty to the innovative designs of traditional timber structures, ancient Chinese scientists and engineers demonstrated incredible ingenuity. They not only created tools to detect and measure seismic activity but also developed methods to predict and prepare for earthquakes. Dive into the world of ancient Chinese seismology and discover how their groundbreaking work continues to influence modern science.
Key Takeaways:
- Ancient Chinese seismology dates back to the Shang Dynasty, with Chang Heng's seismograph being a groundbreaking invention that could detect earthquakes accurately from afar.
- Despite their advanced technology, ancient Chinese believed earthquakes were caused by cosmic forces. Their legacy continues to inspire modern seismological research in China.
Early Earthquake Records and Inventions
Ancient China has a rich history of documenting and understanding earthquakes. Their contributions to seismology are both fascinating and groundbreaking.
- Ancient China has a long history of recording earthquakes, with some of the earliest records dating back to the Shang Dynasty (16th to 11th centuries BCE).
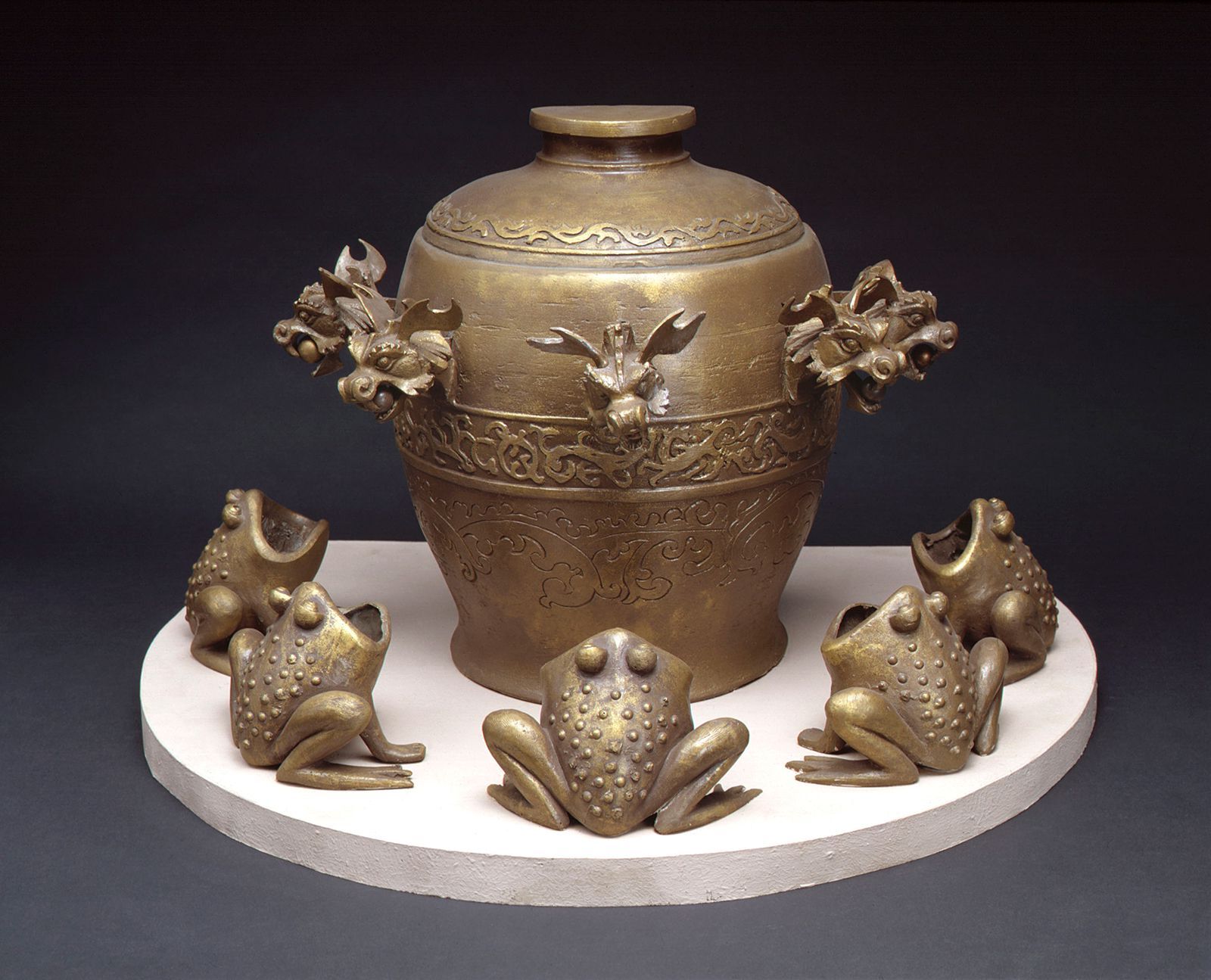
- The most notable invention in ancient Chinese seismology is the seismograph, first developed by Chang Heng in AD 132. This device could detect and indicate the direction of an earthquake.
- Chang Heng's seismograph was a large bronze vessel with eight dragon heads, each holding a small bronze ball. The exact mechanism that caused a ball to drop in the event of an earthquake is still unknown.
Chang Heng's Seismograph
Chang Heng's seismograph was a marvel of ancient engineering. It showcased the advanced state of scientific knowledge in ancient China.
- The seismograph was remarkably accurate in detecting earthquakes from afar and did not rely on shaking or movement in the location where the device was situated.
- Chang Heng's invention of the seismograph predates any similar device in the Western world by over 1,500 years.
- The seismograph could indicate the direction of an earthquake by determining which dragon had released the ball.
- In 138 AD, the seismograph triggered an alarm when an earthquake occurred in the western Long region, hundreds of miles away from the capital city of Luoyang. The accuracy of the device was verified when a messenger arrived a few days later confirming the earthquake.
- In 2005, scientists in Zengzhou, China, replicated Zhang Heng's seismoscope and used it to detect simulated earthquakes based on waves from four different real-life earthquakes in China and Vietnam. The seismoscope detected all of them accurately.
Understanding Earthquakes in Ancient China
Despite their advanced technology, the ancient Chinese had different beliefs about the causes of earthquakes.
- Ancient Chinese did not understand that earthquakes were caused by the shifting of tectonic plates in the Earth's crust. They believed seismic events were disturbances caused by cosmic yin and yang or the heavens' displeasure with acts committed by the ruling dynasty.
- Ancient China was plagued by frequent earthquakes, which often caused significant disruptions and loss of life. The most devastating earthquake in recorded history occurred in 1556, killing over 800,000 people.
- The Chinese kept detailed records of earthquakes, which were often documented in official histories. These records provide valuable insights into the frequency and impact of seismic events in ancient China.
Seismological Tools and Contributions
Apart from the seismograph, ancient Chinese scientists developed other tools to study seismic activity.
- Ancient Chinese scientists developed instruments for measuring seismic waves and monitoring ground movements.
- Chang Heng was a polymath who made significant contributions to astronomy, mathematics, engineering, geography, and invention. He is renowned for inventing the world’s first water-powered armillary sphere for astronomical observation and documenting about 2,500 stars in a detailed star catalogue.
- Chang Heng also improved the water clock, which was an essential tool for timekeeping in ancient China.
- Chang Heng is believed to have invented the first odometer, which measured distances traveled by vehicles.
Seismic Hazard Assessment and Traditional Structures
Ancient Chinese seismologists recognized the importance of assessing seismic hazards and developed methods to predict and prepare for earthquakes.
- They developed methods to predict and prepare for earthquakes, which were often based on observations of natural phenomena and historical data.
- Ancient Chinese timber structures were designed to withstand seismic activity. Researchers have studied the seismic behavior of these structures using dynamic time-history analysis and shaking table tests.
- Studies have shown that traditional Chinese timber frames exhibit complex seismic behavior, including hysteretic responses and energy dissipation mechanisms.
- Experimental investigations have been conducted on traditional Chinese timber structures using shaking table tests and pseudo-static tests.
- Historical timber buildings in China have been studied using pseudo-static tests to understand their degradation laws and hysteretic behavior.
- The seismic performance of traditional Chinese pagodas has been analyzed using dynamic performance tests.
- The effect of column root connections on the dynamic behavior of Chuandou-style timber structures has been investigated.
Modern Seismology and Ancient Insights
China remains one of the most seismically active countries in the world, and modern research continues to build on ancient insights.
- China is one of the most seismically active countries in the world, with frequent earthquakes causing significant damage and loss of life.
- Research on earthquake prediction in China has focused on developing more accurate methods for predicting seismic events.
- Studies have identified precursor-like anomalies before major earthquakes, such as electromagnetic anomalies and changes in ground deformation.
- Seismic hazard assessment applications have evolved from traditional earthquake prediction research to time-variable seismic hazard assessment.
- The 2008 Wenchuan earthquake was a significant seismic event that highlighted the need for advanced seismic hazard assessment and mitigation strategies.
Legacy of Ancient Chinese Seismology
The legacy of ancient Chinese seismology extends beyond the development of the seismograph. It reflects the advanced state of scientific knowledge in ancient China and the importance placed on understanding natural phenomena.
- Apart from the seismograph, ancient Chinese scientists developed other seismological instruments, such as pendulum devices and instruments for measuring seismic waves.
- Seismic monitoring was an essential part of ancient Chinese seismology. Scientists used various methods to monitor seismic activity.
- The directional sensitivity of ancient Chinese seismographs allowed them to indicate the direction of an earthquake.
- Verification of seismic activity was crucial in ancient Chinese seismology. Scientists used various methods to confirm the occurrence of earthquakes.
- Ancient Chinese people believed that seismic activity was related to cosmic yin and yang or the heavens' displeasure with acts committed by the ruling dynasty.
- Seismic hazard mitigation was an important aspect of ancient Chinese seismology. Scientists developed strategies to prepare for and respond to earthquakes.
- Traditional timber construction techniques in ancient China were designed to withstand seismic activity.
- The seismic performance of ancient buildings in China has been studied using various methods.
- The hysteretic behavior of ancient Chinese timber structures has been studied using full-scale experimental tests and analytical models.
- Dynamic response analysis has been used to study the behavior of traditional Chinese timber structures under seismic loads.
- The seismic behavior of Chuan-Dou type timber frames has been investigated using various experimental and analytical methods.
- Seismic hazard assessment in ancient China involved the use of various methods, including observations of natural phenomena and historical data.
- Ancient Chinese seismologists developed various earthquake prediction methods, including the use of precursor-like anomalies and changes in ground deformation.
- Ancient Chinese seismologists used various seismic monitoring techniques, including the use of seismographs and other instruments to detect and record earthquakes.
- The directional indication provided by ancient Chinese seismographs was a significant advancement in seismology.
- Verification of seismic activity was crucial in ancient Chinese seismology. Scientists used various methods to confirm the occurrence of earthquakes.
- Ancient Chinese seismology was deeply rooted in cultural and philosophical beliefs. Seismic activity was often seen as a sign from heaven or related to cosmic yin and yang.
- The contributions of Chang Heng and other ancient Chinese scientists continue to inspire modern seismological research.
The Legacy of Ancient Chinese Seismology
Ancient Chinese seismology left a lasting impact on our understanding of earthquakes. From Chang Heng's seismograph to detailed earthquake records, their innovations were ahead of their time. They didn't just invent tools; they developed methods for seismic hazard assessment and earthquake prediction. Their timber structures showed remarkable resilience against seismic activity, a testament to their engineering prowess. Despite not knowing about tectonic plates, their observations and records were incredibly accurate. The cultural beliefs tied to seismic events also offer a fascinating glimpse into their worldview. Ancient Chinese contributions continue to inspire modern seismology, proving that their legacy is more than just historical—it’s a foundation for ongoing research. Understanding their achievements helps us appreciate the depth of their knowledge and the importance they placed on preparing for natural disasters. Their work remains a cornerstone in the study of earthquakes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.