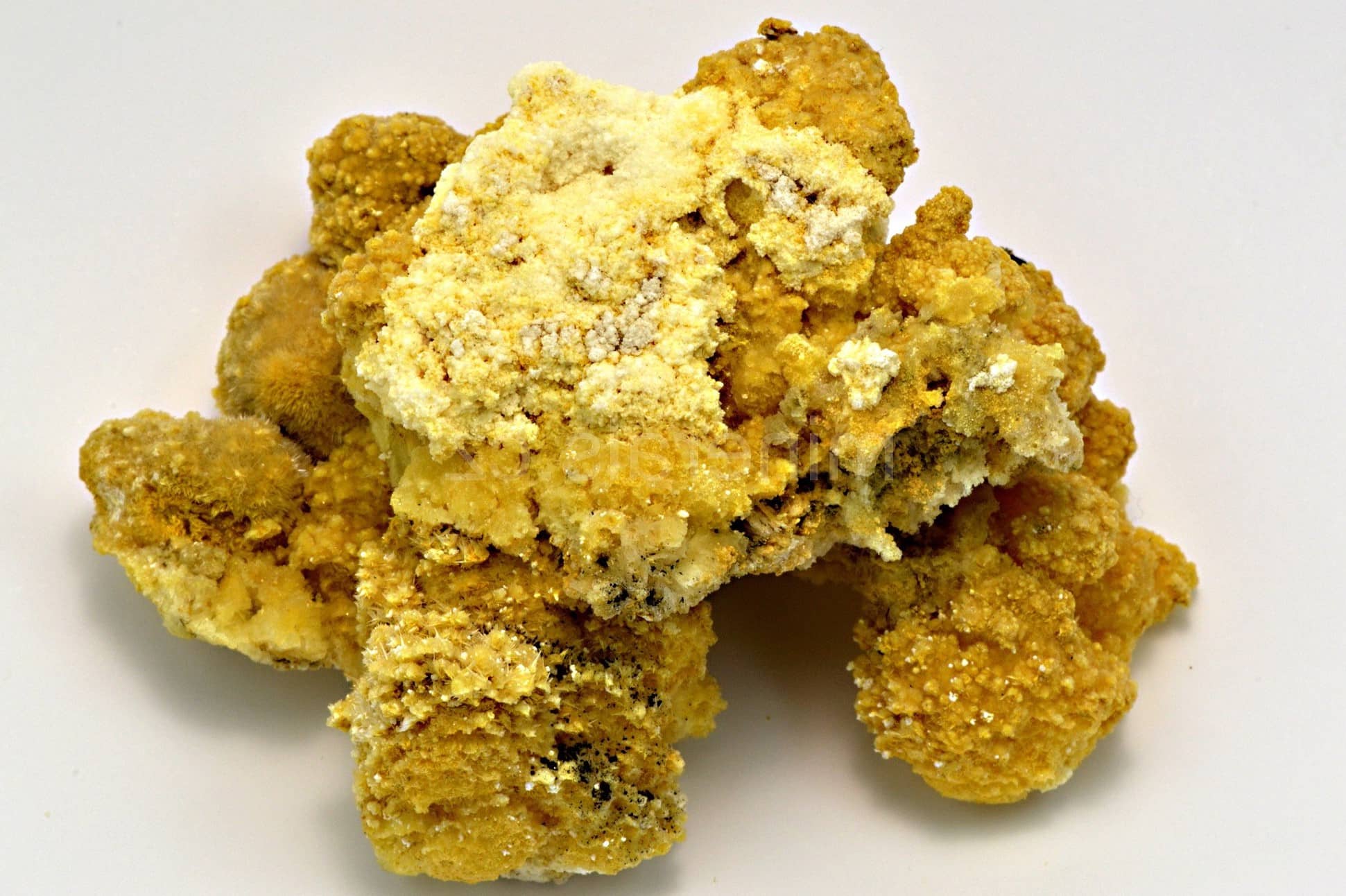
What is Alunogen? Alunogen, also known as feather alum or hair salt, is a fascinating mineral with a unique chemical composition of Al₂(SO₄)₃·17H₂O. This hydrated aluminum sulfate mineral often appears colorless or white, though impurities can give it pale yellow to red hues. Found globally, alunogen forms in various geological settings, including oxidation zones of metal-sulfide deposits and coal mining environments. Its fibrous, needle-like crystals are not just a visual treat but also hold significant industrial value. Used in water purification, paper manufacturing, and leather tanning, alunogen's applications are as diverse as its occurrences. Let's dive into 25 intriguing facts about this remarkable mineral.
Key Takeaways:
- Alunogen is a unique mineral with a chemical formula of Al₂(SO₄)₃·17H₂O, forming in various geological settings. It has distinct physical and optical properties, and is found in oxidation zones of metal-sulfide mineral deposits.
- Alunogen has industrial applications in water purification and potential significance in Martian soil. Its historical names reflect its fibrous appearance, and it forms through the interaction of sulfate solutions with aluminous minerals.
What is Alunogen?
Alunogen, also known as feather alum or hair salt, is a fascinating mineral with a unique set of properties. It is a hydrated aluminum sulfate that forms in various geological settings. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this mineral.
-
Chemical Composition
Alunogen's chemical formula is Al₂(SO₄)₃·17H₂O. This means it consists of aluminum, sulfate, and water molecules. -
Crystal System
It crystallizes in the triclinic crystal system, which lacks the symmetry found in cubic or hexagonal systems. -
Crystal Class
The crystal class of alunogen is pinacoidal (1), indicating it belongs to the triclinic system with minimal symmetry elements. -
Space Group
Alunogen's space group is P1, the most primitive triclinic space group, featuring no symmetry operations other than the identity operation. -
Unit Cell Parameters
The unit cell parameters are a = 7.42 Å, b = 26.97 Å, c = 6.062 Å, α = 89.95°, β = 97.566°, and γ = 91.888°. The unit cell contains two formula units (Z = 2).
Physical Characteristics of Alunogen
Alunogen has distinct physical properties that make it easily identifiable. These characteristics include its color, hardness, and specific gravity.
-
Color and Habit
Typically colorless or white, alunogen can also appear pale yellow to red due to impurities. It often forms fibrous masses, crusts, and efflorescences, with platy to prismatic crystals being rare. -
Twinning
Twinning on the {010} plane is common in alunogen, a feature often seen in triclinic minerals. -
Cleavage
It has perfect cleavage on the {010} plane and probable cleavage on the {100} and {313} planes, meaning it breaks along specific planes. -
Fracture
Alunogen exhibits a subconchoidal fracture, breaking with a smooth, curved surface similar to the inner shell of a snail. -
Mohs Hardness
With a Mohs hardness of 1.5 to 2, alunogen is relatively soft and can be scratched easily by harder minerals like quartz. -
Lustre
The lustre of alunogen is vitreous to silky, giving it a glassy appearance that can sometimes appear smooth or silky. -
Diaphaneity
Alunogen is transparent, allowing light to pass through, which is useful for identifying the mineral under a microscope. -
Specific Gravity
Its specific gravity ranges from 1.72 to 1.77, indicating it is denser than water.
Optical Properties of Alunogen
Alunogen's optical properties are essential for its identification and study under a microscope. These properties include its refractive indices and birefringence.
-
Optical Properties
Alunogen is biaxial positive, meaning it has two refractive indices and its optical properties vary depending on the direction of observation. The refractive indices are nα = 1.473, nβ = 1.474, and nγ = 1.480. -
Birefringence
The birefringence of alunogen is δ = 0.007, a measure of the difference in refractive indices, indicating a relatively small amount of birefringence. -
2V Angle
The 2V angle ranges from 31 to 69 degrees, measured under specific conditions, important for determining the orientation of the mineral's optical axes.
Geological Occurrence and Associations
Alunogen is found in various geological settings and often occurs with other minerals. Its formation and associations provide valuable insights into its geological environment.
-
Geological Occurrence
Commonly found in the oxidation zones of metal-sulfide mineral deposits or tailings impoundments in arid climates, alunogen can also be observed in efflorescences due to the evaporation of sulfate-rich pore waters in shales. It forms as an alteration product of kaolinite by acid sulfate fluids and in incrustations from exhalation-condensation processes related to hydrothermal and gas activities at fumaroles. -
Association with Other Minerals
Alunogen often occurs with minerals like pyrite, marcasite, halotrichite, pickeringite, epsomite, potash alum, melanterite, and gypsum, providing clues about the geological environment in which it forms.
Industrial and Environmental Significance
Alunogen has significant industrial applications and environmental importance. Its uses range from water purification to potential Martian soil components.
-
Industrial Applications
Alunogen is used as an efficient flocculant in sewage treatment and water purification. It also serves as a reagent in paper manufacturing and leather tanning. The synthetic analogue of alunogen is employed in various industrial processes. -
Environmental Significance
Found in coal mining environments, particularly in burning coal mining waste dumps or as deposits from gases exhaled from surface vents associated with underground coal fires, alunogen plays a role in environmental processes related to coal mining. -
Potential Martian Soil Component
Speculation exists that alunogen could be a constituent of Martian soils, based on its presence in similar geological environments on Earth and its potential to form under conditions similar to those on Mars. -
Synthetic Analogues
The synthetic analogue of alunogen is widely used in industrial inorganic chemistry, despite some discrepancies in its exact composition, remaining an important reagent in various industrial processes.
Historical and Formation Insights
Alunogen has a rich history and forms through specific processes. Understanding its formation and historical names provides a deeper appreciation of this mineral.
-
Historical Names
In older literature, alunogen and other hairlike sulfate minerals were referred to as Haarsalz or "hair salts," reflecting the mineral's fibrous appearance. -
Formation Processes
Alunogen forms through the interaction of sulfate solutions with aluminous minerals, typically occurring in environments where sulfate-rich fluids contact aluminum-bearing rocks, leading to the precipitation of hydrated aluminum sulfate. -
Global Distribution
Alunogen is found in over 260 localities worldwide, showcasing its stability and adaptability in various geological settings.
Alunogen: A Mineral with Many Faces
Alunogen, with its unique properties and wide range of occurrences, is more than just a mineral. Its chemical composition of hydrated aluminum sulfate, coupled with its triclinic crystal system, makes it fascinating to study. Found in oxidation zones, coal mining environments, and even potentially on Mars, alunogen's versatility is impressive. Its industrial applications in water purification, paper manufacturing, and leather tanning highlight its practical importance. Despite being soft with a Mohs hardness of 1.5 to 2, its transparency and vitreous to silky lustre make it visually appealing. The mineral's association with other minerals like pyrite and gypsum provides clues about its formation processes. Whether you're a geologist, an industrial chemist, or just a curious mind, alunogen offers a wealth of information and applications. Its global distribution and environmental significance make it a mineral worth knowing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.