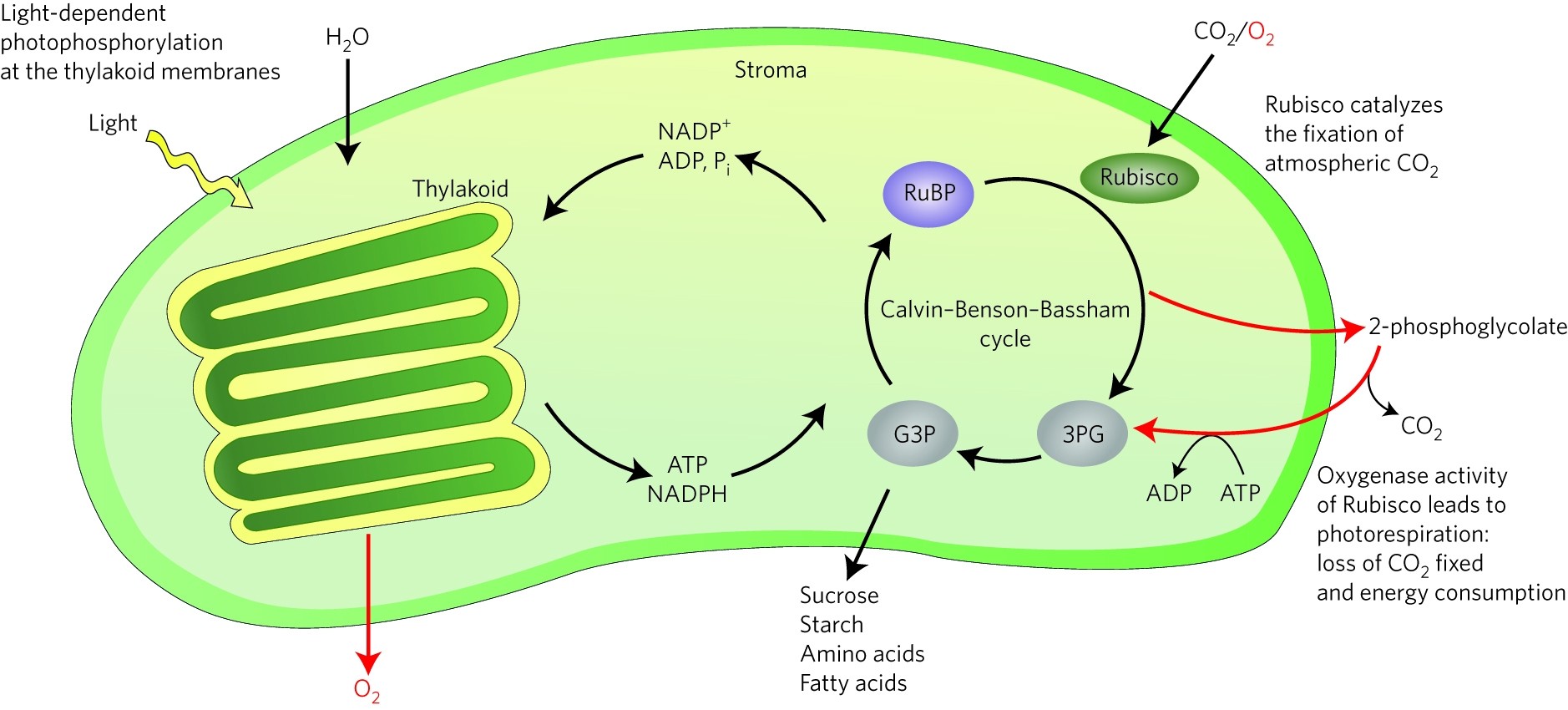
Rubisco, short for ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase, is a crucial enzyme in the process of photosynthesis. Found in plants, algae, and some bacteria, it plays a vital role in converting carbon dioxide into organic compounds. Why is Rubisco so important? It’s the most abundant protein on Earth, making up about 20-30% of the soluble protein in plant leaves. This enzyme is essential for life as it helps produce the oxygen we breathe. Despite its importance, Rubisco is surprisingly inefficient, often grabbing oxygen instead of carbon dioxide, which can slow down photosynthesis. Scientists are working to improve its efficiency to boost crop yields and combat climate change. Understanding Rubisco's function and quirks can shed light on how plants grow and how we might enhance food production in the future.
Key Takeaways:
- Rubisco, the "most important enzyme on Earth," helps plants turn carbon dioxide into energy through photosynthesis. Its inefficiency is a topic of humor among scientists, but it's crucial for life on Earth.
- Researchers are working to improve Rubisco's efficiency, which could increase crop yields by up to 60% and enhance food security. This quirky enzyme has a serious impact on our planet's carbon cycle.
What is Rubisco?
Rubisco, short for ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, is an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis. It helps plants convert carbon dioxide into organic compounds. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this essential enzyme.
- Rubisco is the most abundant protein on Earth.
- It is found in the chloroplasts of plant cells.
- Rubisco catalyzes the first major step in carbon fixation.
- The enzyme can bind both carbon dioxide and oxygen.
- Rubisco's dual function can lead to a process called photorespiration.
- Photorespiration reduces the efficiency of photosynthesis.
- Rubisco is a large enzyme, composed of multiple subunits.
- It has a molecular weight of around 550,000 Daltons.
- The enzyme's structure includes eight large and eight small subunits.
- Rubisco's activity is regulated by light.
Rubisco's Role in Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy. Rubisco plays a pivotal role in this process, making it indispensable for plant life.
- Rubisco catalyzes the reaction between carbon dioxide and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP).
- This reaction produces two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA).
- 3-PGA is then used to produce glucose and other carbohydrates.
- Rubisco's activity is influenced by the concentration of carbon dioxide.
- Higher carbon dioxide levels increase Rubisco's efficiency.
- The enzyme's activity is also affected by temperature.
- Optimal temperature for Rubisco activity is around 25°C.
- Rubisco activase is a protein that helps activate Rubisco.
- Rubisco activase removes inhibitory sugar phosphates from Rubisco.
- The enzyme's activity can be inhibited by oxygen.
Evolution and Diversity of Rubisco
Rubisco has evolved over millions of years and exhibits diversity across different species. This diversity reflects the adaptation of plants to various environmental conditions.
- Rubisco is found in all photosynthetic organisms, including plants, algae, and cyanobacteria.
- There are different forms of Rubisco, known as Form I, Form II, Form III, and Form IV.
- Form I Rubisco is the most common and is found in higher plants and algae.
- Form II Rubisco is found in some bacteria and dinoflagellates.
- Form III Rubisco is present in archaea.
- Form IV Rubisco, also known as Rubisco-like protein, is found in some bacteria.
- The enzyme has evolved to adapt to different atmospheric conditions.
- Ancient Rubisco had a higher affinity for carbon dioxide.
- Modern Rubisco has a lower affinity for carbon dioxide but higher specificity.
- Genetic engineering aims to improve Rubisco's efficiency.
Challenges and Research on Rubisco
Despite its importance, Rubisco has some limitations that researchers are trying to overcome. Improving Rubisco's efficiency could significantly enhance crop yields and address food security issues.
- Rubisco's slow catalytic rate is a major limitation.
- The enzyme's dual affinity for oxygen and carbon dioxide reduces its efficiency.
- Scientists are exploring ways to increase Rubisco's specificity for carbon dioxide.
- Genetic modifications aim to reduce photorespiration.
- Introducing more efficient forms of Rubisco from other species is being studied.
- Synthetic biology approaches are being used to redesign Rubisco.
- Researchers are investigating the role of Rubisco activase in regulating Rubisco.
- Understanding Rubisco's structure helps in designing better enzymes.
- Improving Rubisco could enhance photosynthetic efficiency by up to 60%.
- Enhanced Rubisco could lead to higher crop yields and better food security.
Fun Facts about Rubisco
Rubisco might sound like a serious enzyme, but it has some fun and quirky aspects too. Here are some interesting tidbits about this vital protein.
- Rubisco is sometimes called the "most important enzyme on Earth."
- The enzyme's name is a mouthful, so scientists often use the acronym Rubisco.
- Rubisco's inefficiency is a topic of humor among plant biologists.
- Despite its flaws, Rubisco is essential for life on Earth.
- The enzyme's discovery dates back to the 1940s.
- Rubisco's structure was first determined in the 1980s.
- The enzyme's large subunit is encoded by the chloroplast genome.
- The small subunit is encoded by the nuclear genome.
- Rubisco's activity can be measured using a technique called gas exchange analysis.
- The enzyme's role in carbon fixation makes it a key player in the global carbon cycle.
The Power of Rubisco
Rubisco, short for ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase, plays a crucial role in photosynthesis. This enzyme, found in plants, algae, and some bacteria, helps convert carbon dioxide into organic compounds. Without Rubisco, life as we know it wouldn't exist.
Understanding Rubisco's function highlights its importance in our ecosystem. It’s fascinating how this enzyme, despite being slow and sometimes inefficient, remains vital. Scientists continue to study Rubisco to improve crop yields and address food security.
So, next time you see a plant, remember the tiny enzyme working tirelessly inside. Rubisco might not be a household name, but its impact is immense. From fueling plant growth to sustaining life on Earth, Rubisco truly is a powerhouse.
Keep exploring the wonders of nature, and who knows what other amazing facts you’ll uncover!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
