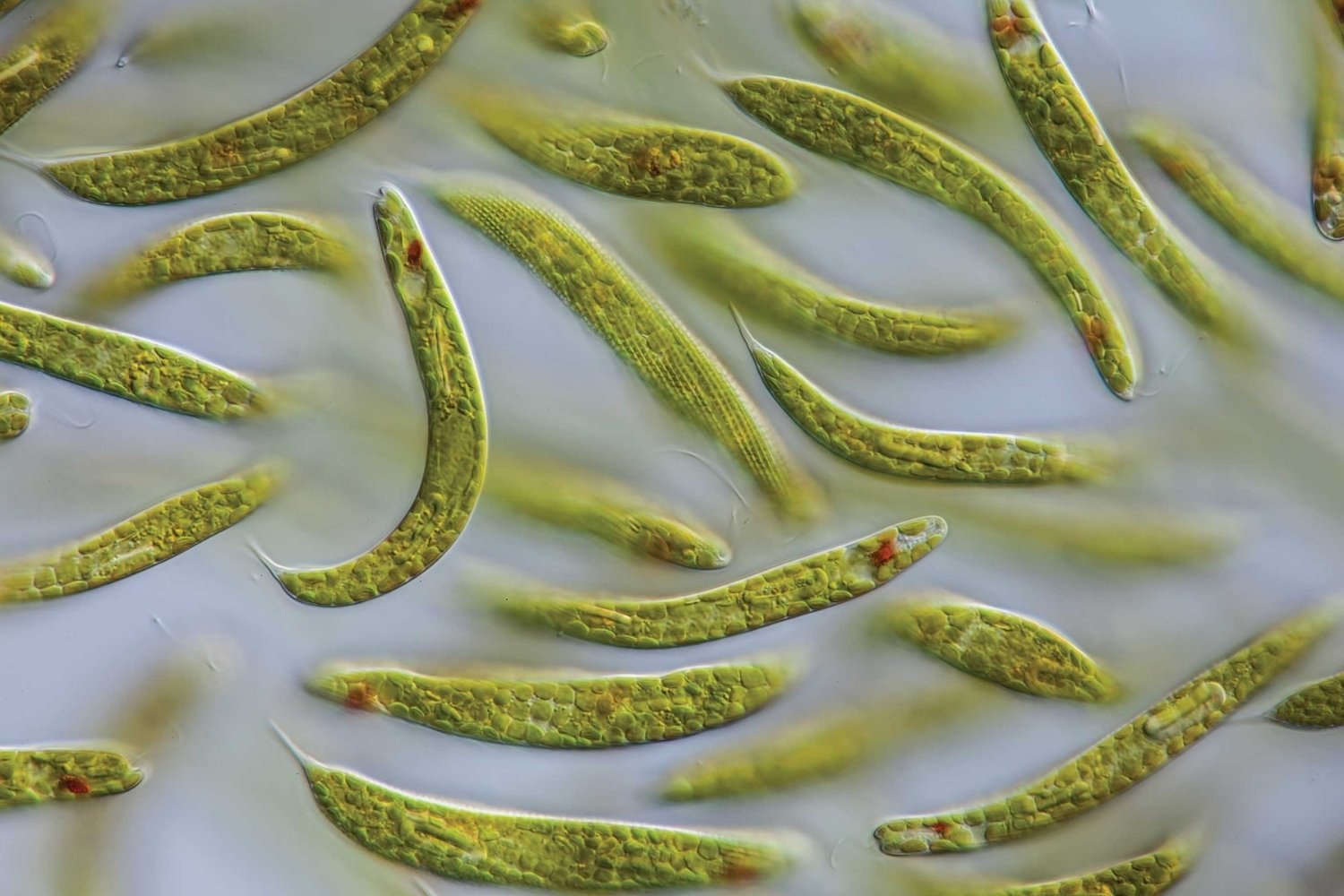
Protists are fascinating organisms that often get overlooked in biology. These tiny creatures, which can be found in water, soil, and even inside other organisms, play crucial roles in ecosystems. But what exactly are protists? Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms that don't fit neatly into the categories of plants, animals, or fungi. They can be single-celled or multicellular and exhibit a wide range of behaviors and characteristics. Some protists are photosynthetic, like algae, while others are more animal-like, such as amoebas. They can reproduce sexually or asexually, and some even have complex life cycles involving multiple stages and hosts. Understanding protists can give us insights into the evolution of more complex life forms and the functioning of ecosystems. Ready to dive into the world of these incredible organisms? Let's explore 38 fascinating facts about protists!
What Are Protists?
Protists are a diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms. They don't fit neatly into the categories of plants, animals, or fungi. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about these unique organisms.
- Protists are mostly unicellular, but some, like algae, can be multicellular.
- They live in various environments, including freshwater, marine, and soil habitats.
- Protists can be autotrophic (make their own food) or heterotrophic (consume other organisms).
- Some protists, like amoebas, move using pseudopodia, which are temporary projections of their cell membrane.
- Others, like paramecia, use tiny hair-like structures called cilia to move.
- Protists can reproduce asexually through binary fission or sexually through the fusion of gametes.
- They play a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems as primary producers and decomposers.
- Some protists, like Plasmodium, are parasites and can cause diseases such as malaria.
- Protists have complex life cycles, often involving multiple hosts or stages.
- They can form cysts to survive harsh conditions, which allows them to remain dormant until favorable conditions return.
Types of Protists
Protists are categorized into three main types: animal-like, plant-like, and fungus-like. Each type has unique characteristics and roles in their ecosystems.
- Animal-like protists, or protozoa, are heterotrophic and often move to find food.
- Plant-like protists, such as algae, perform photosynthesis to produce energy.
- Fungus-like protists, like slime molds, decompose organic material.
- Euglenoids are a group of plant-like protists that can switch between autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition.
- Diatoms, a type of algae, have silica cell walls that form intricate patterns.
- Dinoflagellates, another type of algae, can produce bioluminescence, causing the ocean to glow at night.
- Some dinoflagellates cause harmful algal blooms, known as red tides, which can be toxic to marine life and humans.
- Foraminifera are protozoa with calcium carbonate shells, which contribute to the formation of limestone and chalk deposits.
- Radiolarians, another type of protozoa, have intricate silica skeletons that form part of the ocean floor sediment.
- Slime molds can exist as single cells but aggregate to form multicellular structures when food is scarce.
Protists and Human Health
Protists can have significant impacts on human health, both positive and negative. Understanding these impacts helps in managing diseases and utilizing beneficial protists.
- Plasmodium, the protist responsible for malaria, infects red blood cells and is transmitted by mosquitoes.
- Giardia lamblia causes giardiasis, a diarrheal disease, through contaminated water.
- Trypanosoma brucei, transmitted by tsetse flies, causes African sleeping sickness.
- Entamoeba histolytica causes amoebic dysentery, leading to severe intestinal issues.
- Some protists, like certain algae, produce compounds used in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
- Algae are a source of omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health.
- Protists like Chlorella and Spirulina are used as dietary supplements due to their high nutrient content.
- Research on protists has led to advancements in biotechnology, such as biofuel production from algae.
- Protists play a role in wastewater treatment by breaking down organic pollutants.
- Studying protists helps scientists understand basic biological processes, such as cell division and motility.
Protists in the Environment
Protists are essential components of many ecosystems. Their roles in nutrient cycling, food webs, and environmental health are crucial.
- Phytoplankton, which are plant-like protists, produce a significant portion of the Earth's oxygen through photosynthesis.
- Zooplankton, which include animal-like protists, are a key food source for many marine animals.
- Protists help decompose organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem.
- Some protists form symbiotic relationships with other organisms, such as the algae living in coral reefs.
- Protists can influence the carbon cycle by sequestering carbon dioxide in their biomass.
- They can also affect the nitrogen cycle by converting nitrogen into forms usable by plants.
- Protists are used as bioindicators to monitor environmental health and water quality.
- Studying protists helps scientists understand the impacts of climate change on marine and freshwater ecosystems.
The Fascinating World of Protists
Protists are a diverse group of organisms that play crucial roles in ecosystems. From algae producing oxygen to protozoa breaking down organic matter, these tiny creatures are essential for life on Earth. They come in various shapes and sizes, each with unique characteristics that make them fascinating to study. Some protists are photosynthetic, while others are heterotrophic, consuming bacteria and other small particles. Despite their small size, they have a significant impact on their environments, influencing nutrient cycles and food webs.
Understanding protists helps scientists learn more about the origins of complex life forms. Their study can lead to discoveries in medicine, environmental science, and evolutionary biology. So, next time you think about the smallest creatures in the water or soil, remember the incredible world of protists and their vital contributions to our planet.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
