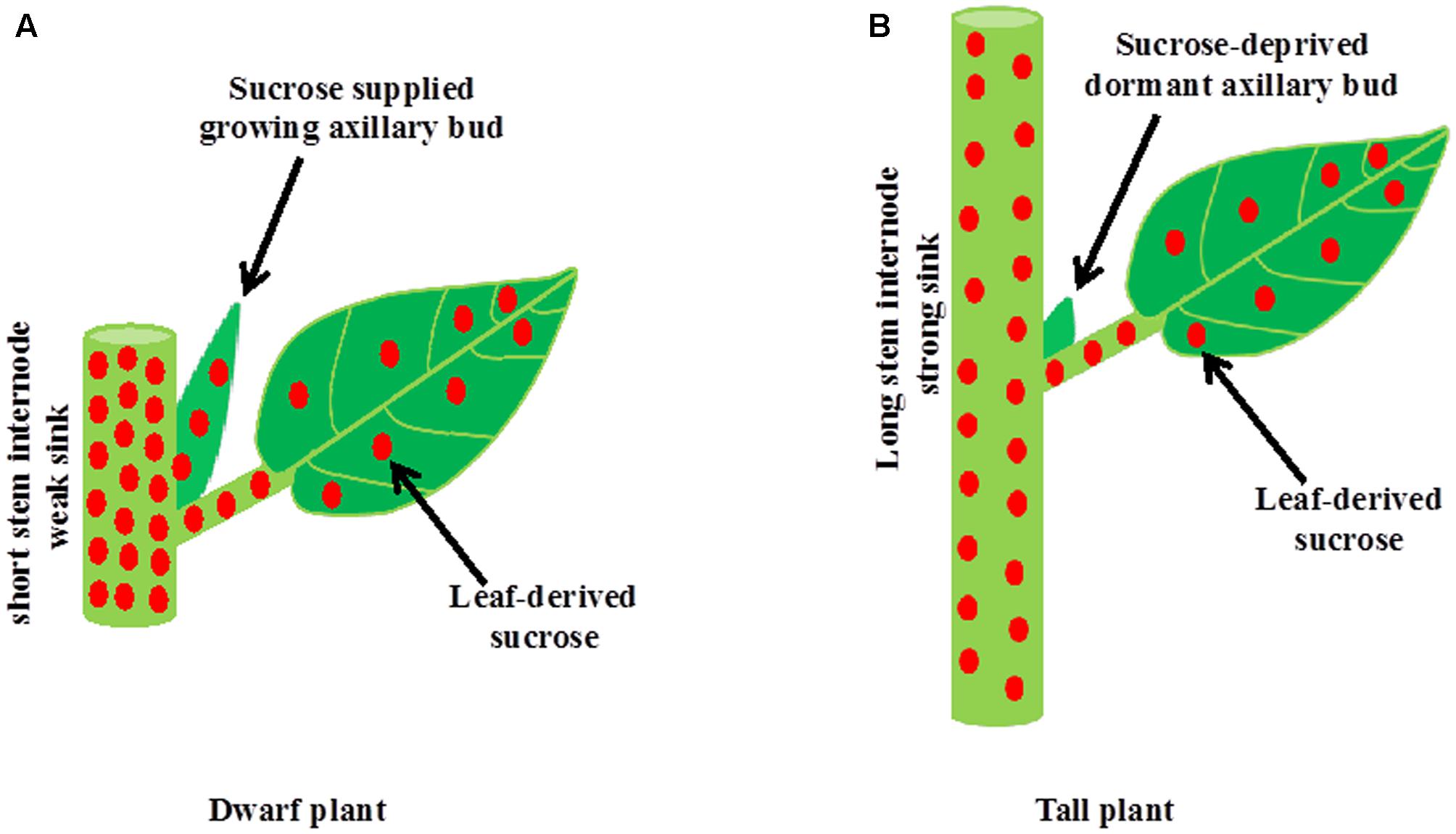
Apical dominance is a fascinating phenomenon in plants where the main, central stem grows more vigorously than the side stems. This happens because the apical bud, located at the tip of the plant, releases hormones called auxins that inhibit the growth of lateral buds. Why does this matter? Understanding apical dominance helps gardeners, farmers, and botanists manipulate plant growth for better yields and shapes. For instance, pruning the apical bud can encourage bushier growth, leading to more flowers or fruits. This natural process is crucial for plant development, ensuring that resources are efficiently used. Ready to learn more? Here are 38 intriguing facts about apical dominance that will deepen your appreciation for plant biology.
What is Apical Dominance?
Apical dominance is a fascinating phenomenon in plants where the main, central stem grows more vigorously than the side stems. This process is controlled by hormones, primarily auxins, which are produced in the apical bud at the tip of the plant. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this botanical marvel.
-
Auxins Control Growth: Auxins are plant hormones that play a crucial role in apical dominance. They are produced in the apical bud and inhibit the growth of lateral buds, ensuring the plant grows taller rather than wider.
-
Sunlight Influence: Sunlight affects auxin distribution. When a plant receives uneven light, auxins move to the shaded side, causing the plant to bend towards the light source.
-
Pruning Effects: Pruning the apical bud can break apical dominance. This encourages the growth of lateral buds, making the plant bushier.
-
Evolutionary Advantage: Apical dominance helps plants compete for sunlight by growing taller. This trait is particularly advantageous in dense forests where light is limited.
-
Hormonal Balance: Besides auxins, other hormones like cytokinins and gibberellins also influence apical dominance. Cytokinins promote lateral growth, while gibberellins can enhance stem elongation.
How Apical Dominance Affects Plant Shape
The shape and structure of a plant are significantly influenced by apical dominance. This section explores how this phenomenon dictates the overall form of various plants.
-
Tree Shapes: In trees, strong apical dominance results in a conical shape, like in pines and spruces. Weak apical dominance leads to a more rounded shape, as seen in oaks and maples.
-
Bush Formation: Shrubs and bushes often have weaker apical dominance, leading to a more branched and bushy appearance. This is why pruning can make garden plants fuller.
-
Vine Growth: Vines exhibit a unique form of apical dominance. They grow rapidly upwards or along surfaces, using tendrils or other structures to support their weight.
-
Flowering Patterns: Apical dominance can influence flowering. In some species, flowers only form on lateral branches once the apical bud is removed or flowers.
-
Fruit Production: In fruit-bearing plants, managing apical dominance through pruning can enhance fruit production by promoting the growth of fruit-bearing lateral branches.
Apical Dominance in Agriculture
Understanding apical dominance is crucial in agriculture and horticulture. Farmers and gardeners use this knowledge to optimize plant growth and yield.
-
Crop Yield: Managing apical dominance through pruning and hormone treatments can increase crop yields. For example, topping tobacco plants encourages the growth of larger leaves.
-
Orchard Management: In orchards, pruning techniques are used to control tree shape and enhance fruit production. This ensures better sunlight penetration and air circulation.
-
Vegetable Gardening: In vegetables like tomatoes, removing the apical bud can promote the growth of side shoots, leading to a bushier plant with more fruits.
-
Flower Cultivation: Florists often pinch the apical buds of flowering plants to encourage more blooms. This technique is common in the cultivation of chrysanthemums and petunias.
-
Bonsai Art: Bonsai artists manipulate apical dominance to create miniature trees with desired shapes. This involves careful pruning and training of branches.
Apical Dominance in Different Plant Species
Apical dominance varies among plant species. Some plants exhibit strong apical dominance, while others show a more balanced growth pattern.
-
Conifers: Coniferous trees like pines and firs have strong apical dominance, resulting in a tall, narrow shape.
-
Deciduous Trees: Many deciduous trees, such as oaks and maples, exhibit weaker apical dominance, leading to a more spreading canopy.
-
Herbaceous Plants: In herbaceous plants, apical dominance is often less pronounced. This allows for more lateral growth and a bushier appearance.
-
Grasses: Grasses show a unique form of apical dominance. The main shoot grows upward, while lateral shoots, called tillers, grow horizontally.
-
Succulents: Some succulents, like cacti, exhibit strong apical dominance, resulting in a single, dominant stem with minimal branching.
The Role of Apical Dominance in Plant Adaptation
Apical dominance plays a significant role in how plants adapt to their environment. This section explores how this phenomenon helps plants survive and thrive.
-
Resource Allocation: Apical dominance allows plants to allocate resources efficiently. By focusing growth on the main stem, plants can reach sunlight and other resources more effectively.
-
Survival Strategy: In harsh environments, strong apical dominance helps plants grow taller quickly, outcompeting other vegetation for sunlight.
-
Stress Response: When a plant experiences stress, such as damage to the apical bud, it can redirect growth to lateral buds. This helps the plant recover and continue growing.
-
Seasonal Changes: Apical dominance can be influenced by seasonal changes. In some plants, apical dominance is stronger during certain times of the year, affecting growth patterns.
-
Climbing Plants: Climbing plants use apical dominance to their advantage. By growing rapidly upwards, they can reach sunlight and support structures more efficiently.
Apical Dominance and Plant Hormones
Plant hormones play a crucial role in regulating apical dominance. This section delves into the hormonal mechanisms behind this phenomenon.
-
Auxin Transport: Auxins are transported from the apical bud down the stem, inhibiting the growth of lateral buds. This transport is essential for maintaining apical dominance.
-
Cytokinin Interaction: Cytokinins promote cell division and lateral growth. The balance between auxins and cytokinins determines the overall growth pattern of the plant.
-
Gibberellins: Gibberellins are another group of hormones that influence stem elongation. They can enhance the effects of auxins, promoting taller growth.
-
Ethylene: Ethylene is a hormone that can counteract the effects of auxins. It promotes the growth of lateral buds, reducing apical dominance.
-
Abscisic Acid: Abscisic acid plays a role in stress responses and can influence apical dominance by affecting hormone levels and growth patterns.
Practical Applications of Apical Dominance
Understanding apical dominance has practical applications in various fields, from agriculture to horticulture. This section highlights some of these applications.
-
Crop Breeding: Plant breeders use knowledge of apical dominance to develop new crop varieties with desired growth patterns and yields.
-
Landscape Design: Landscape architects use pruning techniques to shape plants and trees, creating aesthetically pleasing designs.
-
Greenhouse Management: In greenhouses, controlling apical dominance through hormone treatments and pruning can optimize plant growth and productivity.
-
Forestry: In forestry, managing apical dominance can improve tree growth and timber quality. This involves selective pruning and thinning practices.
-
Urban Gardening: Urban gardeners use apical dominance principles to maximize space and yield in small gardens and container plants.
Challenges and Future Research
While much is known about apical dominance, there are still challenges and areas for future research. This section explores some of these challenges.
-
Hormone Interactions: Understanding the complex interactions between different hormones and their effects on apical dominance remains a challenge for researchers.
-
Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as light, temperature, and soil conditions, can influence apical dominance. Studying these factors can help optimize plant growth.
-
Genetic Regulation: Research into the genetic regulation of apical dominance could lead to new ways to manipulate plant growth for agricultural and horticultural purposes.
Final Thoughts on Apical Dominance
Apical dominance is a fascinating plant behavior that affects how plants grow and develop. The main shoot grows more vigorously than the side shoots because of the hormone auxin. This process helps plants reach for sunlight and grow taller. Gardeners often use pruning to manipulate this natural tendency, encouraging bushier growth and more flowers or fruits.
Understanding apical dominance can help you become a better gardener. By knowing how plants prioritize their growth, you can make informed decisions about pruning and plant care. This knowledge can lead to healthier, more productive plants in your garden.
So, next time you’re out in the garden, remember the role of apical dominance. It’s not just a scientific concept; it’s a practical tool you can use to shape and improve your plants. Happy gardening!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
