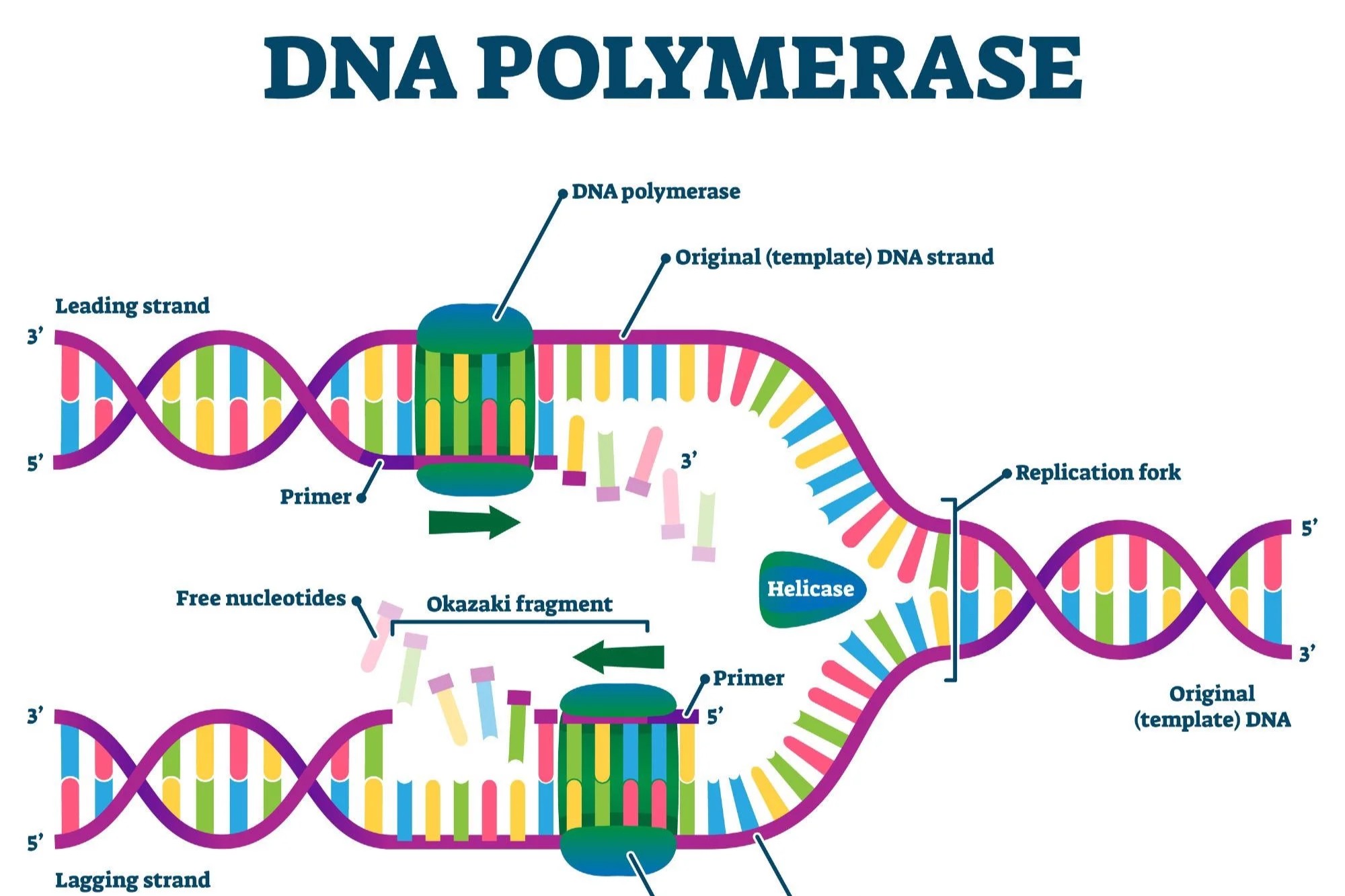
DNA polymerases are essential enzymes that play a crucial role in the replication and repair of DNA. These molecular machines ensure that genetic information is accurately copied and passed on to new cells. Without them, life as we know it wouldn't exist. But what exactly do they do? How do they work? And why are they so important? In this article, we'll explore 35 fascinating facts about DNA polymerases, shedding light on their functions, types, and significance in biology. Whether you're a science enthusiast or just curious about the building blocks of life, you'll find these facts both intriguing and informative.
What Are DNA Polymerases?
DNA polymerases are enzymes that play a crucial role in DNA replication. They synthesize new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to a pre-existing strand. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about these essential enzymes.
-
DNA polymerases are essential for cell division. Without them, cells couldn't replicate their DNA, making cell division impossible.
-
There are several types of DNA polymerases, each with unique functions. For example, DNA polymerase I, II, and III are found in bacteria, while eukaryotes have DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon.
-
DNA polymerase I was the first to be discovered. Arthur Kornberg identified it in 1956, earning him the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1959.
-
DNA polymerases require a primer to start DNA synthesis. This primer is usually a short RNA strand that provides a starting point for nucleotide addition.
-
DNA polymerases have proofreading abilities. They can correct errors during DNA synthesis, ensuring high fidelity in DNA replication.
The Mechanism of DNA Polymerases
Understanding how DNA polymerases work can shed light on their importance in genetic processes. Here are some intriguing details about their mechanism.
-
DNA polymerases add nucleotides in a 5' to 3' direction. This means they add new nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing DNA strand.
-
The enzyme's active site is highly specific. It ensures that only the correct nucleotide pairs with the template strand, maintaining genetic accuracy.
-
DNA polymerases use deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTPs) as substrates. These molecules provide the building blocks for new DNA strands.
-
The enzyme undergoes a conformational change during nucleotide addition. This change ensures the correct positioning of the nucleotide for incorporation into the DNA strand.
-
DNA polymerases can also remove mismatched nucleotides. This exonuclease activity helps maintain the integrity of the genetic code.
Types of DNA Polymerases
Different organisms have various DNA polymerases, each tailored to specific functions. Here are some key types and their roles.
-
DNA polymerase alpha initiates DNA replication in eukaryotes. It synthesizes a short RNA-DNA primer to start the process.
-
DNA polymerase delta takes over from alpha in eukaryotic cells. It extends the DNA strand with high fidelity and speed.
-
DNA polymerase epsilon is involved in leading-strand synthesis. It ensures continuous and efficient DNA replication.
-
DNA polymerase gamma replicates mitochondrial DNA. This enzyme is crucial for maintaining mitochondrial function and energy production.
-
DNA polymerase beta is involved in DNA repair. It helps fix small gaps and nicks in the DNA strand, maintaining genome stability.
DNA Polymerases in Biotechnology
DNA polymerases have numerous applications in biotechnology and research. Here are some ways they are utilized.
-
DNA polymerases are essential for PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction). This technique amplifies specific DNA sequences, making it invaluable for research and diagnostics.
-
Taq polymerase, derived from the bacterium Thermus aquaticus, is widely used in PCR. Its heat stability allows it to withstand the high temperatures required for DNA denaturation.
-
DNA polymerases are used in DNA sequencing. They help synthesize new DNA strands, allowing researchers to determine the sequence of nucleotides in a DNA molecule.
-
DNA polymerases are employed in cloning. They help replicate DNA fragments, enabling the creation of recombinant DNA molecules.
-
DNA polymerases are crucial for gene editing. Techniques like CRISPR-Cas9 rely on these enzymes to introduce specific changes in the DNA sequence.
Evolution and Diversity of DNA Polymerases
The evolution of DNA polymerases has led to a diverse array of enzymes with specialized functions. Here are some interesting facts about their diversity.
-
DNA polymerases have evolved to meet the needs of different organisms. For example, thermophilic bacteria have heat-stable DNA polymerases, while eukaryotes have multiple specialized polymerases.
-
Some viruses have their own DNA polymerases. These enzymes help replicate the viral genome, ensuring the virus can reproduce within the host cell.
-
DNA polymerases can be classified into families based on their structure and function. These families include A, B, C, D, X, and Y.
-
Family A polymerases are primarily involved in DNA replication and repair. They include bacterial DNA polymerase I and T7 DNA polymerase.
-
Family B polymerases are mainly responsible for DNA replication in eukaryotes. They include DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon.
DNA Polymerases and Disease
Mutations in DNA polymerases can lead to various diseases. Here are some examples of how these enzymes are linked to health conditions.
-
Mutations in DNA polymerase gamma can cause mitochondrial diseases. These conditions affect energy production and can lead to muscle weakness, neurological problems, and organ failure.
-
Defects in DNA polymerase beta are associated with cancer. Impaired DNA repair can lead to genomic instability and tumor development.
-
Mutations in DNA polymerase delta can cause immunodeficiency. These mutations affect the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
-
DNA polymerase epsilon mutations are linked to colorectal cancer. These mutations can lead to errors in DNA replication, increasing the risk of cancer.
-
DNA polymerase eta is involved in translesion synthesis. Mutations in this enzyme can cause xeroderma pigmentosum, a condition characterized by extreme sensitivity to UV light and a high risk of skin cancer.
Fun Facts About DNA Polymerases
Let's wrap up with some fun and lesser-known facts about DNA polymerases.
-
DNA polymerases can synthesize DNA at incredible speeds. Some can add up to 1,000 nucleotides per second.
-
The fidelity of DNA polymerases is remarkably high. They make an error only once in every 10 million nucleotides added.
-
Some DNA polymerases can bypass damaged DNA. This ability helps cells survive and replicate even when their DNA is damaged.
-
DNA polymerases are highly conserved across species. This conservation highlights their essential role in maintaining genetic information.
-
Researchers are continually discovering new DNA polymerases. These discoveries expand our understanding of DNA replication and repair, opening new avenues for research and biotechnology.
The Final Word on DNA Polymerases
DNA polymerases are the unsung heroes of genetic replication and repair. These enzymes ensure our genetic information is copied accurately, allowing life to continue and evolve. From their role in PCR to their importance in medical research, DNA polymerases are indispensable in both natural and laboratory settings.
Understanding these enzymes helps us appreciate the complexity and precision of biological processes. Whether you're a student, a researcher, or just curious, knowing about DNA polymerases enriches your grasp of genetics. They might not get the spotlight often, but their work is crucial for life as we know it.
Next time you think about DNA, remember the tiny enzymes working tirelessly to keep our genetic code intact. DNA polymerases are truly fascinating, and their impact on science and medicine is profound. Keep exploring, and you'll find even more amazing facts about these incredible molecules.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
