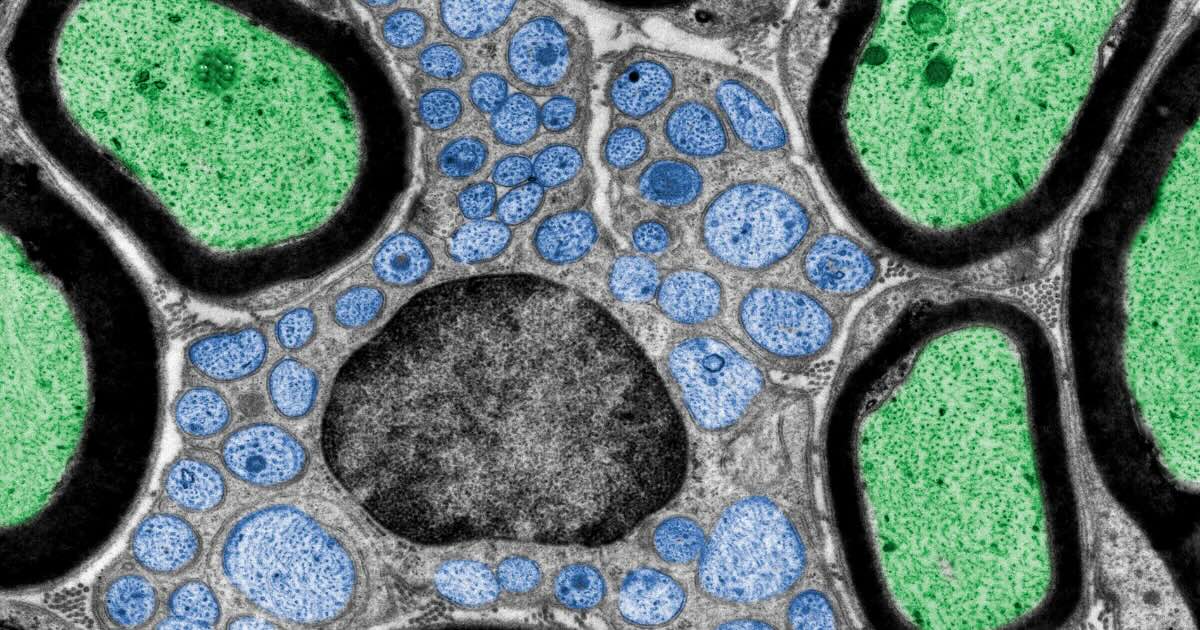
Schwann cells play a crucial role in the nervous system. These cells form the myelin sheath around nerve fibers, which speeds up the transmission of electrical signals. Named after Theodor Schwann, they are essential for nerve regeneration and repair. Did you know that Schwann cells can also help in the healing process after nerve injuries? They not only provide insulation but also support the overall health of neurons. Understanding these cells can give insights into treatments for nerve damage and diseases like multiple sclerosis. Ready to learn more? Here are 32 fascinating facts about Schwann cells!
What Are Schwann Cells?
Schwann cells are a type of glial cell found in the peripheral nervous system. They play a crucial role in nerve function and repair. Here are some fascinating facts about these essential cells.
- Schwann cells are named after Theodor Schwann, a German physiologist who discovered them in the 19th century.
- They are responsible for the myelination of peripheral nerves, which helps speed up the transmission of nerve impulses.
- Each Schwann cell myelinates only one segment of a single axon, unlike oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system that can myelinate multiple axons.
- Schwann cells can also support non-myelinated nerve fibers, providing essential metabolic and structural support.
- They play a key role in nerve regeneration by forming a regeneration tube that guides the growth of new axons after nerve injury.
Functions of Schwann Cells
Schwann cells are not just passive supporters; they actively contribute to nerve health and function. Here are some of their critical functions.
- They produce neurotrophic factors, which are essential for the survival and growth of neurons.
- Schwann cells help in the removal of cellular debris after nerve injury, a process known as phagocytosis.
- They secrete extracellular matrix proteins that provide structural support to nerves.
- Schwann cells can differentiate into a repair phenotype after nerve injury, aiding in the regeneration process.
- They form the myelin sheath, which acts as an insulating layer around nerve fibers, increasing the speed of electrical impulses.
Schwann Cells in Disease and Injury
Schwann cells are involved in various diseases and injuries. Understanding their role can help in developing treatments.
- In Guillain-Barré syndrome, the immune system mistakenly attacks Schwann cells, leading to muscle weakness and paralysis.
- Schwannomas are tumors that arise from Schwann cells, usually benign but can cause nerve damage.
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a genetic disorder affecting Schwann cells, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy.
- Schwann cells are involved in the repair process after peripheral nerve injuries, making them a target for regenerative medicine.
- They can be affected by diabetes, leading to diabetic neuropathy, a condition characterized by nerve damage and pain.
Schwann Cells and Myelination
Myelination is one of the most critical functions of Schwann cells. It ensures the efficient transmission of nerve impulses.
- The myelin sheath is composed of multiple layers of Schwann cell membrane wrapped around the axon.
- Nodes of Ranvier are gaps in the myelin sheath where the axon is exposed, allowing for rapid signal transmission.
- Myelination by Schwann cells begins during fetal development and continues into adulthood.
- Schwann cells can remyelinate axons after injury, although the process is slower than initial myelination.
- The thickness of the myelin sheath is regulated by Schwann cells, affecting the speed of nerve impulse transmission.
Schwann Cells in Research
Research on Schwann cells has led to significant advancements in neuroscience and medicine.
- Scientists are exploring the use of Schwann cells in cell therapy for nerve injuries.
- Schwann cells are being studied for their potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases like ALS and MS.
- Research has shown that Schwann cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent stem cells, offering new avenues for regenerative medicine.
- Studies on Schwann cells have improved our understanding of myelination and demyelination processes.
- Schwann cells are used in tissue engineering to create nerve grafts for repairing damaged nerves.
Interesting Facts About Schwann Cells
Here are some lesser-known but intriguing facts about Schwann cells.
- Schwann cells can communicate with neurons through chemical signals, influencing their function and survival.
- They have a unique ability to switch between myelinating and non-myelinating states depending on the needs of the nerve.
- Schwann cells can form a barrier around nerve fibers, protecting them from harmful substances.
- They are involved in the formation of neuromuscular junctions, where nerves connect with muscles.
- Schwann cells can migrate to the site of nerve injury, playing a crucial role in the repair process.
- They can produce cytokines and growth factors that modulate the immune response during nerve injury.
- Schwann cells have been found to interact with blood vessels, influencing blood flow to nerves.
The Final Word on Schwann Cells
Schwann cells are crucial for the nervous system. They help form the myelin sheath, which speeds up nerve impulses. Without them, nerve signals would be slower, affecting everything from muscle movement to sensory perception. These cells also play a role in nerve regeneration, making them vital for recovery after injuries.
Understanding Schwann cells can lead to breakthroughs in treating nerve damage and diseases like multiple sclerosis. Scientists continue to study these cells to unlock new medical treatments. So, next time you think about how your body moves or feels, remember the tiny Schwann cells working behind the scenes.
In short, Schwann cells are unsung heroes in our bodies. Their importance can't be overstated. Keep an eye on future research; it might just change how we treat nerve-related conditions.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
