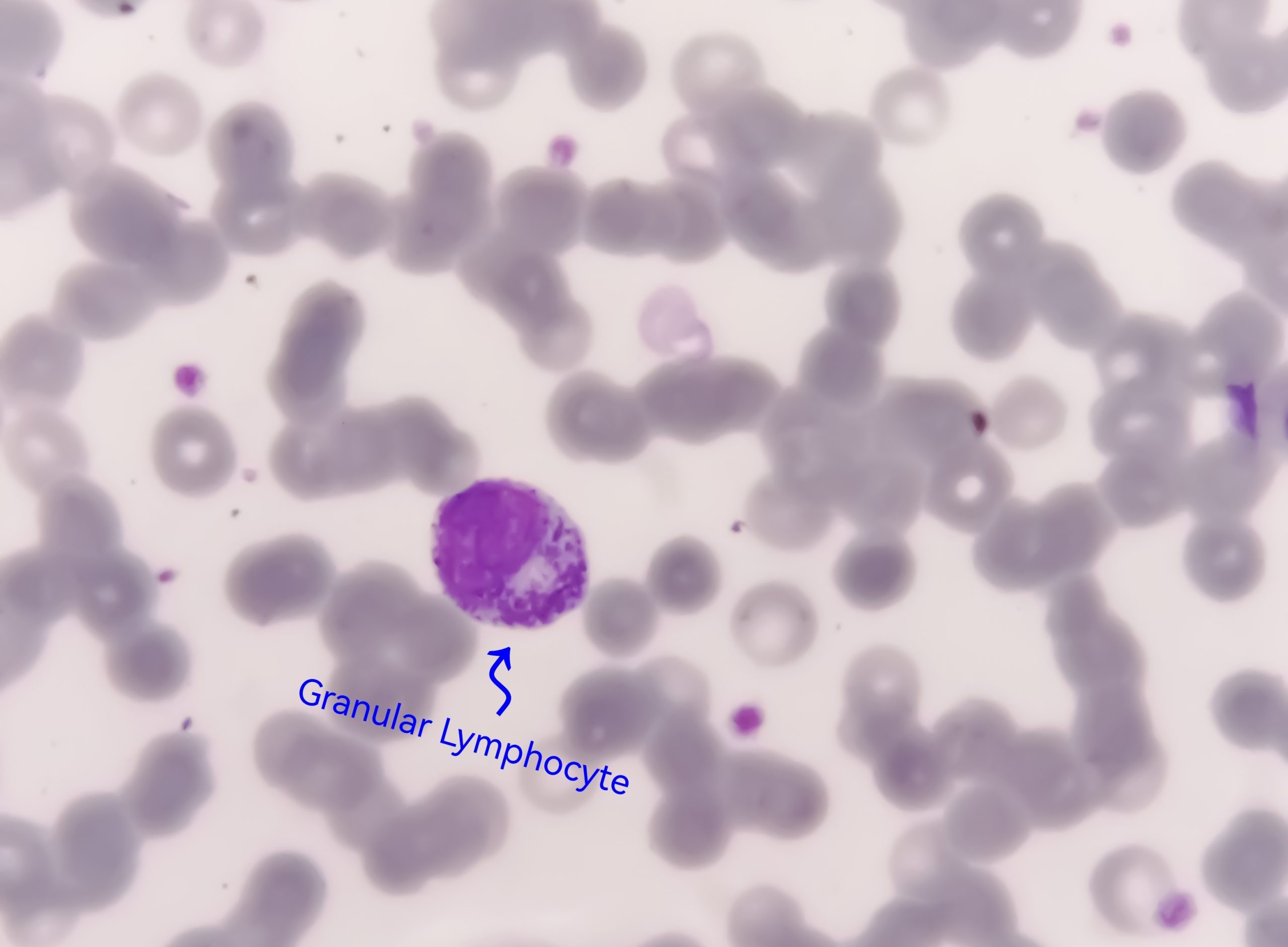
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell crucial for the immune system. They help the body fight infections and other diseases. But what exactly do they do? Lymphocytes come in two main types: B cells and T cells. B cells produce antibodies that attack invading bacteria, viruses, and toxins. T cells destroy the body's own cells that have been taken over by viruses or have become cancerous. These cells are produced in the bone marrow and can be found in the blood and lymphatic system. Understanding lymphocytes can help us appreciate how our bodies defend against illness. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 31 fascinating facts about these tiny warriors!
What Are Lymphocytes?
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell crucial for the immune system. They help the body fight infections and other diseases. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about these tiny warriors.
-
Lymphocytes are part of the body's immune system, specifically the adaptive immune system, which tailors the body's immune response to specific pathogens.
-
There are three main types of lymphocytes: B cells, T cells, and natural killer (NK) cells. Each type has a unique role in defending the body.
-
B cells produce antibodies that bind to antigens, neutralizing them or marking them for destruction by other immune cells.
-
T cells come in two primary forms: helper T cells and cytotoxic T cells. Helper T cells assist other immune cells, while cytotoxic T cells kill infected cells.
-
Natural killer (NK) cells are unique because they can attack and destroy tumor cells and cells infected by viruses without prior sensitization.
Where Are Lymphocytes Found?
Lymphocytes circulate throughout the body, but they are concentrated in certain areas. Here are some key locations where lymphocytes are found.
-
Lymphocytes are produced in the bone marrow, the soft tissue inside bones.
-
After production, some lymphocytes migrate to the thymus, a small organ in the chest, where they mature into T cells.
-
Lymph nodes, small bean-shaped structures, act as filters for harmful substances and are packed with lymphocytes.
-
The spleen, an organ near the stomach, also contains a large number of lymphocytes and helps filter blood.
-
Lymphocytes are present in the blood, allowing them to travel throughout the body to sites of infection or injury.
How Do Lymphocytes Function?
Understanding how lymphocytes work can provide insight into their importance in the immune system. Here are some key functions.
-
Lymphocytes recognize and remember specific pathogens, providing long-term immunity after an infection or vaccination.
-
When a lymphocyte encounters its specific antigen, it becomes activated and multiplies to fight the infection.
-
B cells can differentiate into plasma cells, which produce large quantities of antibodies.
-
Helper T cells release cytokines, signaling molecules that help coordinate the immune response.
-
Cytotoxic T cells release enzymes that induce apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in infected cells.
Lymphocytes and Diseases
Lymphocytes play a role in many diseases, both infectious and non-infectious. Here are some examples.
-
HIV targets and destroys helper T cells, weakening the immune system and leading to AIDS.
-
Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, occur when lymphocytes mistakenly attack the body's own tissues.
-
Lymphoma is a type of cancer that originates in lymphocytes, leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
-
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a cancer of B cells, characterized by the accumulation of abnormal lymphocytes in the blood and bone marrow.
-
Allergies occur when lymphocytes overreact to harmless substances, such as pollen or pet dander.
Interesting Facts About Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes have some surprising characteristics and abilities. Here are a few intriguing facts.
-
Lymphocytes can live for years, providing long-term immunity against previously encountered pathogens.
-
The human body contains approximately 2 trillion lymphocytes, making up about 20-40% of all white blood cells.
-
Lymphocytes can move between the blood and lymphatic system, allowing them to patrol the entire body.
-
Some lymphocytes, known as memory cells, remain in the body after an infection has been cleared, ready to respond quickly if the same pathogen is encountered again.
-
The thymus, where T cells mature, shrinks with age, leading to a decrease in the production of new T cells in older adults.
Lymphocytes in Research and Medicine
Lymphocytes are a focus of extensive research and have numerous medical applications. Here are some notable examples.
-
Monoclonal antibodies, produced by identical B cells, are used in treatments for cancer, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases.
-
CAR-T cell therapy, a type of immunotherapy, involves modifying a patient's T cells to better recognize and attack cancer cells.
-
Vaccines work by stimulating lymphocytes to produce a memory response, providing immunity without causing disease.
-
Researchers are exploring ways to harness lymphocytes to treat conditions like multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes.
-
Lymphocyte counts can be used as a diagnostic tool, with high or low levels indicating potential health issues.
-
Advances in genetic engineering are enabling scientists to create lymphocytes with enhanced abilities to fight specific diseases.
The Final Word on Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are tiny warriors in your immune system. They play a crucial role in fighting off infections and diseases. These cells come in three main types: T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells. Each type has a unique function, from attacking infected cells to producing antibodies.
Understanding lymphocytes helps you appreciate how your body defends itself. They’re essential for maintaining health and combating illnesses. Keeping your immune system strong through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can support lymphocyte function.
Remember, these facts about lymphocytes highlight their importance in your overall well-being. Next time you hear about the immune system, you’ll know just how vital these cells are. Stay informed and take care of your body’s natural defense team.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
