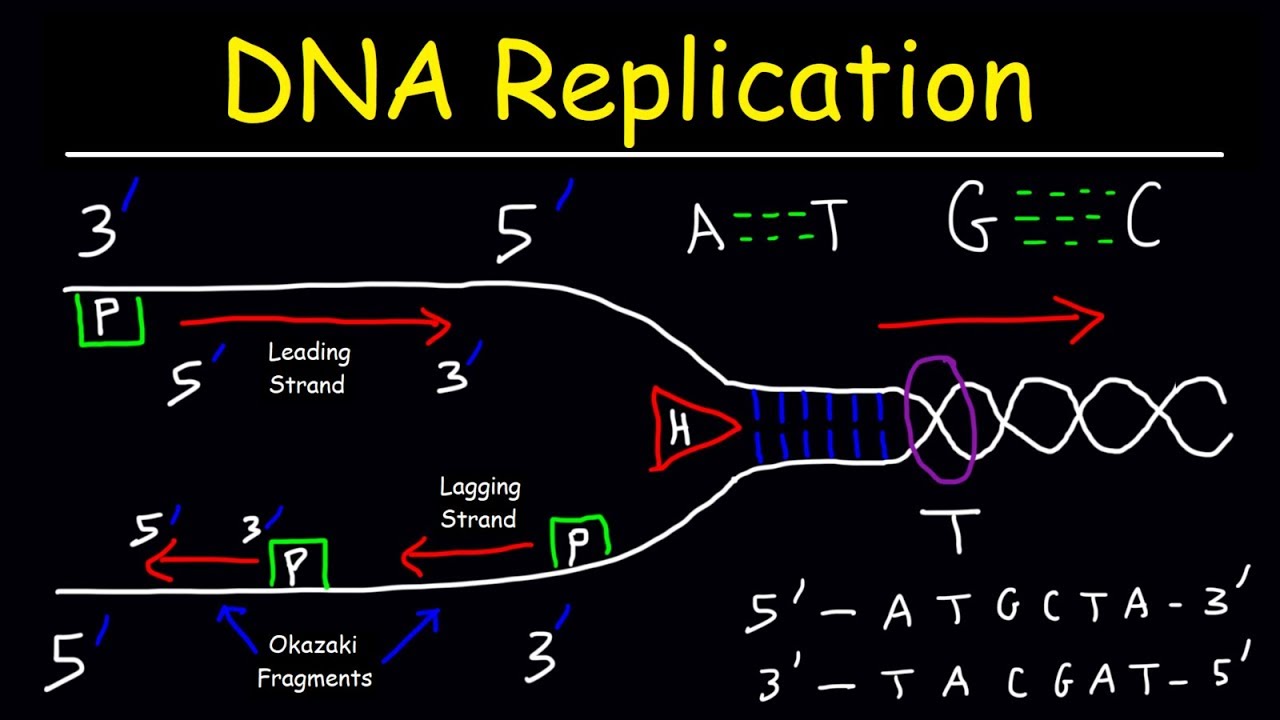
What are Okazaki fragments? These short DNA sequences are crucial during DNA replication. Why are they important? They help ensure that the lagging strand of DNA is copied accurately. Where do they form? Okazaki fragments form on the lagging strand during DNA replication. Who discovered them? Reiji Okazaki and his wife, Tsuneko, discovered these fragments in the 1960s. How do they work? DNA polymerase synthesizes these fragments, which are later joined by DNA ligase to create a continuous strand. When do they appear? They appear during the S phase of the cell cycle. Understanding these fragments is essential for grasping how cells replicate their genetic material accurately.
What Are Okazaki Fragments?
Okazaki fragments are short sequences of DNA nucleotides. They are created on the lagging strand during DNA replication. These fragments are essential for the accurate duplication of genetic material.
- Okazaki fragments are named after Reiji Okazaki, a Japanese molecular biologist who discovered them in the 1960s.
- They are typically 100 to 200 nucleotides long in eukaryotes and about 1,000 to 2,000 nucleotides long in prokaryotes.
- These fragments are synthesized discontinuously, meaning they are made in short bursts rather than in one continuous strand.
- DNA polymerase III is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing Okazaki fragments.
- The lagging strand, where Okazaki fragments form, runs in the 5' to 3' direction, opposite to the leading strand.
How Do Okazaki Fragments Form?
The formation of Okazaki fragments involves several steps and enzymes. Understanding this process helps us appreciate the complexity of DNA replication.
- DNA helicase unwinds the double helix, creating a replication fork.
- Single-strand binding proteins stabilize the unwound DNA strands, preventing them from re-annealing.
- Primase synthesizes a short RNA primer, which provides a starting point for DNA polymerase III.
- DNA polymerase III adds nucleotides to the RNA primer, forming the Okazaki fragment.
- Once an Okazaki fragment is complete, DNA polymerase I removes the RNA primer and replaces it with DNA nucleotides.
Why Are Okazaki Fragments Important?
Okazaki fragments play a crucial role in DNA replication. They ensure that the entire genome is accurately copied.
- They allow the lagging strand to be synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction, which is the only direction DNA polymerase can add nucleotides.
- Without Okazaki fragments, the lagging strand would not be replicated, leading to incomplete DNA replication.
- They help maintain the integrity of genetic information by ensuring that both strands of DNA are accurately copied.
- Okazaki fragments are later joined together by DNA ligase, forming a continuous DNA strand.
- Errors in the formation or joining of Okazaki fragments can lead to mutations, which may cause genetic disorders or cancer.
Enzymes Involved in Okazaki Fragment Processing
Several enzymes work together to ensure that Okazaki fragments are correctly synthesized and joined.
- DNA helicase unwinds the DNA double helix, creating the replication fork.
- Primase synthesizes the RNA primer needed to start the synthesis of Okazaki fragments.
- DNA polymerase III extends the RNA primer, adding nucleotides to form the Okazaki fragment.
- DNA polymerase I removes the RNA primer and replaces it with DNA nucleotides.
- DNA ligase seals the gaps between Okazaki fragments, forming a continuous DNA strand.
Challenges and Errors in Okazaki Fragment Formation
Despite the precision of DNA replication, errors can occur during the formation of Okazaki fragments.
- Mutations in the genes encoding replication enzymes can lead to errors in Okazaki fragment synthesis.
- DNA polymerase can sometimes incorporate incorrect nucleotides, leading to mutations.
- If DNA ligase fails to join Okazaki fragments properly, it can result in fragmented DNA.
- Errors in Okazaki fragment processing can lead to genetic instability, which is a hallmark of cancer cells.
- Some genetic disorders, such as Bloom syndrome, are linked to defects in the enzymes involved in Okazaki fragment processing.
Interesting Facts About Okazaki Fragments
Here are some lesser-known facts about Okazaki fragments that highlight their significance in molecular biology.
- The discovery of Okazaki fragments was a key piece of evidence supporting the semi-discontinuous model of DNA replication.
- Okazaki fragments are not unique to humans; they are found in all organisms that replicate their DNA.
- The length of Okazaki fragments can vary depending on the organism and the conditions under which DNA replication occurs.
- Researchers continue to study Okazaki fragments to understand their role in genetic diseases and cancer.
- Advances in DNA sequencing technology have allowed scientists to study Okazaki fragments in greater detail, leading to new insights into DNA replication.
Wrapping Up the Okazaki Fragments
Okazaki fragments play a crucial role in DNA replication. These short sequences, discovered by Reiji and Tsuneko Okazaki, are essential for synthesizing the lagging strand. Without them, cells couldn't replicate DNA efficiently, leading to genetic instability. Understanding these fragments helps scientists grasp how genetic information is accurately passed on during cell division.
The process involves DNA polymerase, RNA primers, and ligase working together to ensure the fragments are synthesized and joined correctly. This intricate dance of molecules highlights the complexity and precision of cellular mechanisms.
Knowing about Okazaki fragments isn't just for scientists. It sheds light on the fundamental processes that keep all living organisms functioning. Next time you think about DNA, remember these tiny but mighty fragments that make life possible. They might be small, but their impact is enormous.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
