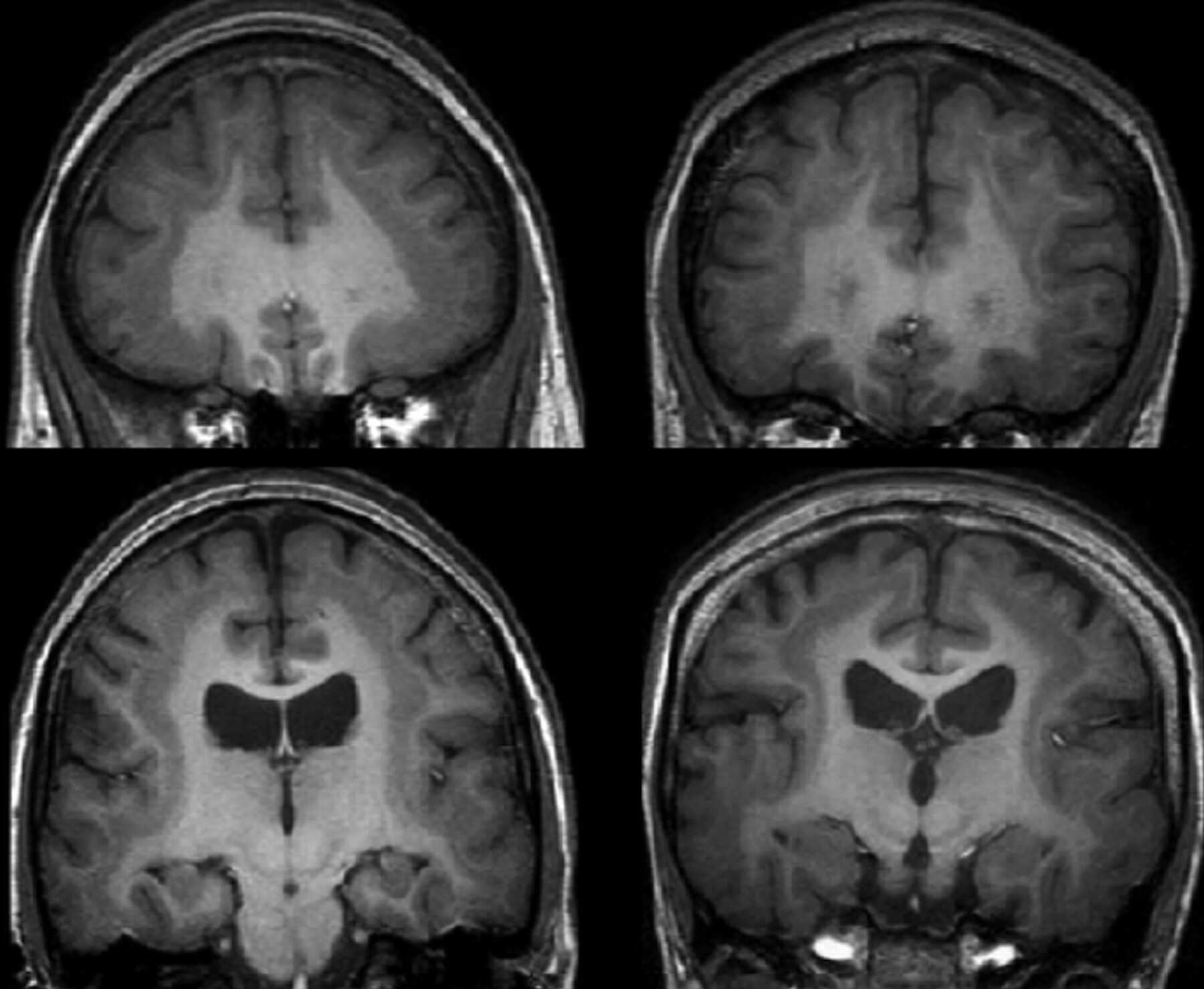
What is a Double Cortex? A double cortex, also known as "band heterotopia," is a rare brain malformation where an extra layer of gray matter forms beneath the normal cortex. This condition arises during brain development when neurons fail to migrate to their proper locations. Why does this happen? It's often linked to genetic mutations, particularly in the DCX gene, which plays a crucial role in neuron movement. What are the effects? Individuals with a double cortex may experience seizures, developmental delays, or learning difficulties. However, the severity can vary widely. How is it diagnosed? MRI scans are typically used to identify this condition. Can it be treated? While there's no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms, such as using medication to control seizures. Understanding this condition helps in providing better care and support for those affected.
Key Takeaways:
- Double cortex is a rare brain condition caused by neuron migration issues. It can lead to seizures, learning difficulties, and challenges in social interaction and independence.
- Research on double cortex aims to understand its genetic causes, develop new therapies, and improve early detection for better outcomes.
What is Double Cortex?
Double cortex, also known as subcortical band heterotopia, is a rare brain malformation. It occurs when neurons fail to migrate properly during brain development. This results in an extra layer of gray matter beneath the cerebral cortex. Let's explore some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Rare Condition: Double cortex is a rare neurological disorder, primarily affecting females. It is estimated to occur in about 1 in 85,000 births.
-
Genetic Cause: The condition is often linked to mutations in the DCX gene. This gene plays a crucial role in neuronal migration during brain development.
-
X-Linked Dominant: Double cortex is inherited in an X-linked dominant pattern. This means that females are more frequently affected than males.
-
Symptoms Vary: Symptoms can range from mild to severe. They may include developmental delays, intellectual disability, and epilepsy.
-
Epilepsy Common: Many individuals with double cortex experience seizures. Epilepsy is one of the most common symptoms associated with this condition.
-
MRI Diagnosis: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the primary tool for diagnosing double cortex. It reveals the characteristic band of gray matter beneath the cortex.
-
Treatment Options: While there is no cure, treatment focuses on managing symptoms. This often involves antiepileptic drugs to control seizures.
-
Research Ongoing: Scientists continue to study double cortex to better understand its causes and develop more effective treatments.
How Does Double Cortex Affect the Brain?
The presence of an extra layer of gray matter can significantly impact brain function. Here's how double cortex affects the brain and its functions.
-
Neuronal Migration: During normal brain development, neurons migrate to form the cerebral cortex. In double cortex, this process is disrupted, leading to the formation of an additional layer.
-
Cognitive Impact: The condition can affect cognitive abilities. Some individuals may experience learning difficulties or intellectual disabilities.
-
Motor Skills: Motor skills can also be impacted. Some people with double cortex may have difficulty with coordination and movement.
-
Behavioral Issues: Behavioral problems, such as hyperactivity or attention deficits, may occur in some individuals.
-
Speech Delays: Speech and language development can be delayed. This may require speech therapy to improve communication skills.
-
Seizure Types: Seizures in double cortex can vary. They may include generalized seizures, focal seizures, or absence seizures.
-
Brain Plasticity: The brain's ability to adapt, known as plasticity, can help compensate for some of the functional deficits caused by double cortex.
What Are the Challenges in Living with Double Cortex?
Living with double cortex presents unique challenges. Understanding these challenges can help in providing better support and care.
-
Educational Support: Individuals may require special education services to address learning difficulties.
-
Social Interaction: Social skills can be affected, making it challenging to form and maintain relationships.
-
Emotional Well-being: Coping with a chronic condition can impact emotional health. Support from family and mental health professionals is crucial.
-
Independence: Achieving independence can be difficult. Some individuals may need assistance with daily activities.
-
Healthcare Access: Access to specialized healthcare services is essential for managing symptoms and improving quality of life.
-
Family Support: Families play a vital role in providing care and support. They may also benefit from joining support groups for shared experiences and advice.
-
Advocacy: Advocacy for individuals with double cortex is important. Raising awareness can lead to better resources and support systems.
What Are the Future Directions for Double Cortex Research?
Research into double cortex is ongoing, with scientists exploring various aspects to improve understanding and treatment.
-
Genetic Studies: Researchers are investigating other genetic factors that may contribute to double cortex.
-
Therapeutic Approaches: New therapies are being explored, including gene therapy and neurostimulation techniques.
-
Early Detection: Efforts are being made to develop methods for earlier detection and intervention, which could improve outcomes for affected individuals.
Final Thoughts on Double Cortex
Double cortex, or band heterotopia, is a rare brain condition where neurons don't migrate properly during development. This results in a second layer of gray matter, which can lead to seizures and developmental delays. Understanding this condition is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. While it primarily affects females due to its link with the DCX gene on the X chromosome, males can also be carriers and exhibit symptoms. MRI scans are essential for diagnosis, revealing the characteristic double layer of gray matter. Treatment often involves managing symptoms, particularly seizures, with medication or, in some cases, surgery. Research is ongoing to better understand the genetic and molecular mechanisms behind this condition, offering hope for more targeted therapies in the future. Awareness and education about double cortex can improve outcomes for those affected and their families.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
