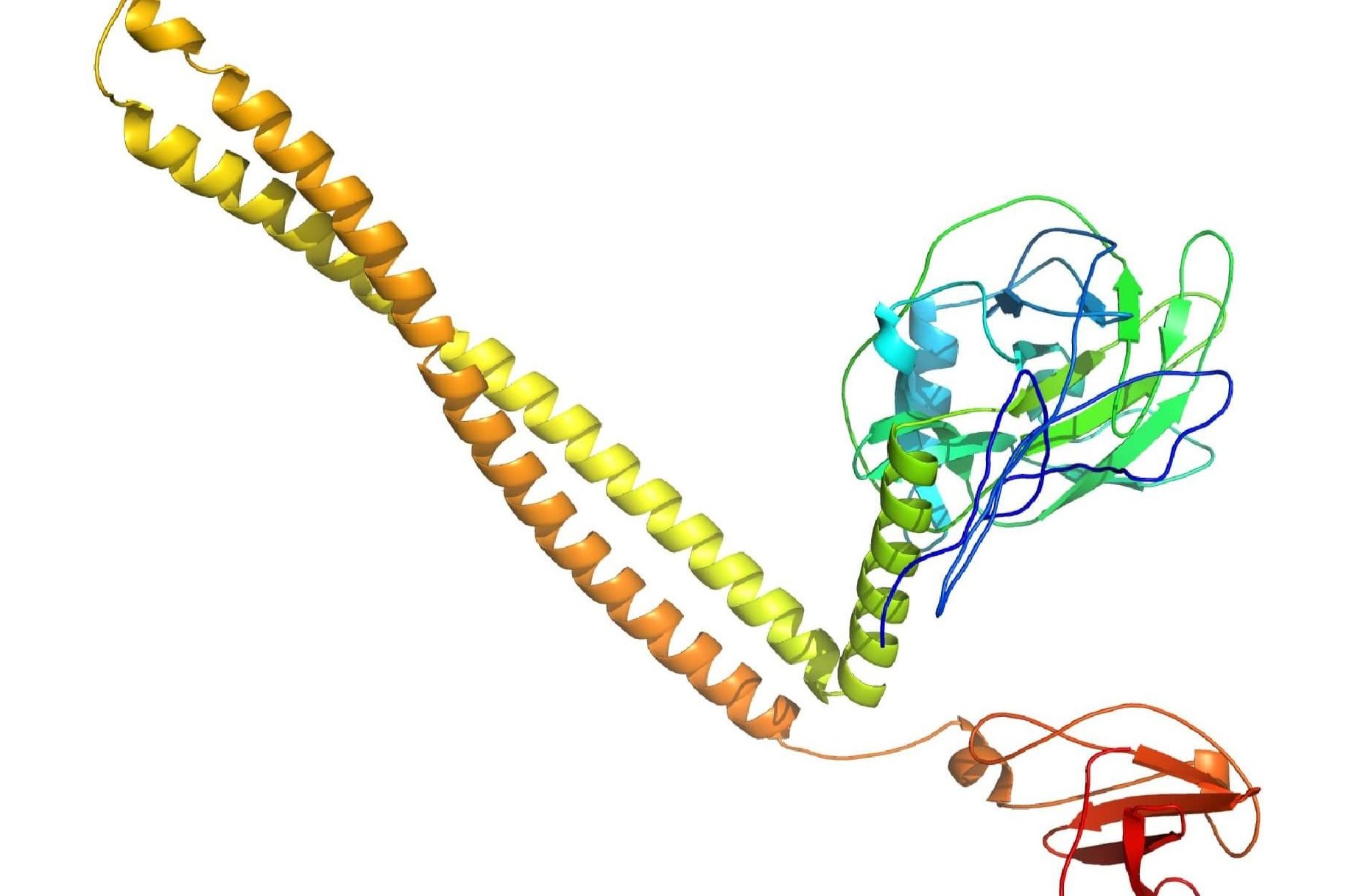
Bacteriocins are fascinating proteins produced by bacteria that can kill or inhibit the growth of other bacteria. These tiny warriors play a crucial role in microbial warfare, helping bacteria compete for resources. But what exactly makes bacteriocins so special? Bacteriocins are unique because they are highly specific, often targeting only closely related bacterial strains. This specificity makes them potential candidates for use in medicine, agriculture, and food preservation. Imagine a world where antibiotics are no longer effective; bacteriocins could be the next big thing in fighting bacterial infections. Ready to learn more? Here are 25 intriguing facts about these microscopic marvels.
What Are Bacteriocins?
Bacteriocins are proteins produced by bacteria that inhibit the growth of similar or closely related bacterial strains. These natural antibiotics have a fascinating role in microbial warfare and offer potential applications in medicine and food preservation.
- Bacteriocins are produced by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
- They are ribosomally synthesized, meaning they are made by the ribosomes within bacterial cells.
- Bacteriocins can target specific bacteria without harming the host organism.
- They are considered a form of natural antibiotic, offering an alternative to traditional antibiotics.
- Some bacteriocins can kill bacteria by forming pores in their cell membranes.
Types of Bacteriocins
Different types of bacteriocins exist, each with unique characteristics and mechanisms of action. Understanding these types can help in their application in various fields.
- Class I bacteriocins, also known as lantibiotics, contain unusual amino acids.
- Class II bacteriocins are small, heat-stable proteins.
- Class III bacteriocins are large proteins that are heat-labile.
- Class IV bacteriocins require additional molecules, like lipids or carbohydrates, to function.
- Nisin is a well-known lantibiotic used in food preservation.
Applications in Medicine
Bacteriocins have promising applications in the medical field, particularly in combating antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Their specificity and potency make them valuable tools.
- Bacteriocins can be used to treat infections caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- They have potential as probiotics, promoting gut health by inhibiting harmful bacteria.
- Bacteriocins can be used in wound dressings to prevent infections.
- They are being researched for use in dental care to prevent cavities and gum disease.
- Bacteriocins may be used in combination with traditional antibiotics to enhance their effectiveness.
Applications in Food Preservation
Bacteriocins are also valuable in the food industry, where they help extend shelf life and ensure food safety. Their natural origin makes them appealing for consumers seeking clean-label products.
- Nisin is commonly used to preserve dairy products like cheese and yogurt.
- Bacteriocins can inhibit the growth of foodborne pathogens like Listeria and Salmonella.
- They are used in meat products to prevent spoilage and extend shelf life.
- Bacteriocins can be applied to fruits and vegetables to reduce microbial contamination.
- They offer a natural alternative to chemical preservatives, appealing to health-conscious consumers.
Mechanisms of Action
Understanding how bacteriocins work can help in developing new applications and enhancing their effectiveness. Their mechanisms of action are diverse and fascinating.
- Some bacteriocins kill bacteria by disrupting their cell membranes.
- Others inhibit cell wall synthesis, preventing bacteria from growing and dividing.
- Bacteriocins can interfere with essential enzymes within bacterial cells.
- They may also induce the production of reactive oxygen species, leading to bacterial cell death.
- Bacteriocins can target specific receptors on bacterial cells, ensuring precision in their action.
The Power of Bacteriocins
Bacteriocins are fascinating. These proteins, produced by bacteria, can kill or inhibit other bacteria. They offer potential in food preservation, medicine, and agriculture. Unlike antibiotics, bacteriocins target specific bacteria, reducing the risk of resistance. This specificity makes them valuable in fighting harmful bacteria without harming beneficial ones.
Research continues to uncover new bacteriocins and their applications. Scientists are exploring ways to harness these natural compounds for safer, more effective treatments. Imagine a world where bacteriocins help combat antibiotic-resistant infections or keep food fresh longer.
Understanding bacteriocins opens doors to innovative solutions. Their unique properties make them a promising tool in various fields. As we learn more, the potential benefits grow. Keep an eye on this exciting area of science. It might just change the way we approach health and safety.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.