The cell wall is a fascinating and essential component of plant cells, providing structure, support, and protection. It serves as a rigid boundary, maintaining the cell's shape and preventing it from bursting in hypotonic environments. However, there's much more to the cell wall than meets the eye. In this article, we'll delve into 15 fun and intriguing facts about the cell wall, shedding light on its diverse functions and remarkable properties. From its composition and role in plant growth to its interactions with the environment, the cell wall plays a pivotal role in the life of a plant cell. So, let's embark on a journey to uncover the captivating world of the cell wall and gain a deeper understanding of its significance in the realm of biology.
Key Takeaways:
- The cell wall is like a superhero cape for cells, giving them strength, shape, and protection. It’s made of different materials in different organisms and helps plants stand tall and fight off bad guys.
- Cell walls are like the cell’s communication network and armor combined. They help cells talk to each other, stay firm and crunchy, and even survive tough times. Plus, they’re important for making renewable fuels and cool new materials!
The cell wall is a rigid layer surrounding the cell membrane.
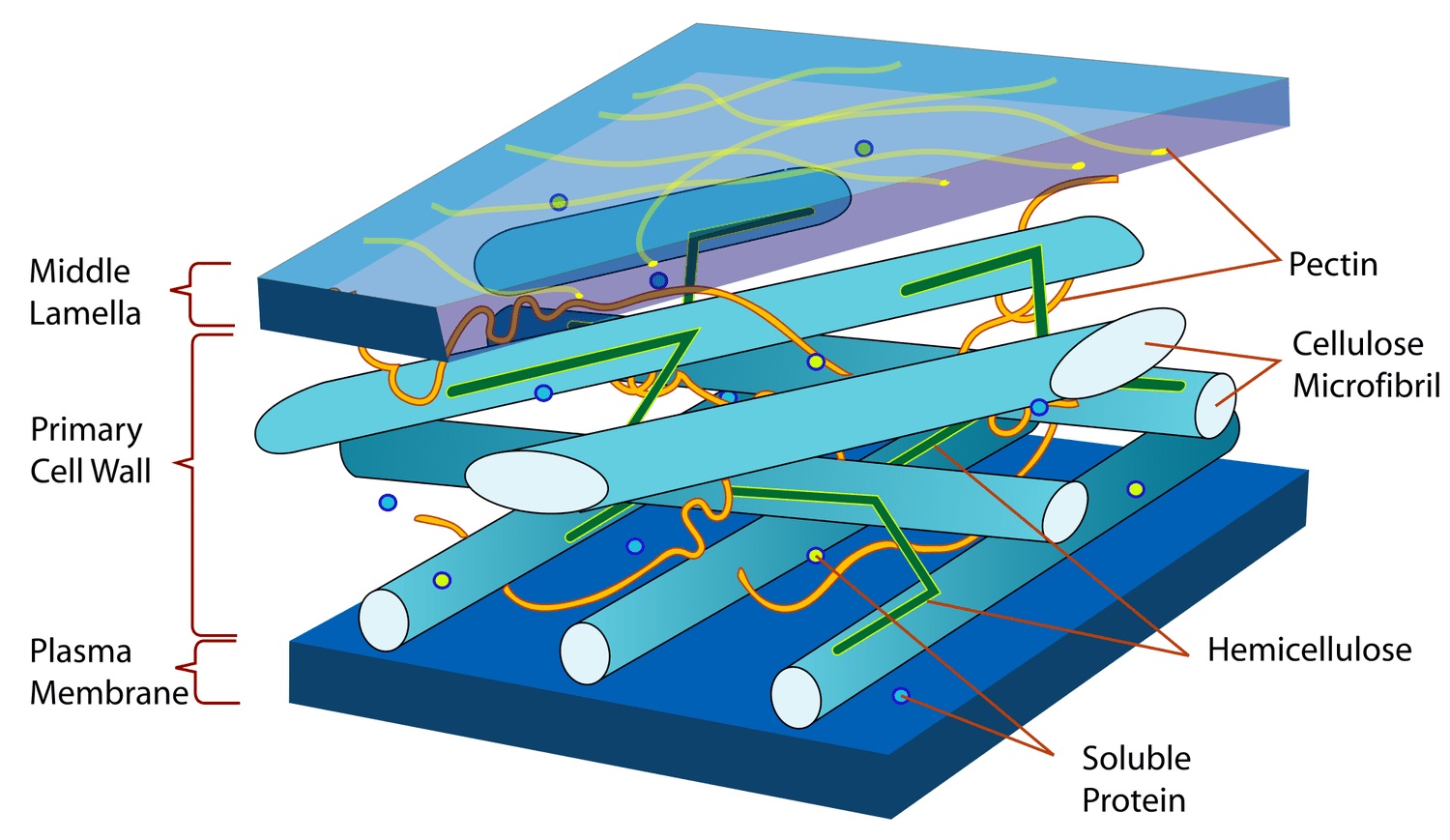
The cell wall is a tough, flexible layer that surrounds the cell membrane, providing support and shape to the cell. It is made up of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin in plant cells, and peptidoglycan in bacterial cells.
It is found in plant cells, bacteria, fungi, algae, and some archaea.
The cell wall is a defining feature of plant cells, where it provides structural support and protection. In bacteria, it helps protect the cell from osmotic lysis and contributes to pathogenicity. In fungi and algae, the cell wall provides rigidity and shape to the cell.
The cell wall helps maintain the shape of the cell.
One of the primary functions of the cell wall is to maintain the shape of the cell and prevent it from bursting in a hypotonic environment. This is crucial for the survival of plant cells, especially in a water-rich environment.
It allows plants to stand upright.
The rigidity provided by the cell wall enables plants to stand upright against the force of gravity. Without the cell wall, plants would be unable to support their own weight and grow upright.
The cell wall plays a role in defense against pathogens.
It acts as a barrier to protect the cell from pathogens and parasites. The tough structure of the cell wall makes it difficult for pathogens to invade the cell, contributing to the plant’s defense mechanisms.
It is permeable, allowing for the passage of water and nutrients.
While providing structural support, the cell wall is also permeable, allowing for the passage of water, nutrients, and other essential substances into and out of the cell.
The composition of the cell wall varies among different organisms.
While cellulose is the primary component of plant cell walls, bacterial cell walls contain peptidoglycan. Fungal cell walls consist of chitin, glucans, and other complex carbohydrates, showcasing the diversity in cell wall composition.
Cell walls contribute to the texture of fruits and vegetables.
The firmness and texture of fruits and vegetables are influenced by the composition and structure of their cell walls. For example, the crispness of an apple is due in part to the integrity of its cell walls.
It provides protection from physical stress.
The cell wall offers protection from physical stress, such as wind, rain, and other environmental factors. It helps plants withstand external pressures and maintain their structural integrity.
Cell walls are involved in cell-to-cell communication.
Cell walls contain receptors and signaling molecules that facilitate communication between neighboring cells. This communication is essential for coordinating growth, development, and responses to environmental stimuli.
They contribute to the buoyancy of algae in water.
The cell walls of algae provide buoyancy, allowing them to float on the water’s surface and access sunlight for photosynthesis. This buoyancy is essential for the survival and growth of many algal species.
The cell wall can undergo modifications in response to environmental cues.
Environmental factors such as drought, temperature changes, and pathogen attacks can trigger modifications in the cell wall composition and structure, enabling the cell to adapt to changing conditions.
It is essential for the formation of spores in fungi and bacteria.
The cell wall plays a vital role in the formation and protection of spores in fungi and bacteria, allowing them to survive harsh conditions and facilitating their dispersal to new environments.
Cell walls contribute to the bioconversion of biomass.
In the field of bioenergy, cell walls are of great interest for their potential in the bioconversion of biomass into renewable fuels and chemicals, highlighting their significance beyond biological functions.
The study of cell wall structure and function is crucial for various industries.
Understanding the intricacies of cell wall composition and properties has applications in agriculture, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and materials science, driving innovation and advancements in these fields.
Conclusion
The cell wall is a fascinating and essential structure found in plant cells, bacteria, fungi, and some protists. It provides crucial support and protection, and also plays a role in maintaining the shape and integrity of the cell. Understanding the cell wall and its functions is vital in various fields, including biology, agriculture, and medicine. By learning about the cell wall, we gain insights into the unique characteristics of different organisms and the ways in which they interact with their environments. Exploring the intricate details of the cell wall not only enhances our knowledge of cellular biology, but also opens up possibilities for innovative research and applications in biotechnology and healthcare.
FAQs
What is the cell wall?
The cell wall is a rigid layer of polysaccharides and proteins that surrounds the cell membrane of plant cells, bacteria, fungi, and some protists.
What is the function of the cell wall?
The cell wall provides structural support, protection, and shape to the cell. It also helps regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Is the cell wall found in animal cells?
No, animal cells do not have a cell wall. They are surrounded by a flexible cell membrane but lack the rigid cell wall found in plant cells.
Can the cell wall be targeted for medical purposes?
Research is ongoing to explore the potential of targeting bacterial cell walls for developing new antibiotics. Understanding the cell wall structure of pathogens can aid in the development of effective treatments.
How does the cell wall contribute to plant growth?
The cell wall provides structural support to plant cells, allowing them to maintain rigidity and withstand the forces of turgor pressure, which is essential for plant growth and development.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
