Have you ever heard of the Siberian Ice Maiden? This ancient mummy, discovered in 1993, has fascinated archaeologists and historians alike. Found in the Altai Mountains, she dates back to the 5th century BCE. Why is she so special? Her preservation is remarkable, with tattoos and clothing still intact. The Ice Maiden offers a glimpse into the Pazyryk culture, known for their artistry and craftsmanship. Her burial site included six horses, symbolizing her high status. Some believe she was a priestess or noblewoman. Curious about more details? Let's dive into 35 intriguing facts about this enigmatic figure.
Key Takeaways:
- The Siberian Ice Maiden, a 2,500-year-old mummy, offers a fascinating glimpse into ancient culture and beliefs, with her tattoos and artifacts revealing the rich heritage of the Altai region.
- The controversy surrounding the Ice Maiden's repatriation highlights the delicate balance between scientific study and indigenous rights, sparking discussions about the respectful treatment of ancient remains.
The Discovery of the Siberian Ice Maiden
The Siberian Ice Maiden, also known as the Princess of Ukok, is a fascinating archaeological find. Her discovery has shed light on ancient cultures and practices.
- In 1993, Russian archaeologist Natalia Polosmak discovered the Siberian Ice Maiden in the Altai Mountains of Siberia.
- The burial site was found on the Ukok Plateau, a remote and high-altitude region.
- The Ice Maiden is believed to have lived around the 5th century BCE.
- Her body was preserved in permafrost, which kept her remarkably intact for over 2,500 years.
- The Ice Maiden was buried in a wooden chamber within a large burial mound called a kurgan.
The Burial and Artifacts
The artifacts found with the Siberian Ice Maiden provide insight into her life and the culture she belonged to.
- She was buried with six horses, which were likely sacrificed for her journey to the afterlife.
- The horses were adorned with elaborate harnesses and saddles.
- The Ice Maiden's burial chamber contained a variety of grave goods, including a wooden table and dishes.
- She was dressed in a long, flowing gown made of silk and wool.
- Her headdress was decorated with intricate carvings and gold leaf.
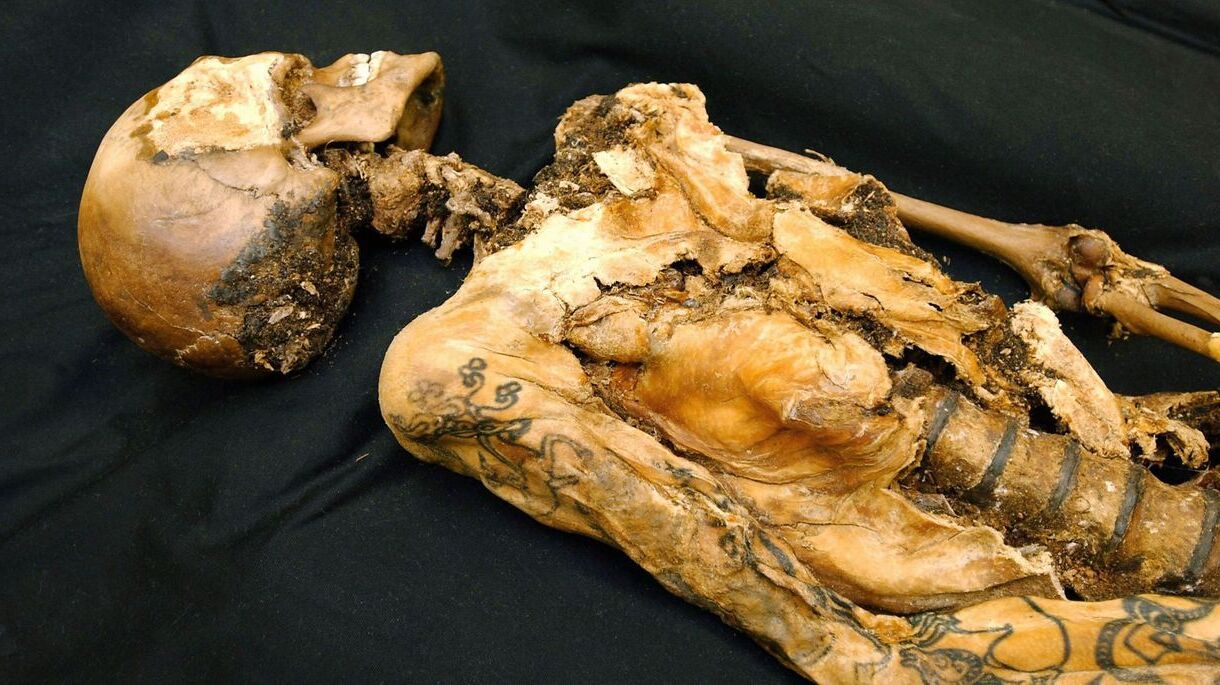
The Tattoos of the Siberian Ice Maiden
One of the most intriguing aspects of the Siberian Ice Maiden is her tattoos, which offer a glimpse into the artistry and beliefs of her people.
- The Ice Maiden's body is covered in elaborate tattoos, primarily on her arms and shoulders.
- The tattoos depict mythical creatures, including griffins and deer with elaborate antlers.
- These tattoos are considered some of the best-preserved examples of ancient body art.
- The designs are thought to have had spiritual or protective significance.
- The tattoos were created using a method that involved pricking the skin and rubbing in soot.
The Cultural Significance
The Siberian Ice Maiden provides valuable information about the Pazyryk culture, a nomadic people who lived in the Altai region.
- The Pazyryk culture is known for its skilled horsemanship and elaborate burial practices.
- The Ice Maiden's burial suggests she held a high status within her community.
- Her clothing and jewelry indicate she was likely a priestess or a noblewoman.
- The Pazyryk people practiced mummification, as evidenced by other similar burials in the region.
- The Ice Maiden's burial mound was part of a larger necropolis, indicating a well-organized society.
The Controversy and Repatriation
The discovery of the Siberian Ice Maiden has not been without controversy, particularly regarding her final resting place.
- Some local indigenous groups, such as the Altai people, believe the Ice Maiden should be reburied in her original location.
- They argue that her removal has disturbed the spirits and caused natural disasters in the region.
- The Ice Maiden is currently housed in the Anokhin National Museum in Gorno-Altaisk, Russia.
- Efforts have been made to balance scientific study with respect for local beliefs and traditions.
- The debate over her repatriation continues, highlighting the complex relationship between archaeology and indigenous rights.
The Scientific Studies
Scientific studies of the Siberian Ice Maiden have provided a wealth of information about her life and the environment she lived in.
- DNA analysis has revealed that the Ice Maiden had European ancestry.
- Isotope analysis of her hair suggests she had a diet rich in meat and dairy products.
- Pollen analysis from her burial chamber indicates she was buried in the summer.
- Studies of her clothing and textiles have provided insights into ancient weaving and dyeing techniques.
- The Ice Maiden's well-preserved brain has allowed researchers to study ancient brain structures and diseases.
The Legacy of the Siberian Ice Maiden
The Siberian Ice Maiden continues to captivate researchers and the public alike, offering a unique window into the past.
- Her discovery has inspired numerous documentaries, books, and exhibitions.
- The Ice Maiden has become a symbol of the rich cultural heritage of the Altai region.
- Her tattoos have influenced modern tattoo artists and enthusiasts.
- The Ice Maiden has sparked interest in the preservation of other ancient mummies and archaeological sites.
- Her story serves as a reminder of the importance of respecting and preserving our shared human history.
The Legacy of the Siberian Ice Maiden
The Siberian Ice Maiden offers a fascinating glimpse into ancient cultures. Her well-preserved remains and intricate tattoos tell stories of a time long past. Found in the Altai Mountains, she has sparked interest among archaeologists and historians alike. Her burial site, filled with treasures, suggests she held a significant position in her society. The discovery has provided valuable insights into the Pazyryk culture, known for their artistry and craftsmanship.
Despite controversies surrounding her excavation and display, the Ice Maiden remains a symbol of historical curiosity. Her story continues to captivate those interested in ancient civilizations. As we learn more about her, we gain a deeper understanding of human history and the cultural practices that shaped our world. The Siberian Ice Maiden stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of the past, bridging the gap between ancient traditions and modern scholarship.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
