Ever wondered how the body communicates with the brain? The vagus nerve plays a huge role in this process. This nerve, the longest in the autonomic nervous system, connects the brain to various organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. A vagus nerve stimulator (VNS) is a device implanted under the skin that sends electrical impulses to this nerve, helping treat conditions like epilepsy and depression. Understanding the VNS can be a game-changer for those seeking alternative treatments. Here are 32 facts that will shed light on the fascinating world of vagus nerve stimulators. Buckle up for an enlightening read!
What is a Vagus Nerve Stimulator?
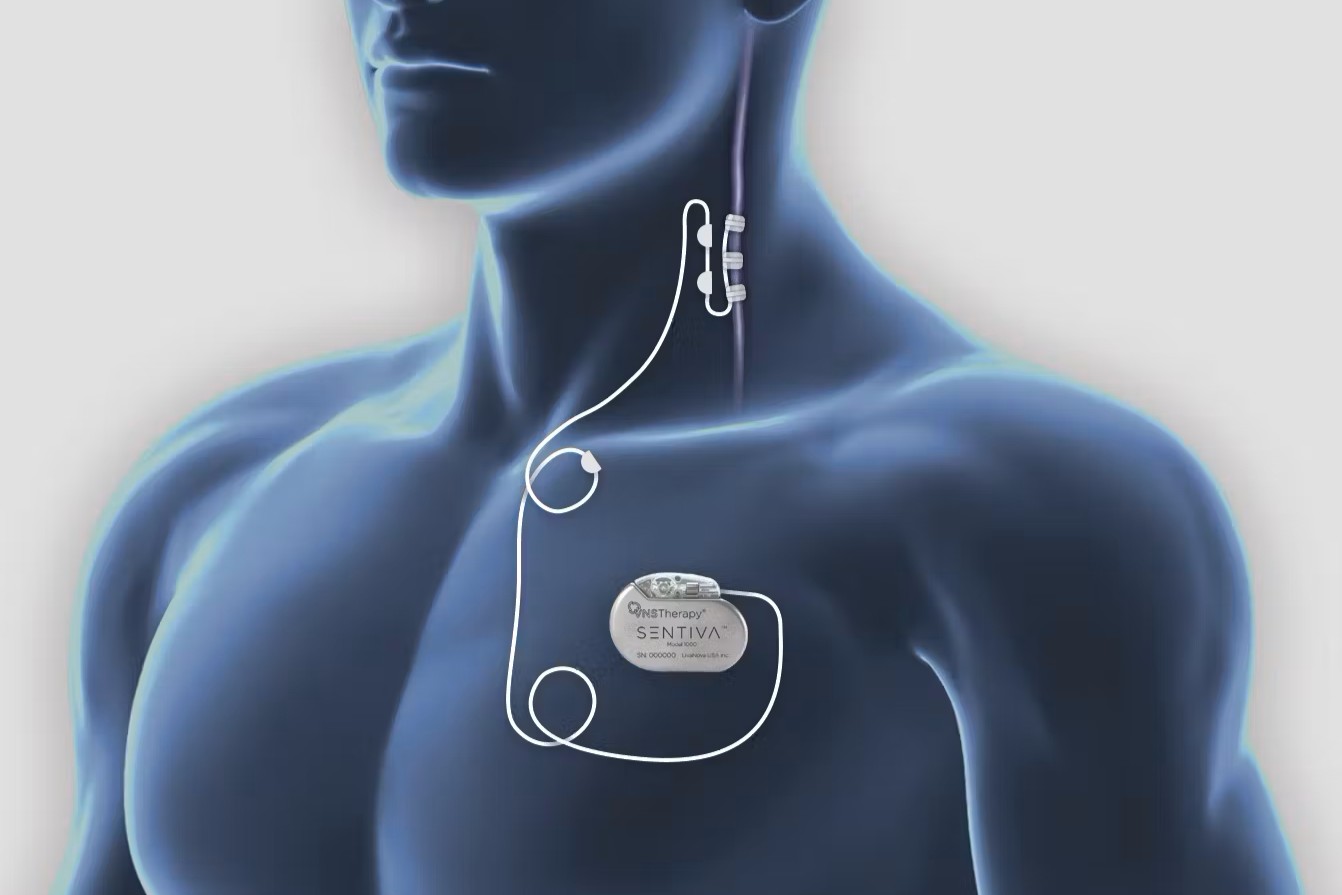
A Vagus Nerve Stimulator (VNS) is a medical device used to treat certain conditions by sending electrical impulses to the vagus nerve. This nerve plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions. Here are some interesting facts about VNS.
- The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve in the body, extending from the brainstem to the abdomen.
- VNS was first approved by the FDA in 1997 for treating epilepsy.
- The device is implanted under the skin in the chest, with a wire connecting it to the vagus nerve in the neck.
- VNS is also used to treat depression, especially in patients who do not respond to other treatments.
- The electrical impulses are sent at regular intervals, which can be adjusted by a healthcare provider.
- VNS therapy can reduce the frequency and severity of seizures in epilepsy patients.
- The device is powered by a battery that typically lasts 5 to 10 years.
- VNS can also help improve mood and cognitive function in some patients.
- The exact mechanism of how VNS works is not fully understood, but it is believed to modulate brain activity.
- Side effects can include hoarseness, throat pain, and coughing, but these often diminish over time.
How Does Vagus Nerve Stimulation Work?
Understanding how VNS works can help demystify its benefits and potential side effects. Here are some key points about its operation.
- The device sends mild electrical pulses to the vagus nerve, which then transmits signals to the brain.
- These signals can help regulate abnormal electrical activity in the brain, reducing seizures.
- VNS can also influence neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine, which are involved in mood regulation.
- The stimulation is usually set to occur at regular intervals, but it can also be activated manually using a magnet.
- Patients often undergo a trial period to determine the optimal settings for their specific condition.
- Adjustments to the device settings are made using a special programming wand and computer.
- The procedure to implant the device is minimally invasive, usually taking about 1 to 2 hours.
- Recovery from the surgery typically takes a few days to a week.
- Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor the device and make any needed adjustments.
- Some patients may experience an improvement in symptoms within a few weeks, while for others, it may take several months.
Benefits of Vagus Nerve Stimulation
The benefits of VNS extend beyond just seizure control. Here are some of the advantages that patients might experience.
- VNS can significantly reduce the frequency of seizures in epilepsy patients.
- It can also help improve the quality of life by reducing the severity of seizures.
- For patients with depression, VNS can offer relief when other treatments have failed.
- Some studies suggest that VNS can improve cognitive function and memory.
- VNS therapy can be used in conjunction with other treatments, such as medication and therapy.
- The device can be adjusted to meet the changing needs of the patient over time.
- VNS has been shown to have long-term benefits, with some patients experiencing continued improvement for years.
- The therapy is generally well-tolerated, with manageable side effects.
- VNS can also help reduce the need for medication in some patients, lowering the risk of drug-related side effects.
- The therapy can be a life-changing option for patients who have not found relief through other treatments.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While VNS offers many benefits, it is important to be aware of the potential risks and side effects. Here are some things to consider.
- Common side effects include hoarseness, throat pain, and coughing.
- Some patients may experience shortness of breath or difficulty swallowing, especially during stimulation.
Final Thoughts on Vagus Nerve Stimulators
Vagus nerve stimulators (VNS) offer a fascinating glimpse into the intersection of neuroscience and technology. These devices have shown promise in treating conditions like epilepsy, depression, and even migraines. By sending electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, they help regulate brain activity and improve quality of life for many patients.
While VNS isn't a cure-all, it's a valuable tool in the medical arsenal. Ongoing research continues to uncover new applications and refine existing treatments. If you're considering VNS, consult with a healthcare professional to weigh the benefits and risks.
Understanding the basics of VNS can empower you to make informed decisions about your health. Stay curious, stay informed, and always prioritize your well-being.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
