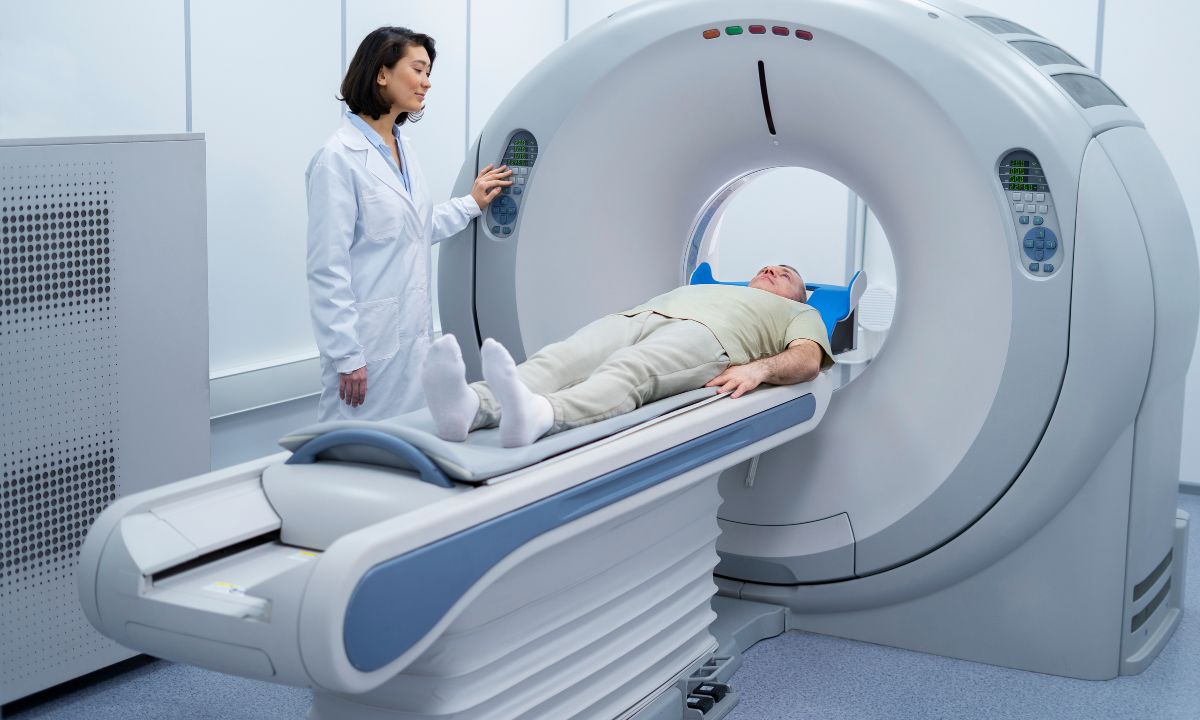
What is a Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) scanner? A SPECT scanner is a medical imaging device that helps doctors see how blood flows to tissues and organs. It uses a special camera and a radioactive substance to create 3D pictures of the inside of your body. These images can help diagnose conditions like heart disease, brain disorders, and bone problems. Unlike regular X-rays, which only show bones, SPECT scans can show how well organs and tissues are working. This makes it a powerful tool for doctors to understand what's happening inside you and plan the best treatment.
What is a Single-photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) Scanner?
A Single-photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) scanner is a type of nuclear imaging test that shows how blood flows to tissues and organs. It combines nuclear medicine and computed tomography (CT) to create detailed 3D images. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this technology.
-
SPECT scanners use gamma rays to create images of the body. These rays are emitted by a radioactive tracer injected into the patient.
-
The radioactive tracer used in SPECT scans is usually a form of technetium-99m, which has a short half-life, making it safer for patients.
-
SPECT scans are particularly useful for diagnosing and monitoring heart diseases, brain disorders, and bone conditions.
-
Unlike traditional X-rays, SPECT scans provide functional information about organs and tissues, not just structural details.
-
The process involves rotating gamma cameras around the patient to capture images from multiple angles.
How Does a SPECT Scanner Work?
Understanding the mechanics behind a SPECT scanner can help appreciate its capabilities. Here are some key points about its operation.
-
The patient is injected with a small amount of radioactive material, known as a radiotracer.
-
As the radiotracer travels through the body, it emits gamma rays, which are detected by the scanner.
-
The gamma cameras rotate around the patient, capturing images from various angles.
-
A computer processes these images to create detailed 3D pictures of the inside of the body.
-
The entire scanning process typically takes about 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the area being examined.
Applications of SPECT Scanners
SPECT scanners have a wide range of applications in the medical field. Here are some of the most common uses.
-
SPECT scans are often used to evaluate blood flow to the heart, helping diagnose coronary artery disease.
-
They can detect areas of the brain affected by conditions like epilepsy, stroke, and Alzheimer's disease.
-
SPECT imaging is useful in identifying bone abnormalities, such as fractures, infections, or tumors.
-
It helps in assessing the function of organs like the liver, spleen, and kidneys.
-
SPECT scans can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of treatments for various conditions.
Advantages of SPECT Scanners
There are several benefits to using SPECT scanners in medical diagnostics. Here are some of the key advantages.
-
SPECT scans provide detailed 3D images, offering more information than traditional 2D imaging techniques.
-
They can detect abnormalities at an early stage, often before symptoms appear.
-
The scans are non-invasive and generally safe, with minimal exposure to radiation.
-
SPECT imaging can be combined with other imaging techniques, like CT or MRI, for more comprehensive results.
-
The technology is versatile, with applications in cardiology, neurology, oncology, and orthopedics.
Limitations and Challenges of SPECT Scanners
Despite their many benefits, SPECT scanners also have some limitations and challenges. Here are a few to consider.
-
The resolution of SPECT images is lower than that of PET scans, another type of nuclear imaging.
-
The accuracy of the scan can be affected by patient movement during the procedure.
-
SPECT scans may not be suitable for pregnant women or individuals with severe allergies to the radiotracer.
-
The cost of SPECT scans can be high, which may limit accessibility for some patients.
-
There is a small risk of radiation exposure, although it is generally considered safe for most patients.
Future Developments in SPECT Technology
The field of SPECT imaging is continually evolving, with new advancements on the horizon. Here are some exciting future developments.
-
Researchers are working on improving the resolution and sensitivity of SPECT scanners.
-
New radiotracers are being developed to target specific diseases more effectively.
-
Advances in computer technology are enhancing the processing and analysis of SPECT images, leading to faster and more accurate diagnoses.
SPECT Scanners: A Quick Recap
SPECT scanners are game-changers in medical imaging. They provide detailed 3D images of internal organs, helping doctors diagnose and treat various conditions. These scanners use gamma rays and a special camera to create images, offering insights into blood flow, brain activity, and heart function. They're especially useful for detecting cancers, heart diseases, and brain disorders.
The technology behind SPECT scanners is constantly evolving, making them more accurate and efficient. They play a crucial role in personalized medicine, allowing for tailored treatments based on individual patient needs. While the procedure is generally safe, it's essential to follow medical guidelines to minimize any risks.
Understanding how SPECT scanners work and their applications can help you appreciate their importance in modern healthcare. They truly are a vital tool in the fight against many serious health conditions.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
