Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a medical marvel that has transformed the lives of many people with neurological disorders. But what exactly is DBS? DBS involves implanting electrodes in specific areas of the brain to send electrical impulses, which help regulate abnormal brain activity. This technique is often used to treat conditions like Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. DBS can significantly improve symptoms, offering a better quality of life for patients who may not respond well to medication. Curious about how this technology works, its benefits, and potential risks? Keep reading to uncover 25 fascinating facts about deep brain stimulation.
What is Deep Brain Stimulation?
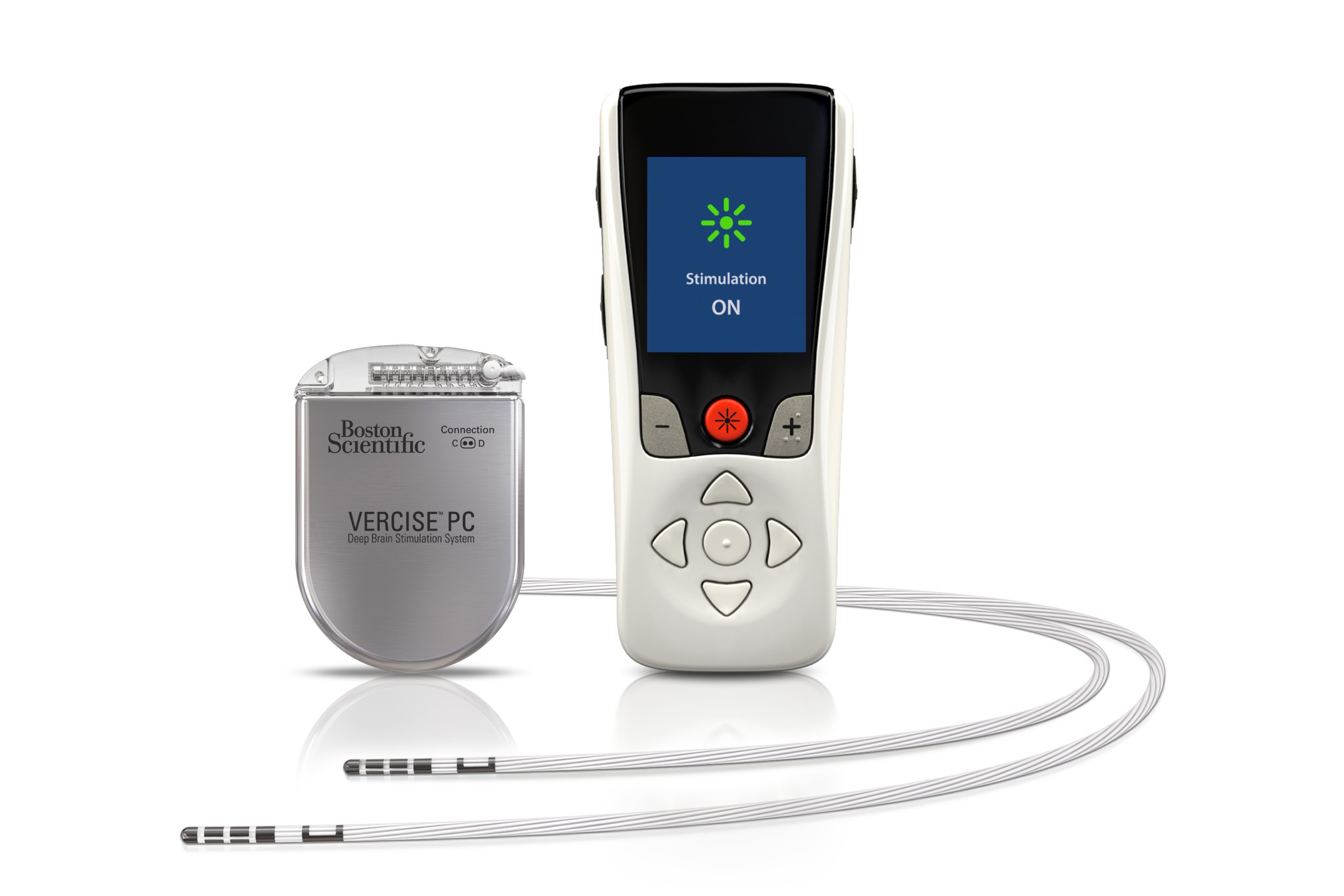
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure used to treat neurological conditions. It involves implanting electrodes in specific areas of the brain. These electrodes produce electrical impulses that regulate abnormal brain activity.
-
DBS was first approved by the FDA in 1997 for treating essential tremor, a condition causing involuntary shaking.
-
The procedure is reversible. Unlike some other brain surgeries, DBS can be turned off or removed if necessary.
-
DBS is often used to treat Parkinson's disease. It helps manage symptoms like tremors, stiffness, and difficulty walking.
-
The system includes three main components: electrodes, a pulse generator, and extension wires connecting them.
-
DBS can also treat dystonia. This condition causes muscles to contract uncontrollably.
How Does DBS Work?
Understanding how DBS works can help demystify its effectiveness. The system sends electrical impulses to specific brain regions, disrupting abnormal signals.
-
Electrodes are implanted in the brain. These are placed in targeted areas depending on the condition being treated.
-
A pulse generator is implanted in the chest. This device sends electrical impulses to the electrodes.
-
Extension wires connect the electrodes to the pulse generator. These wires run under the skin.
-
The electrical impulses can be adjusted. Doctors can fine-tune the settings to optimize treatment.
-
DBS does not destroy brain tissue. Unlike some other treatments, it does not cause permanent damage.
Benefits of Deep Brain Stimulation
DBS offers several advantages over other treatments. It can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with certain neurological conditions.
-
DBS can reduce medication needs. Patients often require fewer drugs, which can lessen side effects.
-
The procedure can improve motor function. Many patients experience better control over their movements.
-
DBS can be adjusted as needed. Settings can be changed to adapt to the patient's condition over time.
-
It can treat multiple conditions. Besides Parkinson's and dystonia, DBS is also used for epilepsy and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
-
The effects are usually long-lasting. Many patients experience sustained benefits for years.
Risks and Considerations
Like any medical procedure, DBS comes with risks. It's essential to weigh these against the potential benefits.
-
Surgery carries inherent risks. These include infection, bleeding, and complications from anesthesia.
-
There can be side effects. Some patients experience mood changes, speech problems, or balance issues.
-
DBS is not a cure. It helps manage symptoms but does not eliminate the underlying condition.
-
Regular follow-ups are necessary. Patients need ongoing care to monitor and adjust the system.
-
Not everyone is a candidate. Certain medical conditions or psychological issues may disqualify someone from receiving DBS.
Future of Deep Brain Stimulation
Research continues to expand the potential uses and improve the technology of DBS. The future looks promising for this innovative treatment.
-
New targets are being explored. Researchers are investigating other brain areas that could benefit from DBS.
-
Technological advancements are ongoing. Improvements in hardware and software make the system more effective and easier to use.
-
DBS may help with depression. Studies are exploring its use for treatment-resistant depression.
-
Non-invasive alternatives are being developed. Researchers are working on methods that don't require surgery.
-
Personalized treatment is the goal. Future advancements aim to tailor DBS settings to individual patients for optimal results.
The Power of Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has revolutionized how we treat neurological disorders. By sending electrical impulses to specific brain areas, DBS can significantly improve symptoms of conditions like Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. This technique offers hope to those who haven't found relief through medication alone.
DBS isn't a cure, but it can enhance the quality of life for many patients. The procedure involves implanting electrodes in the brain, connected to a device similar to a pacemaker. Adjustments can be made to tailor the treatment to each individual's needs.
While DBS has risks, such as infection or bleeding, the benefits often outweigh these concerns. As research continues, DBS may become even more effective and accessible. For now, it's a beacon of hope for those struggling with debilitating neurological conditions, offering a chance at a better, more manageable life.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
