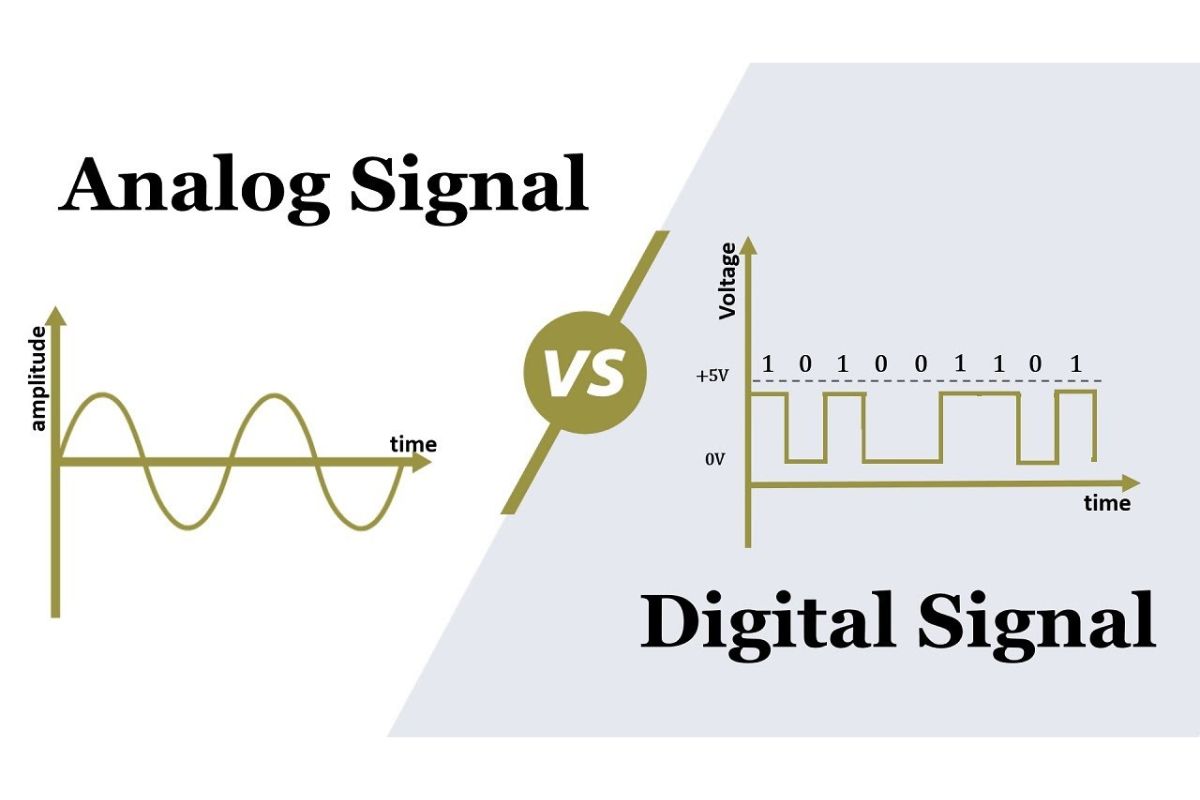
What are digital signals? Digital signals are a way of representing information using binary code, which consists of 0s and 1s. This method is used in computers, smartphones, and other electronic devices to process and transmit data efficiently. Unlike analog signals, which vary continuously, digital signals are discrete, making them less prone to noise and interference. This makes them ideal for modern communication systems, ensuring clearer and more reliable data transmission. Understanding digital signals is crucial for anyone interested in technology, as they form the backbone of most digital communication and processing systems today.
What Are Digital Signals?
Digital signals are a way to represent information using binary code, which consists of 0s and 1s. These signals are essential in modern technology, from computers to smartphones.
-
Digital signals use binary code: Binary code is a system of representing text or computer processor instructions using the binary number system's two binary digits, 0 and 1.
-
More resistant to noise: Unlike analog signals, digital signals are less affected by noise, making them more reliable for transmitting data over long distances.
-
Easier to encrypt: Digital signals can be encrypted more easily than analog signals, providing better security for data transmission.
-
Used in computers: Computers use digital signals to process and store information, making them fundamental to modern computing.
How Digital Signals Work
Understanding how digital signals work can help you appreciate their importance in technology. They convert analog signals into a digital format that can be processed by electronic devices.
-
Analog-to-digital conversion: This process involves converting continuous analog signals into discrete digital signals.
-
Sampling rate: The sampling rate is the number of samples taken per second from a continuous signal to make a digital signal. Higher rates result in better quality.
-
Quantization: Quantization is the process of mapping input values from a large set to output values in a smaller set, crucial for digital signal processing.
-
Pulse code modulation (PCM): PCM is a method used to digitally represent analog signals, commonly used in digital telephony and audio.
Applications of Digital Signals
Digital signals have a wide range of applications in various fields. From communication to entertainment, they play a crucial role in our daily lives.
-
Telecommunications: Digital signals are used in telecommunication systems to transmit voice and data over long distances.
-
Digital audio: Music and sound are often stored and transmitted as digital signals, providing high-quality audio experiences.
-
Digital video: Movies and videos are encoded as digital signals, allowing for high-definition viewing and easy editing.
-
Medical imaging: Techniques like MRI and CT scans use digital signals to create detailed images of the human body.
Advantages of Digital Signals
Digital signals offer several advantages over analog signals, making them the preferred choice in many applications.
-
Higher quality: Digital signals can be processed to remove noise and distortion, resulting in higher quality output.
-
Easier to store: Digital data can be stored more efficiently and compactly than analog data.
-
Better compression: Digital signals can be compressed to save space, making it easier to store and transmit large amounts of data.
-
Scalability: Digital systems can be easily scaled up or down, making them versatile for different applications.
Challenges with Digital Signals
Despite their advantages, digital signals also come with some challenges. Understanding these can help in better managing and utilizing digital technology.
-
Sampling errors: If the sampling rate is too low, important information can be lost, leading to errors.
-
Quantization noise: This type of noise occurs during the quantization process and can affect the quality of the digital signal.
-
Bandwidth requirements: Digital signals often require more bandwidth than analog signals, which can be a limitation in some applications.
-
Power consumption: Digital devices can consume more power than their analog counterparts, which can be a concern for battery-operated devices.
Future of Digital Signals
The future of digital signals looks promising with advancements in technology. These signals will continue to evolve and improve, offering new possibilities.
-
5G technology: The rollout of 5G networks will enhance the speed and reliability of digital signal transmission.
-
Quantum computing: Quantum computers will use digital signals in new ways, potentially revolutionizing computing.
-
Artificial intelligence: AI systems rely on digital signals for processing vast amounts of data, leading to smarter and more efficient technologies.
-
Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices use digital signals to communicate, creating interconnected systems that can improve our daily lives.
Fun Facts About Digital Signals
Digital signals are not just about technology; they have some interesting and fun aspects too.
-
First digital computer: The ENIAC, built in the 1940s, was one of the first digital computers and used digital signals for calculations.
-
Digital vs. analog clocks: Digital clocks display time using numbers, while analog clocks use hands on a dial.
-
Digital pets: Remember Tamagotchis? These digital pets used simple digital signals to simulate life.
-
Video games: Early video games like Pong used digital signals to create simple graphics and gameplay.
Real-World Examples of Digital Signals
Digital signals are everywhere in our daily lives. Here are some real-world examples that you might encounter regularly.
-
Smartphones: Your smartphone uses digital signals for everything from making calls to browsing the internet.
-
Television: Modern TVs use digital signals to provide high-definition video and audio.
-
GPS systems: GPS devices use digital signals to provide accurate location information.
-
Digital cameras: These cameras convert light into digital signals to create images.
-
Streaming services: Platforms like Netflix and Spotify use digital signals to stream video and audio content to your devices.
The Final Word on Digital Signals
Digital signals shape our modern world. From the way we communicate to how we consume media, these signals are everywhere. They offer precision, efficiency, and reliability that analog signals just can't match. Understanding digital signals helps us appreciate the technology we often take for granted. Whether it's your smartphone, computer, or even your smart home devices, digital signals make it all possible.
Knowing the basics can also help you troubleshoot tech issues and make informed decisions about new gadgets. So next time you stream a movie or send a text, remember the digital magic behind it. Digital signals aren't just a tech term; they're the backbone of our connected lives. Keep exploring, stay curious, and you'll find there's always more to learn about this fascinating topic.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
