TCP/IP is the backbone of the internet, making it possible for computers to communicate with each other. But what exactly is TCP/IP? TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol, while IP stands for Internet Protocol. Together, they form a set of rules that dictate how data is sent and received over networks. TCP/IP ensures that data packets reach their destination accurately and in the correct order. Without it, our online experiences would be chaotic and unreliable. From web browsing to email, streaming videos to online gaming, TCP/IP plays a crucial role in our daily digital lives. Curious to learn more? Here are 28 fascinating facts about TCP/IP that will deepen your understanding of this essential technology.
What is TCP/IP?
TCP/IP stands for Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. It's the backbone of the internet, allowing computers to communicate with each other. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about TCP/IP.
-
TCP/IP Origins: Developed in the 1970s by DARPA, TCP/IP was designed to create a robust, fault-tolerant communication system.
-
First Use: The first successful TCP/IP transmission occurred on January 1, 1983, marking the birth of the modern internet.
-
Two Layers: TCP/IP consists of two main layers: TCP handles data transmission, while IP manages addressing and routing.
-
Packet Switching: TCP/IP uses packet switching, breaking data into small packets for efficient transmission.
-
Connection-Oriented: TCP is connection-oriented, meaning it establishes a connection before data transfer begins.
-
Error Checking: TCP includes error-checking mechanisms to ensure data integrity during transmission.
TCP/IP in Everyday Life
TCP/IP isn't just for techies; it impacts daily life in many ways. Here are some examples of how TCP/IP is used every day.
-
Web Browsing: Every time you visit a website, TCP/IP protocols are at work behind the scenes.
-
Email: Sending and receiving emails relies on TCP/IP to ensure messages reach their destination.
-
Streaming: Watching videos on platforms like YouTube or Netflix uses TCP/IP to deliver content smoothly.
-
Online Gaming: Multiplayer games use TCP/IP to connect players from around the world.
-
Social Media: Platforms like Facebook and Twitter use TCP/IP to connect users and share content.
-
Smart Devices: IoT devices, like smart thermostats and security cameras, use TCP/IP for communication.
Technical Aspects of TCP/IP
Understanding the technical side of TCP/IP can be complex, but it's fascinating. Here are some technical facts about TCP/IP.
-
IPv4 vs. IPv6: IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, allowing for more unique IP addresses.
-
Port Numbers: TCP/IP uses port numbers to identify specific processes or services on a device.
-
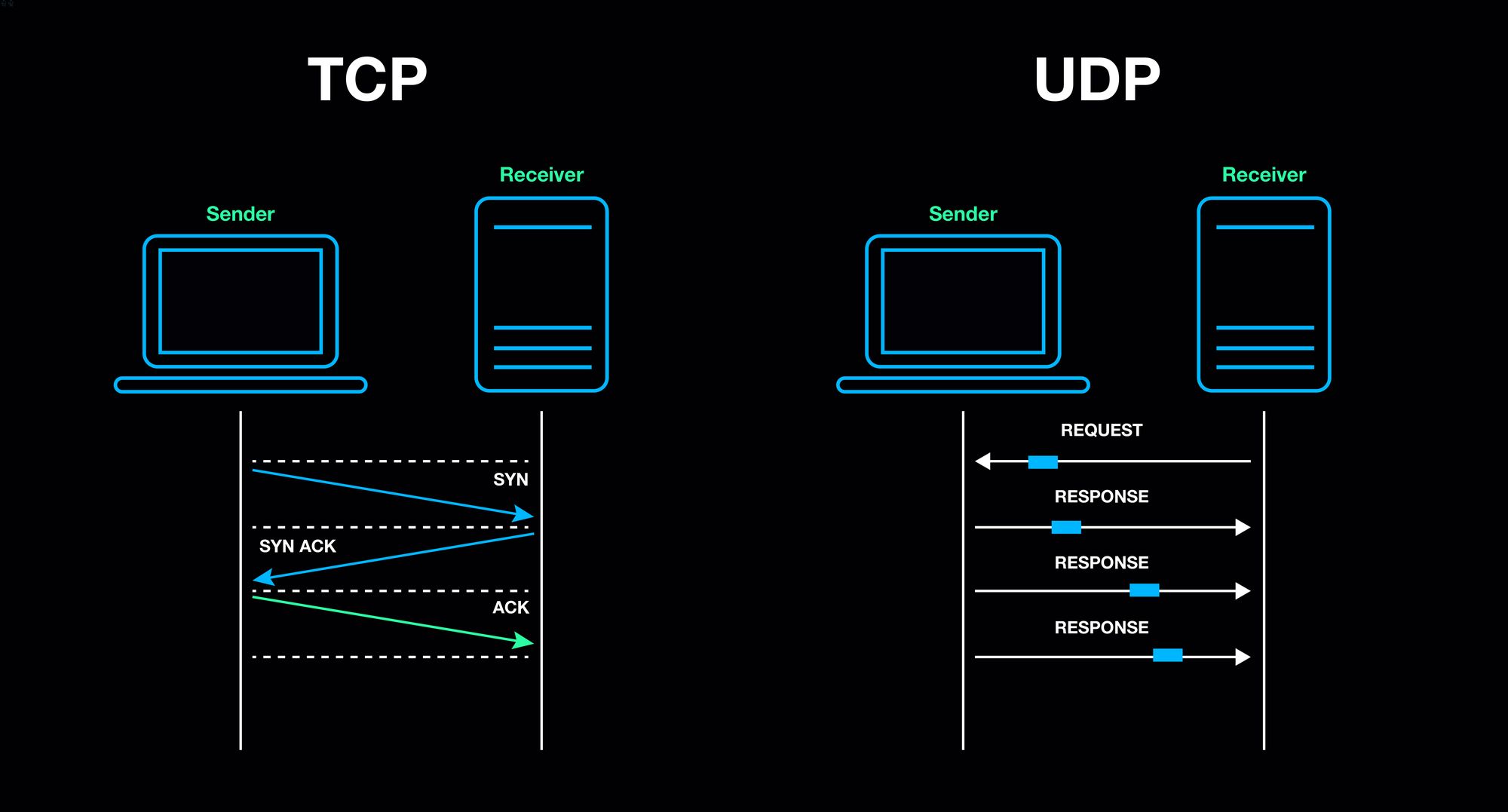
Three-Way Handshake: TCP establishes a connection using a three-way handshake process involving SYN, SYN-ACK, and ACK packets.
-
Flow Control: TCP uses flow control to manage data transmission speed and prevent network congestion.
-
Congestion Control: TCP includes congestion control mechanisms to avoid overwhelming the network.
-
Checksum: TCP uses a checksum to verify data integrity during transmission.
Security and TCP/IP
Security is a critical aspect of TCP/IP. Here are some facts about how TCP/IP handles security.
-
SSL/TLS: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols encrypt data transmitted over TCP/IP.
-
Firewalls: Firewalls use TCP/IP to filter and block unauthorized access to networks.
-
VPNs: Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) use TCP/IP to create secure, encrypted connections over the internet.
-
IPSec: Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) provides end-to-end security for IP communications.
-
DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks exploit TCP/IP vulnerabilities to overwhelm networks.
TCP/IP in Networking
TCP/IP is the foundation of modern networking. Here are some networking-related facts about TCP/IP.
-
Routers: Routers use TCP/IP to direct data packets between networks.
-
Switches: Network switches use TCP/IP to manage data traffic within a local network.
-
Subnetting: TCP/IP supports subnetting, dividing a network into smaller, more manageable segments.
-
DNS: The Domain Name System (DNS) translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses using TCP/IP.
-
NAT: Network Address Translation (NAT) allows multiple devices on a local network to share a single public IP address using TCP/IP.
Final Thoughts on TCP/IP
TCP/IP is the backbone of the internet. It ensures data gets from point A to point B reliably. Without it, our online world would be chaotic. This protocol suite, developed in the 1970s, has stood the test of time. It’s flexible, scalable, and robust. From email to streaming, TCP/IP makes it all possible. Understanding its basics helps us appreciate the technology we often take for granted. So next time you send a message or watch a video, remember TCP/IP is working behind the scenes. It’s a testament to human ingenuity and the power of collaboration. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just curious, knowing a bit about TCP/IP enriches your digital experience. Keep exploring, stay curious, and appreciate the tech that connects us all.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
