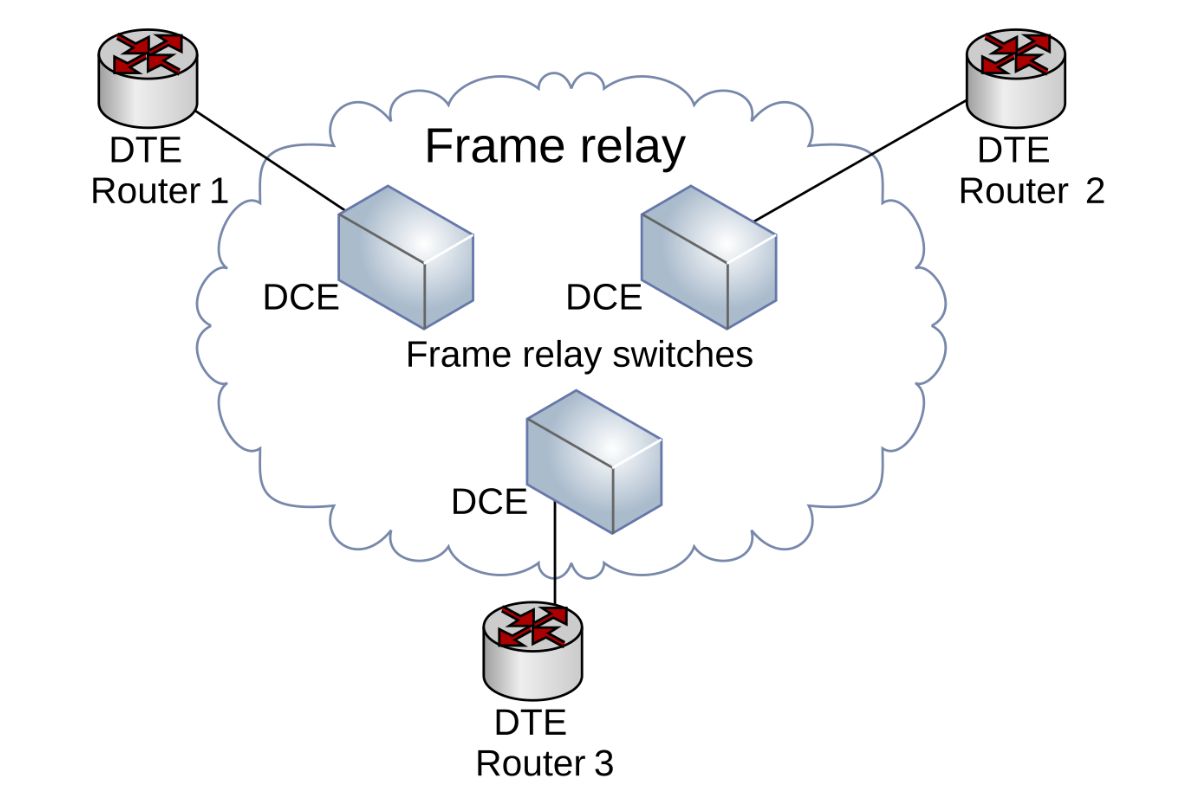
What is Frame Relay? Frame Relay is a high-performance WAN protocol that operates at the data link layer of the OSI model. It was designed for cost-efficient data transmission for intermittent traffic between local area networks (LANs) and between endpoints in a wide area network (WAN). Why is Frame Relay important? It offers a streamlined method for data transfer, reducing the overhead compared to older technologies like X.25. This makes it faster and more efficient for businesses needing reliable communication channels. How does Frame Relay work? It uses a technique called packet switching, where data is broken into packets and sent through a shared network. Each packet can take a different path to the destination, ensuring efficient use of network resources. Is Frame Relay still used today? While newer technologies like MPLS and VPNs have largely replaced it, some legacy systems still rely on Frame Relay for specific applications.
What is Frame Relay?
Frame Relay is a high-performance WAN protocol that operates at the physical and data link layers of the OSI model. It was designed for cost-efficient data transmission for intermittent traffic between local area networks (LANs) and between endpoints in a wide area network (WAN).
-
Origin: Frame Relay was developed in the late 1980s and became popular in the 1990s as a faster, more efficient alternative to X.25.
-
Layers: It operates at the physical and data link layers of the OSI model, which are layers 1 and 2.
-
Efficiency: Frame Relay is known for its efficiency in handling bursty data traffic, making it ideal for applications like video conferencing and voice over IP.
How Does Frame Relay Work?
Understanding the mechanics of Frame Relay can help grasp its efficiency and reliability in data transmission.
-
Frames: Data is transmitted in variable-sized units called frames.
-
Virtual Circuits: It uses virtual circuits to create a logical path between endpoints.
-
Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs): These are pre-established paths that remain active even when not in use.
-
Switched Virtual Circuits (SVCs): These are temporary paths established and terminated as needed.
Advantages of Frame Relay
Frame Relay offers several benefits that have made it a popular choice for WAN communications.
-
Cost-Effective: It is generally cheaper than leased lines because it uses shared network resources.
-
Scalability: Easily scalable to accommodate growing network demands.
-
Flexibility: Supports multiple types of traffic, including data, voice, and video.
-
Speed: Offers higher speeds compared to older technologies like X.25.
Frame Relay vs. Other Technologies
Comparing Frame Relay to other technologies can highlight its unique advantages and limitations.
-
X.25: Unlike X.25, Frame Relay does not perform error correction, making it faster but less reliable.
-
ATM: Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is faster but more complex and expensive.
-
MPLS: Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) offers better performance and flexibility but at a higher cost.
Technical Specifications
Frame Relay has specific technical characteristics that define its operation and performance.
-
Data Rates: Supports data rates from 56 Kbps to 45 Mbps.
-
Frame Size: Frames can be up to 1,600 bytes in size.
-
Congestion Control: Uses mechanisms like Forward Explicit Congestion Notification (FECN) and Backward Explicit Congestion Notification (BECN).
-
Error Handling: Relies on higher-layer protocols for error correction.
Applications of Frame Relay
Frame Relay is used in various applications due to its efficiency and reliability.
-
Corporate Networks: Commonly used to connect different branches of a company.
-
Internet Access: Provides a reliable method for connecting to the internet.
-
VoIP: Supports Voice over IP applications due to its low latency.
-
Video Conferencing: Ideal for video conferencing because of its ability to handle bursty traffic.
Frame Relay in Modern Networks
Although newer technologies have emerged, Frame Relay still has a place in modern networks.
-
Legacy Systems: Many legacy systems still rely on Frame Relay for connectivity.
-
Backup Solutions: Often used as a backup for more modern WAN technologies.
-
Cost Considerations: Remains a cost-effective solution for certain applications.
Challenges and Limitations
Frame Relay is not without its challenges and limitations.
-
Error Correction: Lack of built-in error correction can be a drawback.
-
Obsolescence: Newer technologies like MPLS are gradually replacing Frame Relay.
-
Limited Features: Offers fewer features compared to modern WAN technologies.
The Final Word on Frame Relay
Frame Relay, a once-popular WAN technology, has played a significant role in the evolution of networking. It provided a cost-effective way to connect multiple locations, offering reliable and efficient data transmission. However, with the advent of newer technologies like MPLS and SD-WAN, Frame Relay has seen a decline in usage.
Understanding its history and functionality helps appreciate how far we've come in the world of networking. While it may not be the go-to choice today, Frame Relay's impact on network design and communication can't be ignored. It laid the groundwork for more advanced solutions, proving that even outdated technologies have their place in the tech timeline.
So, whether you're a tech enthusiast or just curious about networking, knowing about Frame Relay adds another layer to your understanding of how our digital world connects.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
