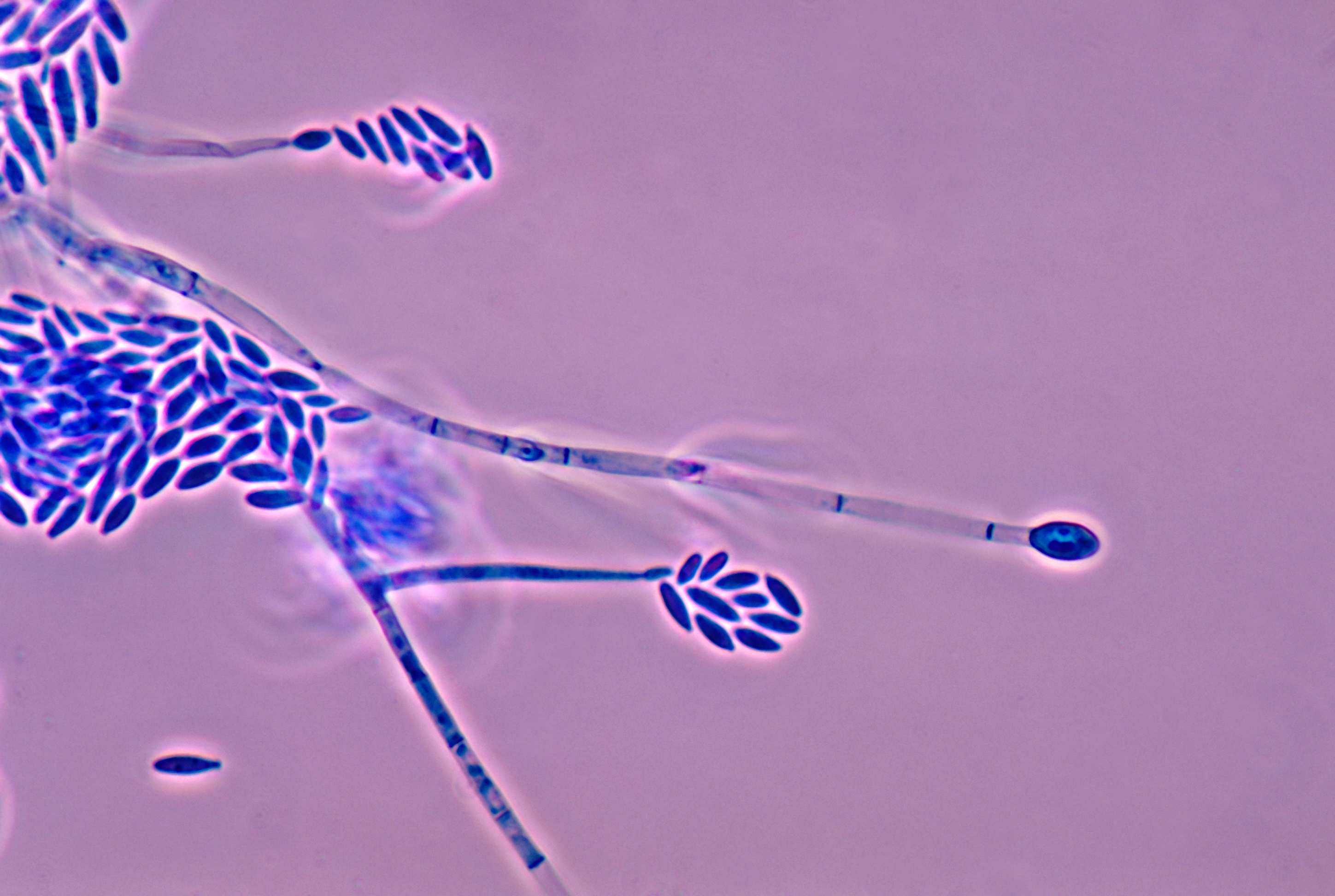
Fusarium is a type of fungus that can be both fascinating and frightening. Found in soil and plants, it plays a significant role in agriculture and medicine. But what exactly makes Fusarium so interesting? Fusarium species are known for causing diseases in crops like wheat, corn, and bananas, leading to significant economic losses. On the flip side, some species produce valuable antibiotics. Understanding Fusarium can help farmers protect their crops and scientists develop new medicines. Whether you're a student, farmer, or just curious, these 40 facts about Fusarium will give you a deeper insight into this complex fungus.
What is Fusarium?
Fusarium is a genus of fungi widely known for its impact on agriculture, human health, and the environment. These fungi can be found in soil and plants, often causing diseases in crops and humans. Here are some fascinating facts about Fusarium.
-
Fusarium species are filamentous fungi, meaning they have thread-like structures called hyphae.
-
These fungi are commonly found in soil and plant debris, where they play a role in decomposing organic matter.
-
Fusarium species can infect a wide range of plants, including cereals, legumes, and vegetables.
-
Fusarium oxysporum is one of the most notorious species, causing wilt diseases in over 100 plant species.
-
Fusarium head blight, caused by Fusarium graminearum, is a significant disease in wheat and barley, leading to reduced yield and grain quality.
Fusarium and Agriculture
Fusarium fungi have a substantial impact on agriculture, affecting crop yields and food safety. Understanding their role in agriculture can help mitigate their negative effects.
-
Fusarium species produce mycotoxins, which are toxic compounds that can contaminate food and feed.
-
Deoxynivalenol (DON), also known as vomitoxin, is a mycotoxin produced by Fusarium graminearum that can cause vomiting and feed refusal in animals.
-
Fusarium verticillioides produces fumonisins, mycotoxins that can cause diseases in livestock and humans.
-
Crop rotation and resistant plant varieties are common strategies to manage Fusarium infections in agriculture.
-
Biological control methods, such as using beneficial microbes, are being explored to combat Fusarium diseases.
Fusarium and Human Health
Fusarium fungi can also affect human health, causing infections and producing harmful mycotoxins. Here are some key facts about Fusarium's impact on health.
-
Fusarium species can cause infections in humans, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
-
Fusarium infections in humans are known as fusariosis, which can affect the skin, eyes, and respiratory system.
-
Contact lens wearers are at higher risk of developing Fusarium keratitis, an infection of the cornea.
-
Fusarium mycotoxins can contaminate food and pose health risks when ingested.
-
Chronic exposure to Fusarium mycotoxins has been linked to various health issues, including cancer and immune suppression.
Environmental Role of Fusarium
Fusarium fungi play a crucial role in the environment, contributing to nutrient cycling and soil health. Here are some interesting facts about their environmental role.
-
Fusarium species help decompose organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the soil.
-
These fungi can form symbiotic relationships with plants, aiding in nutrient uptake and growth.
-
Fusarium species can also act as pathogens, causing diseases in wild plants and affecting natural ecosystems.
-
Some Fusarium species are used in bioremediation to degrade environmental pollutants.
-
Fusarium fungi can influence soil structure and fertility through their interactions with other soil organisms.
Fusarium in Research and Biotechnology
Fusarium fungi are studied extensively in research and biotechnology for their unique properties and potential applications. Here are some notable facts about their role in science.
-
Fusarium species are used as model organisms in fungal biology research.
-
The genome of Fusarium graminearum has been sequenced, providing insights into its pathogenic mechanisms.
-
Fusarium fungi produce a wide range of secondary metabolites, some of which have pharmaceutical potential.
-
Enzymes from Fusarium species are used in industrial applications, such as producing biofuels and bioplastics.
-
Fusarium species are being explored for their potential in biocontrol, using their natural enemies to manage pests and diseases.
Fusarium and Climate Change
Climate change can influence the distribution and impact of Fusarium fungi, affecting agriculture and ecosystems. Here are some facts about Fusarium in the context of climate change.
-
Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns can alter the prevalence of Fusarium diseases in crops.
-
Climate change can affect the production and distribution of Fusarium mycotoxins, posing new challenges for food safety.
-
Fusarium species may adapt to changing environmental conditions, potentially increasing their pathogenicity.
-
Monitoring and predicting Fusarium outbreaks are essential for developing effective management strategies in a changing climate.
-
Research is ongoing to understand how climate change will impact Fusarium-host interactions and disease dynamics.
Fusarium in History and Culture
Fusarium fungi have been recognized and studied for centuries, with their impact on agriculture and health documented throughout history. Here are some historical and cultural facts about Fusarium.
-
The first recorded outbreak of Fusarium head blight occurred in Japan in the 1890s, causing significant crop losses.
-
Fusarium species were identified as the cause of Panama disease, which devastated banana plantations in the early 20th century.
-
The discovery of Fusarium mycotoxins in the mid-20th century led to increased awareness of food safety issues.
-
Fusarium fungi have been used in traditional medicine for their antimicrobial properties.
-
Fusarium species are sometimes depicted in art and literature, symbolizing decay and disease.
Fusarium and Food Safety
Ensuring food safety is a critical concern when dealing with Fusarium fungi and their mycotoxins. Here are some important facts about Fusarium and food safety.
-
Fusarium mycotoxins can contaminate a wide range of food products, including cereals, nuts, and fruits.
-
Mycotoxin contamination can occur at any stage of the food production process, from field to storage.
-
Regular monitoring and testing of food products are essential to detect and manage Fusarium mycotoxins.
-
Proper storage conditions, such as low humidity and temperature, can help prevent Fusarium growth and mycotoxin production.
-
International regulations and guidelines are in place to limit mycotoxin levels in food and feed, ensuring consumer safety.
Final Thoughts on Fusarium
Fusarium is a fascinating fungus with a significant impact on agriculture and health. From causing diseases in plants to producing mycotoxins harmful to humans and animals, its influence is widespread. Understanding its behavior helps in developing better strategies to manage its effects. Farmers, researchers, and health professionals all benefit from this knowledge, leading to healthier crops and safer food supplies.
While it poses challenges, ongoing research offers hope for effective control methods. Awareness and education about Fusarium are crucial for mitigating its negative impacts. By staying informed and proactive, we can better protect our crops and health from this persistent fungus.
Thanks for sticking with us through these 40 facts. We hope you found them as intriguing as we did. Stay curious and keep learning!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
