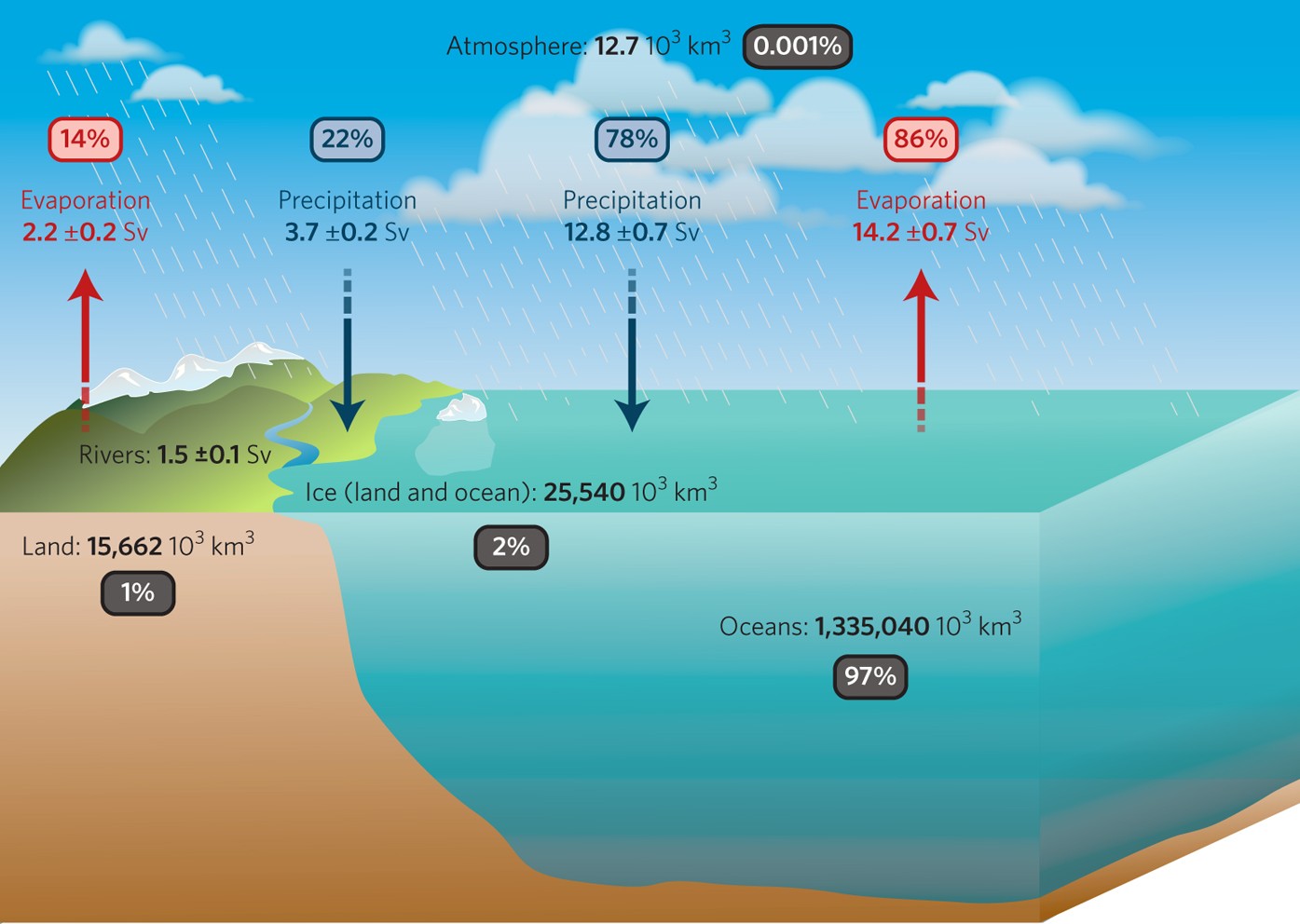
Salinity is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in water. Why is salinity important? Salinity affects water quality, marine life, and even climate patterns. High salinity can make water undrinkable and harm crops. Oceans have high salinity due to the accumulation of salts from rivers and underwater volcanic activity. Freshwater sources like rivers and lakes have low salinity. Changes in salinity can indicate environmental shifts, such as melting ice caps or pollution. Understanding salinity helps in managing water resources and protecting ecosystems. Dive into these 31 intriguing facts about salinity to learn more about its impact on our world.
What is Salinity?
Salinity measures the amount of dissolved salts in water. It affects ecosystems, agriculture, and even human health. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about salinity.
-
Salinity is usually measured in parts per thousand (ppt). This means for every thousand parts of water, there are a certain number of parts of dissolved salts.
-
The average salinity of ocean water is about 35 ppt. This means 35 grams of salt per liter of seawater.
-
Freshwater has a salinity of less than 0.5 ppt. Rivers, lakes, and streams fall into this category.
Salinity in Oceans
Oceans cover over 70% of Earth's surface, and their salinity plays a crucial role in global climate and marine life.
-
The Dead Sea has a salinity of around 300 ppt. This makes it one of the saltiest bodies of water on Earth.
-
The Red Sea is one of the saltiest seas, with a salinity of about 40 ppt. High evaporation rates and low freshwater inflow contribute to this.
-
Polar oceans have lower salinity. Melting ice dilutes the seawater, reducing its salt content.
Salinity and Marine Life
Marine organisms have adapted to various salinity levels, but drastic changes can be harmful.
-
Coral reefs thrive in waters with salinity between 32 and 42 ppt. Any significant deviation can stress or even kill corals.
-
Some fish can live in both freshwater and saltwater. Species like salmon and eels migrate between the two during their life cycles.
-
Brine shrimp are found in highly saline environments. They can survive in salinities up to 300 ppt.
Salinity and Climate
Salinity influences ocean circulation, which in turn affects global climate patterns.
-
High salinity water is denser and sinks. This process drives deep ocean currents.
-
Low salinity water is less dense and stays on the surface. This can lead to stratification in the ocean.
-
Changes in salinity can affect the global conveyor belt. This is a system of ocean currents that distribute heat around the planet.
Salinity and Agriculture
Salinity isn't just an oceanic phenomenon; it also impacts agriculture and soil health.
-
Soil salinity can reduce crop yields. High salt levels in soil can inhibit plant growth.
-
Irrigation can increase soil salinity. Water used for irrigation often contains dissolved salts, which accumulate in the soil over time.
-
Salt-tolerant crops are being developed. Scientists are working on genetically modifying crops to withstand higher salinity levels.
Salinity and Human Health
Salinity also has implications for human health and daily life.
-
Drinking water should have a salinity of less than 1 ppt. Higher levels can make water taste salty and be harmful to health.
-
Desalination plants remove salt from seawater. These plants provide fresh water in arid regions.
-
High salinity can cause dehydration. Consuming too much salt can lead to an imbalance in body fluids.
Salinity in Different Regions
Different regions around the world experience varying levels of salinity due to natural and human factors.
-
The Mediterranean Sea has a higher salinity than the Atlantic Ocean. This is due to high evaporation rates and limited freshwater inflow.
-
Estuaries have fluctuating salinity levels. These areas where rivers meet the sea experience changes in salinity with tides and seasons.
-
Inland seas like the Caspian Sea have varying salinity. Factors like river inflow and evaporation rates influence these levels.
Salinity and Technology
Advancements in technology help us understand and manage salinity better.
-
Satellites measure ocean salinity from space. These measurements help scientists monitor changes in global salinity patterns.
-
Salinity sensors are used in oceanographic research. These devices provide accurate, real-time data on salt levels in water.
-
Soil salinity sensors help farmers. These tools allow for better management of irrigation and soil health.
Interesting Salinity Facts
Here are some more intriguing tidbits about salinity that might surprise you.
-
The Great Salt Lake in Utah has a salinity of up to 270 ppt. This makes it one of the saltiest lakes in the world.
-
Salinity affects the boiling and freezing points of water. Saltwater boils at a higher temperature and freezes at a lower temperature than freshwater.
-
Salinity can influence sound speed in water. Higher salinity increases the speed at which sound travels through water.
Salinity in Everyday Life
Salinity isn't just a scientific concept; it affects our daily lives in various ways.
-
Table salt is harvested from seawater. Salt pans and evaporation ponds are used to extract salt from seawater.
-
Salinity is important in cooking. Salt enhances flavor and acts as a preservative in food.
-
Aquariums must maintain proper salinity levels. Marine aquariums require careful monitoring to keep fish and other organisms healthy.
-
Salinity affects swimming. Higher salinity increases water density, making it easier to float.
Salinity's Impact on Our World
Salinity shapes our planet in ways we often overlook. It affects ocean currents, marine life, and even climate patterns. High salinity levels can make water undrinkable, impacting communities and ecosystems. On the flip side, salt is essential for life, playing a crucial role in bodily functions and food preservation.
Understanding salinity helps us manage resources better, from agriculture to freshwater supplies. It’s fascinating how something as simple as salt can have such a profound impact. Whether it’s the salt in our oceans or the salt on our tables, its presence is felt everywhere.
Next time you sprinkle salt on your food, remember its journey and significance. Salinity isn’t just a scientific term; it’s a vital part of our world. Keep exploring and appreciating the wonders of salinity in everyday life.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
