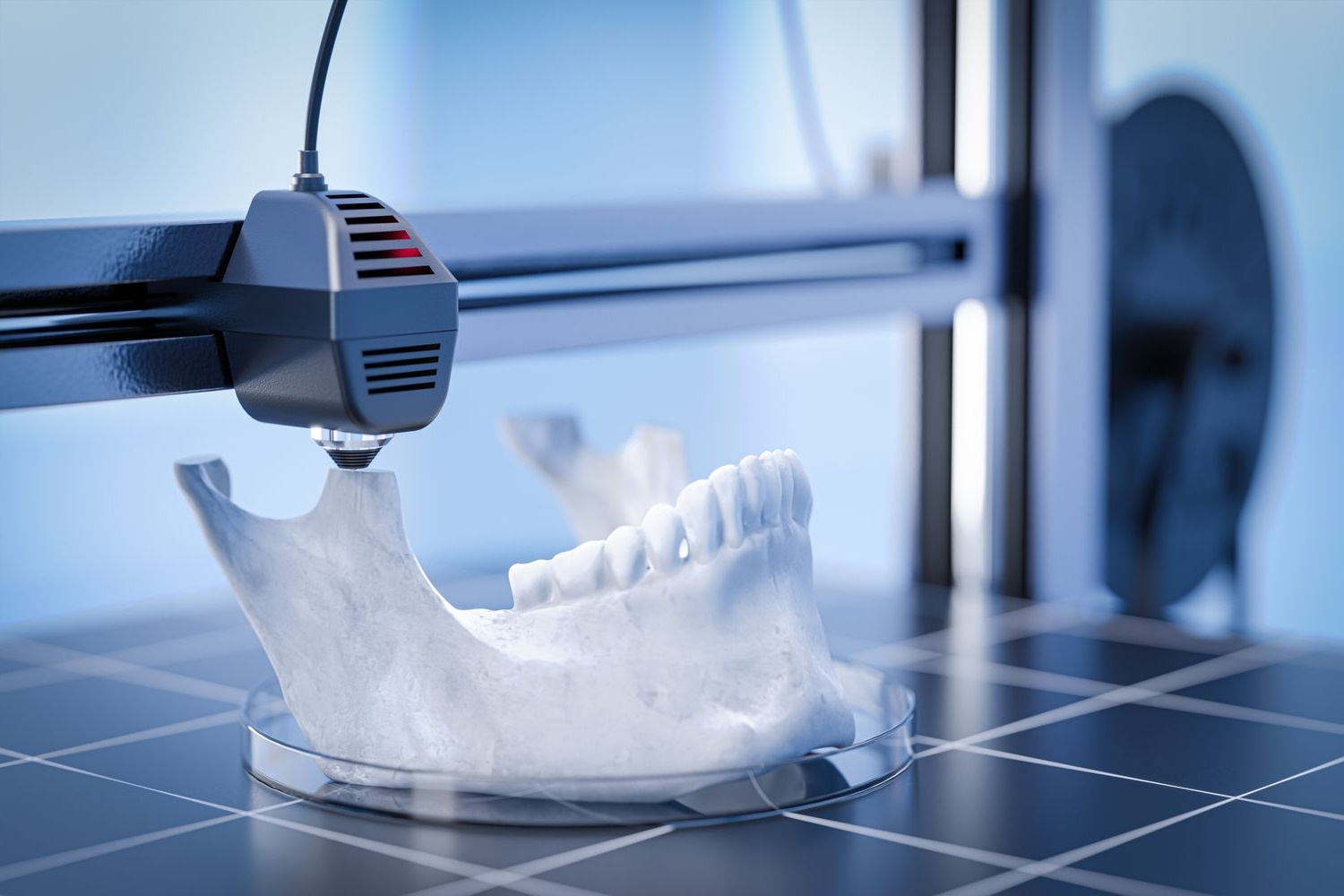
Bioprinting is a groundbreaking technology that merges biology and 3D printing to create living tissues and organs. But what exactly is bioprinting? In simple terms, it involves using bio-inks made from living cells to print structures that mimic natural tissues. This innovation holds promise for medical advancements, including organ transplants, drug testing, and regenerative medicine. Imagine a future where organ shortages are a thing of the past, and custom-made tissues can be printed on demand. From heart patches to skin grafts, bioprinting is pushing the boundaries of what's possible in healthcare. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 36 fascinating facts about this cutting-edge technology.
What is Bioprinting?
Bioprinting is a fascinating technology that combines biology and 3D printing to create living tissues and organs. It holds immense potential for medical advancements, from organ transplants to drug testing.
-
Bioprinting uses bio-ink: Bio-ink is a material made from living cells that can be printed layer by layer to form tissues.
-
First bioprinter was developed in 2003: Scientists at Clemson University created the first bioprinter, which laid the groundwork for future innovations.
-
Organovo is a pioneer: This company was among the first to commercialize bioprinting technology, focusing on creating human tissues for medical research.
-
Stem cells are often used: Stem cells can differentiate into various cell types, making them ideal for bioprinting complex tissues.
-
Bioprinting can create skin: This technology has been used to print skin grafts for burn victims, offering a quicker and more effective healing process.
How Does Bioprinting Work?
Understanding the mechanics behind bioprinting can help appreciate its complexity and potential.
-
Layer-by-layer approach: Similar to traditional 3D printing, bioprinting builds tissues layer by layer, allowing for precise control over the structure.
-
CAD software designs the tissue: Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software is used to create a digital model of the tissue or organ to be printed.
-
Hydrogels support the structure: Hydrogels provide a scaffold that supports the cells as they grow and form tissues.
-
UV light can solidify bio-ink: Some bioprinters use UV light to harden the bio-ink, helping to maintain the shape of the printed tissue.
-
Bioreactors aid growth: After printing, tissues are often placed in bioreactors that provide the necessary conditions for cell growth and maturation.
Applications of Bioprinting
Bioprinting isn't just a futuristic concept; it's already being used in various fields to solve real-world problems.
-
Drug testing: Bioprinted tissues can be used to test new drugs, reducing the need for animal testing and speeding up the development process.
-
Personalized medicine: Doctors can use bioprinting to create tissues that match a patient's unique genetic makeup, improving treatment outcomes.
-
Organ transplants: While still in the experimental stage, bioprinting holds the promise of creating fully functional organs for transplantation.
-
Cancer research: Scientists can print tumor tissues to study cancer progression and test new treatments.
-
Cosmetic testing: Bioprinted skin can be used to test cosmetics, offering a cruelty-free alternative to animal testing.
Challenges in Bioprinting
Despite its potential, bioprinting faces several hurdles that need to be overcome.
-
Cell viability: Ensuring that cells remain alive and functional during and after printing is a significant challenge.
-
Complexity of organs: Organs like the heart and liver are incredibly complex, making them difficult to replicate accurately.
-
Ethical concerns: The idea of printing human tissues and organs raises ethical questions that society must address.
-
Regulatory hurdles: Bioprinted tissues and organs must meet stringent regulatory standards before they can be used in medical treatments.
-
Cost: The technology is still expensive, limiting its accessibility for widespread use.
Future of Bioprinting
The future of bioprinting looks promising, with ongoing research and technological advancements paving the way for new possibilities.
-
Multi-material printing: Future bioprinters may be able to use multiple materials simultaneously, creating more complex tissues.
-
Integration with AI: Artificial intelligence could optimize the bioprinting process, improving accuracy and efficiency.
-
On-demand printing: Hospitals might one day have bioprinters that can create tissues and organs on demand, reducing wait times for transplants.
-
Space exploration: NASA is exploring bioprinting for creating tissues and organs in space, which could be crucial for long-term space missions.
-
Educational tools: Bioprinted tissues can be used as educational tools for medical students, providing a hands-on learning experience.
Interesting Facts About Bioprinting
Here are some intriguing tidbits that highlight the unique aspects of bioprinting.
-
First bioprinted blood vessels: In 2010, researchers successfully printed blood vessels, a crucial step toward creating functional organs.
-
Bioprinting in veterinary medicine: This technology is also being used to create tissues for animals, helping to treat injuries and diseases.
-
Bioprinted ears: Scientists have successfully printed human ears, which could be used for reconstructive surgery.
-
3D bioprinted corneas: Researchers have printed corneas that could potentially restore vision for millions of people.
-
Bioprinted meat: Companies are exploring bioprinting to create lab-grown meat, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional livestock farming.
Companies Leading the Way
Several companies are at the forefront of bioprinting, pushing the boundaries of what's possible.
-
Cellink: This company specializes in bioprinters and bio-inks, providing tools for researchers worldwide.
-
Allevi: Known for its versatile bioprinters, Allevi aims to make bioprinting accessible to more researchers and institutions.
-
Aspect Biosystems: Focuses on creating 3D bioprinted tissues for drug development and disease research.
-
TissueLabs: This company offers bioprinting solutions for creating complex tissues, including heart and liver models.
-
Cyfuse Biomedical: Uses a unique approach called the "Kenzan method" to create scaffold-free 3D tissues.
-
RegenHU: Provides bioprinting platforms that integrate with other technologies, enhancing the capabilities of researchers.
The Future of Bioprinting
Bioprinting is changing the game in medicine and research. From creating custom tissues to potentially printing entire organs, the possibilities seem endless. Scientists are working hard to overcome challenges like vascularization and immune response. Once these hurdles are cleared, bioprinting could revolutionize transplants and personalized medicine.
This tech isn't just for humans. Veterinary medicine could see benefits too, with custom implants and treatments for animals. The environmental impact is also promising, as lab-grown tissues could reduce the need for animal testing.
While still in its early stages, bioprinting holds incredible promise. It's a field worth watching as it develops. The future might bring solutions we can't even imagine yet. Keep an eye on this exciting technology; it could change lives in ways we never thought possible.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
