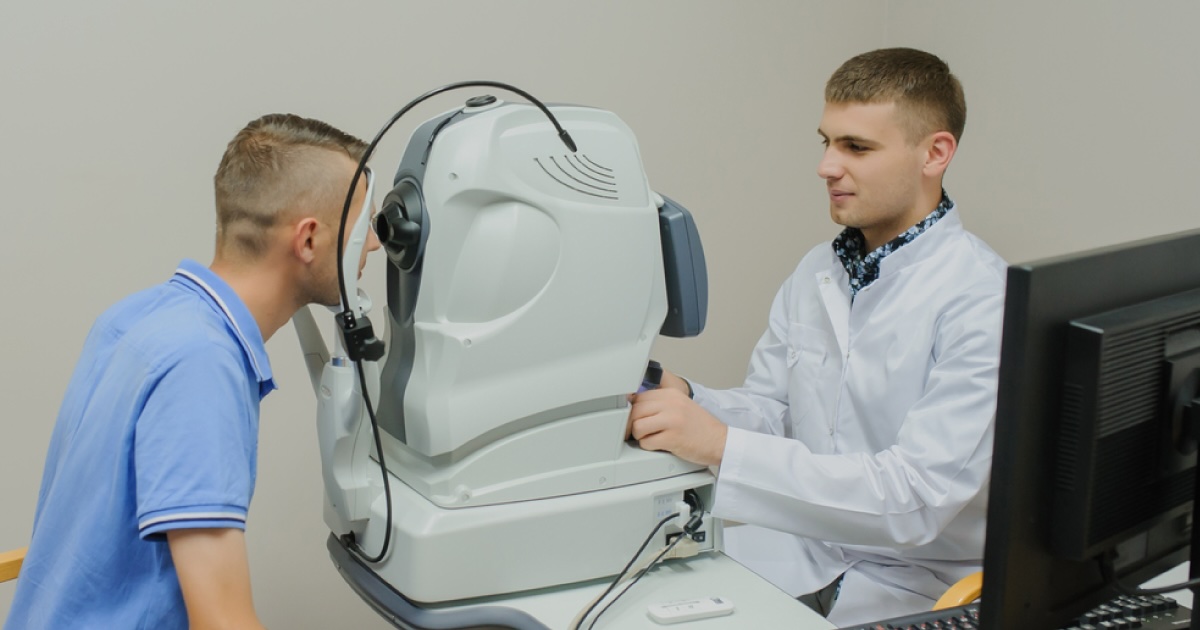
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of your retina. But what exactly makes OCT so special? This technology allows doctors to see each of the retina's distinctive layers, helping with early detection and treatment of eye conditions like glaucoma and macular degeneration. Why should you care about OCT? Because it can catch eye diseases before symptoms appear, potentially saving your vision. How does it work? By using light waves, OCT creates detailed images that are much clearer than traditional imaging methods. Want to know more? Keep reading to uncover 31 fascinating facts about this groundbreaking technology.
What is Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)?
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging technique used to capture detailed images of the retina. It’s like an ultrasound, but instead of sound waves, OCT uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of your retina.
-
OCT uses light waves to create detailed images of the retina, allowing doctors to see each of the retina’s distinctive layers.
-
Non-invasive means no needles or incisions are required, making the procedure painless and quick.
-
Developed in the 1990s, OCT has revolutionized the field of ophthalmology by providing high-resolution images of the eye’s internal structures.
How Does OCT Work?
Understanding the mechanics behind OCT can help appreciate its significance in medical diagnostics.
-
Low-coherence interferometry is the principle behind OCT, where light waves are split into two beams: one directed at the tissue and the other at a reference mirror.
-
Interference patterns are created when the reflected light waves from the tissue and the mirror combine, forming detailed images.
-
High-resolution images are produced, often with a resolution of 1 to 15 micrometers, allowing for the visualization of minute structures within the eye.
Applications of OCT in Ophthalmology
OCT is primarily used in eye care, but its applications extend beyond just diagnosing eye conditions.
-
Diagnosing glaucoma: OCT helps in detecting changes in the optic nerve, crucial for early glaucoma diagnosis.
-
Monitoring macular degeneration: It tracks the progression of age-related macular degeneration by capturing detailed images of the macula.
-
Diabetic retinopathy: OCT identifies fluid or blood leakage in the retina, a common complication of diabetes.
-
Retinal detachment: It helps in detecting and assessing the severity of retinal detachment.
Beyond Ophthalmology: Other Uses of OCT
While OCT is best known for its use in eye care, it has applications in other medical fields as well.
-
Cardiology: OCT is used to visualize coronary arteries, helping in the assessment of plaque buildup and guiding stent placement.
-
Dermatology: It aids in examining skin layers, useful in diagnosing skin cancers and other skin conditions.
-
Oncology: OCT can help in the early detection of tumors by providing detailed images of tissue structures.
Advantages of OCT
OCT offers several benefits that make it a preferred choice for both patients and healthcare providers.
-
Non-invasive and painless: Patients experience no discomfort during the procedure.
-
Quick procedure: The entire process usually takes just a few minutes.
-
High-resolution images: Provides detailed images that are crucial for accurate diagnosis and monitoring.
-
No radiation exposure: Unlike X-rays or CT scans, OCT does not expose patients to harmful radiation.
Limitations of OCT
Despite its numerous advantages, OCT has some limitations that need to be considered.
-
Limited penetration depth: OCT cannot image very deep tissues, limiting its use in certain medical conditions.
-
Cost: The equipment is expensive, which can make the procedure costly for patients.
-
Operator dependency: The quality of the images can depend on the skill and experience of the operator.
Future of OCT
The future of OCT looks promising with ongoing research and technological advancements.
-
Swept-source OCT: A newer technology that provides even faster and higher-resolution images.
-
Functional OCT: Combines OCT with other imaging techniques to provide more comprehensive diagnostic information.
-
Portable OCT devices: Development of portable devices could make OCT more accessible, especially in remote areas.
-
Artificial intelligence: AI integration could enhance image analysis, making diagnosis faster and more accurate.
Interesting Facts About OCT
Here are some fun and lesser-known facts about OCT.
-
Inspired by radar technology: The concept of OCT was inspired by radar and sonar technologies used in military applications.
-
First clinical use: The first clinical use of OCT was in 1993 for imaging the retina.
-
Nobel Prize: The development of OCT was recognized with a Nobel Prize in Physics in 2014.
-
OCT in art conservation: OCT is used to examine and preserve artworks by providing detailed images of paint layers and underlying sketches.
-
Animal research: OCT is used in veterinary medicine to study the eyes of animals, including pets and wildlife.
-
Space exploration: NASA has considered using OCT to monitor astronauts' eye health during long space missions.
-
Educational tool: OCT images are used in medical education to teach students about eye anatomy and pathology.
The Future of Eye Care
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) has revolutionized eye care. This non-invasive imaging technique provides detailed cross-sectional images of the retina, helping doctors detect and monitor conditions like glaucoma, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy. By catching these issues early, OCT can prevent vision loss and improve patient outcomes.
OCT's precision and speed make it a valuable tool in both clinical and research settings. Its ability to provide real-time images allows for immediate diagnosis and treatment planning. As technology advances, OCT will likely become even more integral to eye care, offering even higher resolution images and new applications.
Understanding OCT's capabilities and benefits can help patients make informed decisions about their eye health. Staying informed about the latest advancements ensures that you receive the best possible care. So, next time you're at the eye doctor, don't hesitate to ask about OCT.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
