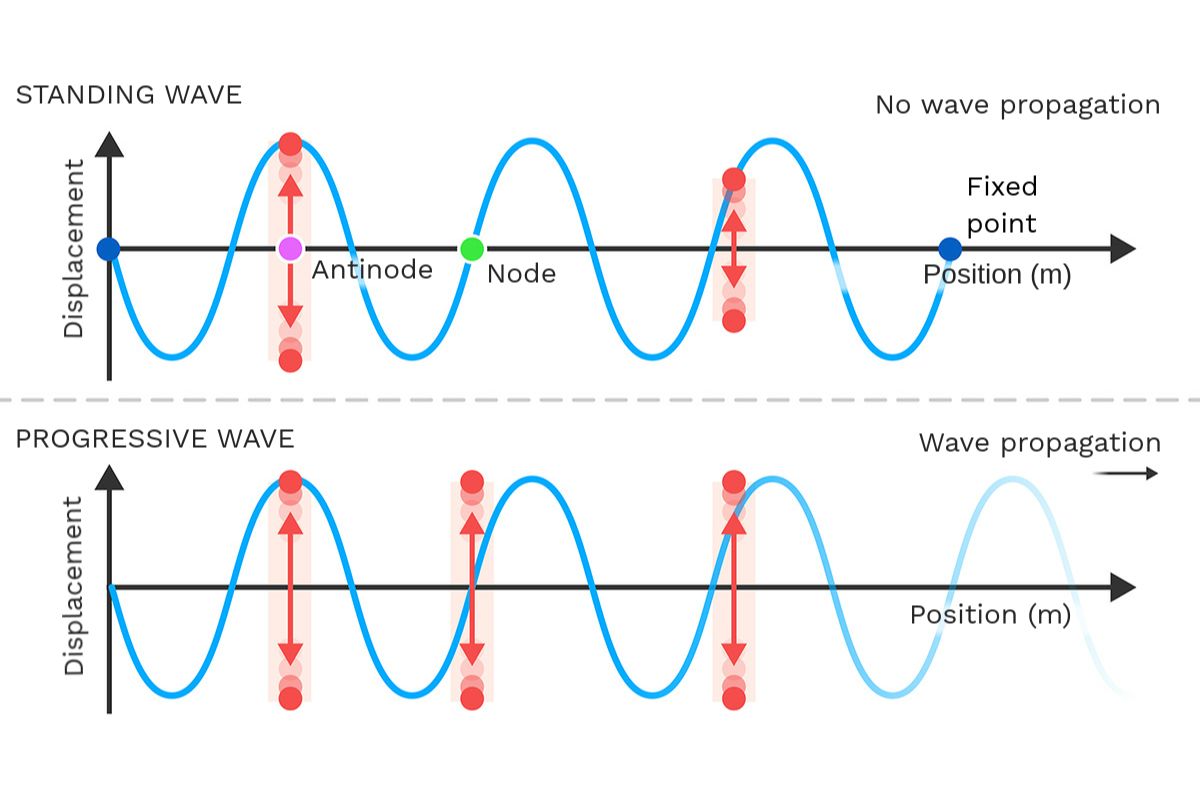
Standing waves are fascinating phenomena in physics, often seen in musical instruments, water waves, and even in the air. But what exactly are they? Standing waves occur when two waves of the same frequency and amplitude travel in opposite directions, creating points that appear to stand still. These points are called nodes, while the points of maximum displacement are called antinodes. Understanding standing waves can help explain how sound travels, how musical notes are produced, and even how certain structures vibrate. Ready to dive into some intriguing facts about standing waves? Let's get started!
What Are Standing Waves?
Standing waves, also known as stationary waves, are fascinating phenomena in physics. They occur when two waves of the same frequency and amplitude travel in opposite directions and interfere with each other. This interference creates points that appear to be standing still, hence the name.
-
Standing waves can be observed in musical instruments like guitars and violins, where the strings vibrate to produce sound.
-
They are also seen in microwave ovens, where microwaves bounce around and create hot and cold spots in the food.
-
The concept of standing waves is crucial in understanding resonance, which is the tendency of a system to oscillate at maximum amplitude at certain frequencies.
How Do Standing Waves Form?
Understanding the formation of standing waves involves a bit of wave mechanics. When two waves of the same frequency and amplitude travel in opposite directions, they interfere with each other.
-
Nodes are points in a standing wave where there is no movement. These points occur at regular intervals.
-
Antinodes are points where the wave has maximum amplitude. These points are located halfway between nodes.
-
The distance between two consecutive nodes or antinodes is half the wavelength of the wave.
Applications of Standing Waves
Standing waves are not just theoretical concepts; they have practical applications in various fields.
-
In telecommunications, standing waves are used in the design of antennas to ensure efficient transmission and reception of signals.
-
In musical instruments, the length of the string or air column determines the pitch of the note produced, which is a direct application of standing wave principles.
-
In medical imaging, standing waves are used in techniques like ultrasound to create detailed images of the inside of the body.
Interesting Facts About Standing Waves
Standing waves have some intriguing properties and behaviors that make them a subject of study in various scientific fields.
-
The speed of the wave does not affect the formation of standing waves; only the frequency and amplitude matter.
-
Standing waves can occur in any medium, including air, water, and solid materials.
-
The phenomenon of standing waves can be used to measure the speed of sound in different materials.
Standing Waves in Nature
Nature provides several examples of standing waves, often in ways that are both beautiful and scientifically significant.
-
Ocean waves can form standing waves when they reflect off a barrier, creating patterns that appear to stand still.
-
Earthquakes can generate standing waves in the Earth's crust, leading to significant ground movement in certain areas.
-
In the atmosphere, standing waves can form in the jet stream, affecting weather patterns and flight paths.
Mathematical Representation of Standing Waves
The mathematics behind standing waves involves wave equations and boundary conditions, which can be quite complex but are essential for understanding the phenomenon.
-
The general equation for a standing wave is a combination of two traveling wave equations.
-
Boundary conditions, such as fixed or free ends, determine the specific form of the standing wave.
-
The frequency of the standing wave is determined by the length of the medium and the speed of the wave.
Historical Context of Standing Waves
The study of standing waves has a rich history, with contributions from several notable scientists.
-
Daniel Bernoulli was one of the first to describe standing waves in the context of vibrating strings.
-
Joseph Fourier developed the Fourier series, which is used to analyze standing waves in complex systems.
-
Hermann von Helmholtz made significant contributions to the understanding of resonance and standing waves in acoustics.
Standing Waves in Technology
Modern technology leverages the principles of standing waves in various innovative ways.
-
In laser technology, standing waves are used to create stable laser beams with precise frequencies.
-
In radio broadcasting, standing waves help in tuning antennas for optimal signal transmission.
-
In fiber optics, standing waves are used to enhance signal strength and quality over long distances.
Fun Facts About Standing Waves
Standing waves can be fun to observe and experiment with, offering a hands-on way to learn about wave mechanics.
-
You can create standing waves at home using a jump rope or a slinky.
-
Musical instruments like the didgeridoo and the flute rely on standing waves to produce their unique sounds.
-
The Tacoma Narrows Bridge collapse in 1940 was partly due to standing wave resonance caused by wind.
Standing Waves in Quantum Mechanics
In the realm of quantum mechanics, standing waves play a crucial role in understanding the behavior of particles.
-
Electrons in atoms form standing wave patterns, which determine the electron's energy levels.
-
The concept of wave-particle duality in quantum mechanics is closely related to standing waves.
-
Quantum standing waves are used in the design of semiconductors and other electronic devices.
Standing Waves in Education
Standing waves are a staple topic in physics education, helping students grasp fundamental concepts of wave behavior.
-
Physics labs often include experiments with standing waves to teach students about wave interference and resonance.
-
Educational simulations and software can model standing waves, providing a visual and interactive learning experience.
-
Understanding standing waves is essential for students pursuing careers in engineering, physics, and related fields.
Standing Waves in Art and Culture
The influence of standing waves extends beyond science, finding a place in art and culture.
-
Visual artists have used the concept of standing waves to create mesmerizing kinetic sculptures.
-
Musicians and composers often explore the acoustic properties of standing waves to innovate new sounds and musical techniques.
The Final Wave
Standing waves are more than just a cool phenomenon. They play a crucial role in music, engineering, and even nature. From the strings of a guitar to the design of bridges, understanding these waves helps us create and innovate. They show up in everyday life, often unnoticed, yet they shape the world around us.
Knowing about standing waves can deepen your appreciation for many things you encounter daily. Next time you hear a musical note or see a ripple in a pond, you'll know there's some fascinating physics at play.
So, whether you're a student, a musician, or just someone curious about the world, standing waves offer a glimpse into the hidden patterns that govern our universe. Keep exploring, keep questioning, and you'll find there's always more to learn.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
