Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis are fundamental principles in chemistry and physics that explain how electric currents cause chemical reactions. Michael Faraday, a British scientist, formulated these laws in the 19th century. They describe the relationship between the amount of electric charge passed through an electrolyte and the amount of substance that undergoes oxidation or reduction at the electrodes. Faraday's First Law states that the mass of a substance altered at an electrode during electrolysis is proportional to the quantity of electricity used. Faraday's Second Law asserts that the mass of different substances altered by the same amount of electricity is proportional to their equivalent weights. These laws are crucial for understanding processes like electroplating, battery operation, and industrial electrolysis.
What Are Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis?
Faraday's laws of electrolysis are fundamental principles in chemistry and physics. They explain how electric current causes chemical reactions. These laws were formulated by Michael Faraday in the 19th century. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about these laws.
-
Faraday's first law states that the amount of substance produced at an electrode during electrolysis is proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte.
-
Faraday's second law states that the amounts of different substances produced by the same quantity of electricity are proportional to their equivalent weights.
The Man Behind the Laws: Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday was a pioneering scientist whose work laid the groundwork for modern electrochemistry. His contributions extend beyond electrolysis.
-
Faraday was born in 1791 in England and had little formal education.
-
He started his career as a bookbinder's apprentice, where he developed a love for reading and science.
-
Faraday discovered electromagnetic induction, which is the principle behind electric transformers and generators.
-
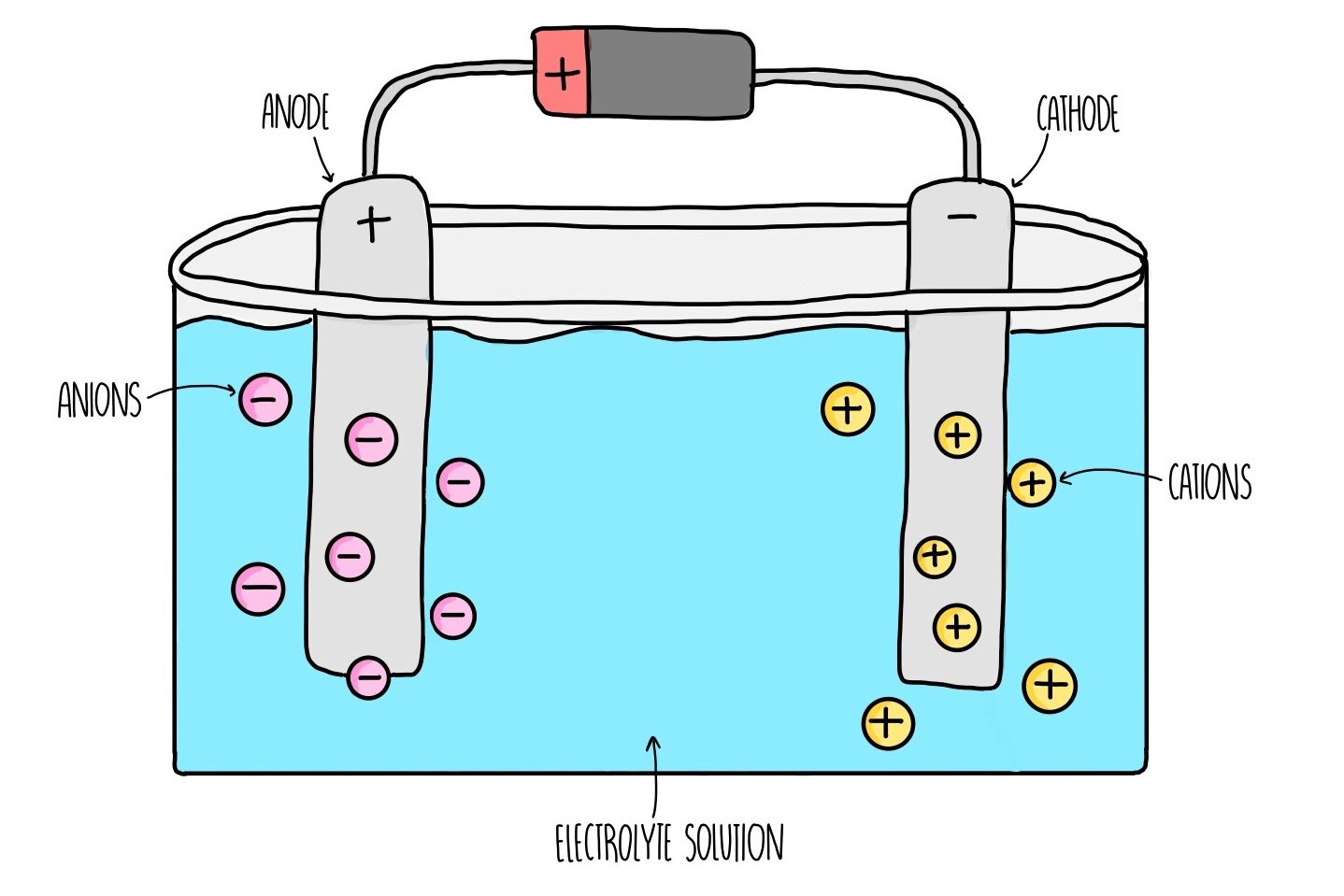
He also coined terms like "electrode," "cathode," "anode," and "ion."
The First Law of Electrolysis
The first law of electrolysis is crucial for understanding how electric current interacts with chemical compounds.
-
This law can be mathematically expressed as m = ZIt, where m is the mass of the substance, Z is the electrochemical equivalent, I is the current, and t is the time.
-
The electrochemical equivalent (Z) is a constant that depends on the substance being electrolyzed.
-
This law helps in calculating the amount of metal deposited during electroplating.
-
It is also used in industries for processes like electrorefining and electroforming.
The Second Law of Electrolysis
The second law of electrolysis provides insights into the relationship between different substances and their equivalent weights.
-
Equivalent weight is the mass of a substance that combines with or displaces 1.008 grams of hydrogen.
-
This law can be expressed as m1/m2 = E1/E2, where m1 and m2 are the masses of different substances, and E1 and E2 are their equivalent weights.
-
The second law is particularly useful in determining the purity of substances.
-
It also helps in understanding the stoichiometry of electrochemical reactions.
Applications of Faraday's Laws
Faraday's laws have numerous practical applications in various fields, from industrial processes to scientific research.
-
These laws are essential for the electroplating industry, where metals are coated onto surfaces.
-
They are used in the production of pure metals through electrorefining.
-
Faraday's laws help in the manufacturing of batteries and fuel cells.
-
They are also crucial in the field of analytical chemistry for quantitative analysis.
Real-World Examples
Understanding Faraday's laws can be easier with real-world examples that illustrate their principles.
-
In electroplating, a thin layer of gold can be deposited onto jewelry using these laws.
-
During the electrolysis of water, hydrogen and oxygen gases are produced in a ratio of 2:1.
-
In the Hall-Héroult process, aluminum is extracted from its ore using electrolysis.
-
Electrorefining of copper involves purifying impure copper using these principles.
Historical Impact
Faraday's laws have had a significant impact on the development of modern science and technology.
-
These laws paved the way for the development of modern electrochemistry.
-
They influenced the work of other scientists like James Clerk Maxwell and Albert Einstein.
-
Faraday's research contributed to the understanding of electromagnetism and its applications.
Fun Facts About Faraday's Laws
Let's look at some interesting tidbits that make Faraday's laws even more fascinating.
-
Faraday's work was initially met with skepticism but later gained widespread acceptance.
-
He conducted over 16,000 experiments during his lifetime.
-
Faraday's laws are still taught in schools and universities worldwide.
-
His discoveries have applications in fields as diverse as medicine and environmental science.
Faraday's Legacy
Michael Faraday's contributions extend far beyond his laws of electrolysis, leaving a lasting legacy in the scientific community.
-
Faraday was a devout Christian and believed his scientific work was a way to understand God's creation.
-
He declined a knighthood and other honors, preferring to remain "plain Mr. Faraday."
-
Faraday's work inspired future generations of scientists and engineers.
-
His discoveries laid the foundation for the development of electric motors and generators.
-
Faraday's name is immortalized in the unit of electrical capacitance, the farad.
The Impact of Faraday's Laws
Faraday's Laws of Electrolysis have shaped modern science and technology. These principles explain how electric currents cause chemical reactions, laying the groundwork for electroplating, battery technology, and even the production of aluminum. Michael Faraday's work in the 19th century still influences today's innovations.
Understanding these laws helps in various fields like chemistry, physics, and engineering. They provide a clear relationship between electric charge and chemical change, making complex processes easier to predict and control. This knowledge is crucial for developing new materials and improving energy storage solutions.
Faraday's contributions extend beyond just electrolysis. His research in electromagnetism and electrochemistry has had a lasting impact, proving that curiosity and rigorous experimentation can lead to groundbreaking discoveries. Faraday's legacy continues to inspire scientists and engineers, proving that the pursuit of knowledge can change the world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
