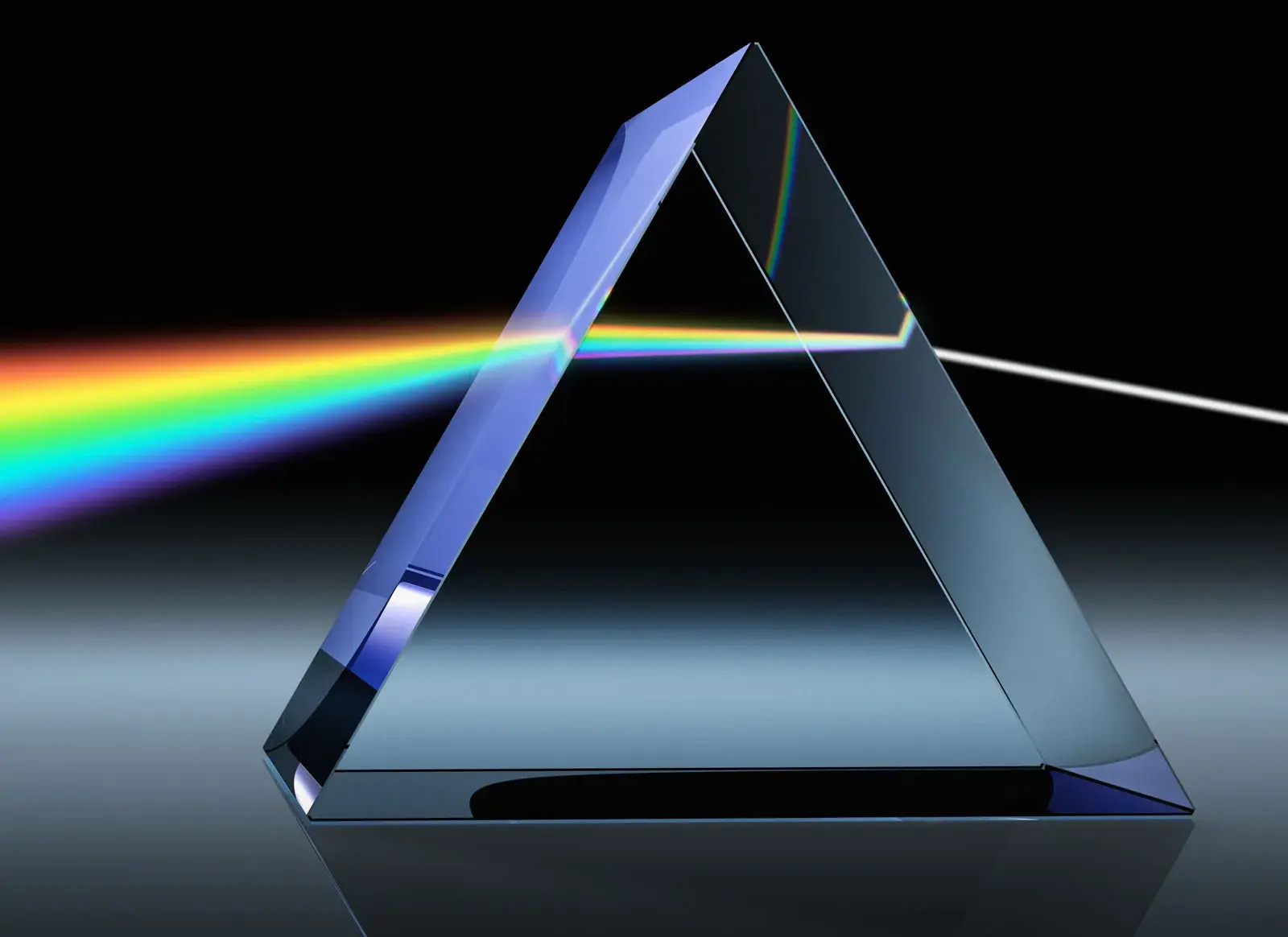
What is the dispersion of light? Dispersion of light happens when white light splits into its colorful components. This phenomenon occurs because different colors of light bend by different amounts when passing through a medium like a prism. Isaac Newton first demonstrated this with a glass prism, showing that white light is a mix of all visible colors. Each color has a unique wavelength, causing them to refract at different angles. This bending creates a spectrum, often seen in rainbows. Understanding dispersion helps in fields like optics, astronomy, and even art. Ready to dive into 32 amazing facts about this colorful phenomenon? Let's get started!
What is Dispersion of Light?
Dispersion of light is a fascinating phenomenon where white light splits into its constituent colors. This happens when light passes through a medium like a prism. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this colorful occurrence.
-
Isaac Newton's Discovery: Isaac Newton first demonstrated light dispersion in 1666 using a glass prism. He showed that white light is composed of different colors.
-
Seven Colors: The visible spectrum of light consists of seven colors: red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet. These colors are often remembered by the acronym ROYGBIV.
-
Prism Effect: A prism disperses light because different colors travel at different speeds in glass. This causes them to bend by different amounts.
-
Rainbows: Rainbows are natural examples of light dispersion. Water droplets in the atmosphere act like tiny prisms, splitting sunlight into its constituent colors.
-
Wavelengths: Each color of light has a different wavelength. Red has the longest wavelength, while violet has the shortest.
How Does Dispersion Occur?
Understanding how dispersion occurs can help us appreciate its beauty and complexity. Here are some key points about the process.
-
Refraction: Dispersion happens due to refraction, which is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another. Different colors bend by different amounts.
-
Angle of Incidence: The angle at which light enters a prism affects the degree of dispersion. A steeper angle results in more pronounced color separation.
-
Material Matters: The type of material the light passes through also affects dispersion. Glass and water are common dispersive materials.
-
Speed of Light: Light travels at different speeds in different media. This variation in speed causes the light to bend and separate into colors.
-
Critical Angle: When light hits a medium at a certain angle, known as the critical angle, it can cause total internal reflection, enhancing the dispersion effect.
Applications of Light Dispersion
Light dispersion isn't just a pretty sight; it has practical applications in various fields. Let's explore some of these uses.
-
Spectroscopy: Scientists use dispersion in spectroscopy to analyze the composition of substances. By studying the light spectrum, they can identify different elements.
-
Optical Instruments: Telescopes and microscopes use lenses and prisms to disperse light, improving image clarity and detail.
-
Fiber Optics: Dispersion is crucial in fiber optic communication. It helps in transmitting data over long distances with minimal loss.
-
Photography: Camera lenses use dispersion to correct color distortions, ensuring accurate color reproduction in photographs.
-
Art and Design: Artists and designers use the principles of light dispersion to create stunning visual effects and color schemes.
Fun Facts About Light Dispersion
Light dispersion has some quirky and fun aspects that make it even more interesting. Here are a few fun facts.
-
Double Rainbows: Sometimes, you can see a double rainbow. The second rainbow is fainter and has its colors reversed due to a second reflection inside the water droplets.
-
Moonbows: Moonbows are rainbows created by moonlight instead of sunlight. They are rare and usually appear white due to the low light intensity.
-
Haloes: Ice crystals in the atmosphere can cause haloes around the sun or moon. These are circular rings of light caused by dispersion.
-
Green Flash: Occasionally, just before sunrise or after sunset, a green flash can be seen. This is due to the dispersion of light in the atmosphere.
-
Auroras: The Northern and Southern Lights, or auroras, are caused by the dispersion of light in the Earth's atmosphere, creating stunning displays of color.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Dispersion of light has played a role in history and culture, influencing art, science, and even mythology. Here are some notable points.
-
Ancient Observations: Ancient civilizations, like the Greeks and Egyptians, observed and documented the dispersion of light, although they didn't fully understand it.
-
Mythology: In many cultures, rainbows are seen as bridges between the earthly and divine realms. Norse mythology, for example, describes the Bifröst as a rainbow bridge connecting Earth to the heavens.
-
Artistic Inspiration: Artists like Claude Monet and Vincent van Gogh were inspired by the effects of light dispersion, using it to create vibrant and dynamic paintings.
-
Scientific Milestones: Newton's work on light dispersion laid the foundation for modern optics and our understanding of light and color.
-
Cultural Symbolism: Rainbows are often used as symbols of hope, diversity, and unity in various cultures and movements.
Modern Research and Innovations
Research on light dispersion continues to evolve, leading to new discoveries and innovations. Here are some recent developments.
-
Quantum Optics: Scientists are exploring the quantum aspects of light dispersion, which could lead to advancements in quantum computing and communication.
-
Metamaterials: Researchers are developing metamaterials that can control light dispersion in unprecedented ways, potentially leading to new optical devices.
-
Solar Energy: Understanding light dispersion helps improve the efficiency of solar panels by optimizing the absorption of different wavelengths of light.
-
Medical Imaging: Advanced imaging techniques use light dispersion to provide clearer and more detailed images for medical diagnostics.
-
Environmental Monitoring: Dispersion-based sensors are used to monitor environmental conditions, such as air and water quality, by analyzing light spectra.
Everyday Examples of Light Dispersion
Light dispersion isn't just a scientific concept; it's something we encounter in everyday life. Here are some common examples.
-
CDs and DVDs: The shiny surface of CDs and DVDs creates a rainbow effect due to light dispersion.
-
Soap Bubbles: The thin film of soap bubbles disperses light, creating a colorful display.
Light's Colorful Journey
Light dispersion is more than just a pretty rainbow. It’s a fascinating phenomenon that reveals the hidden spectrum within white light. From prisms to raindrops, this process shows how different wavelengths bend at different angles, creating a spectrum of colors. Understanding this helps in fields like optics, meteorology, and even art.
Knowing these facts can make you appreciate everyday occurrences like rainbows or the colors in a soap bubble. It also highlights the importance of light in technology, from fiber optics to cameras. Next time you see a rainbow, remember the science behind it. Light’s colorful journey is a reminder of the wonders of nature and the intricate details that make up our world. Keep exploring, stay curious, and let the light guide your way.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
