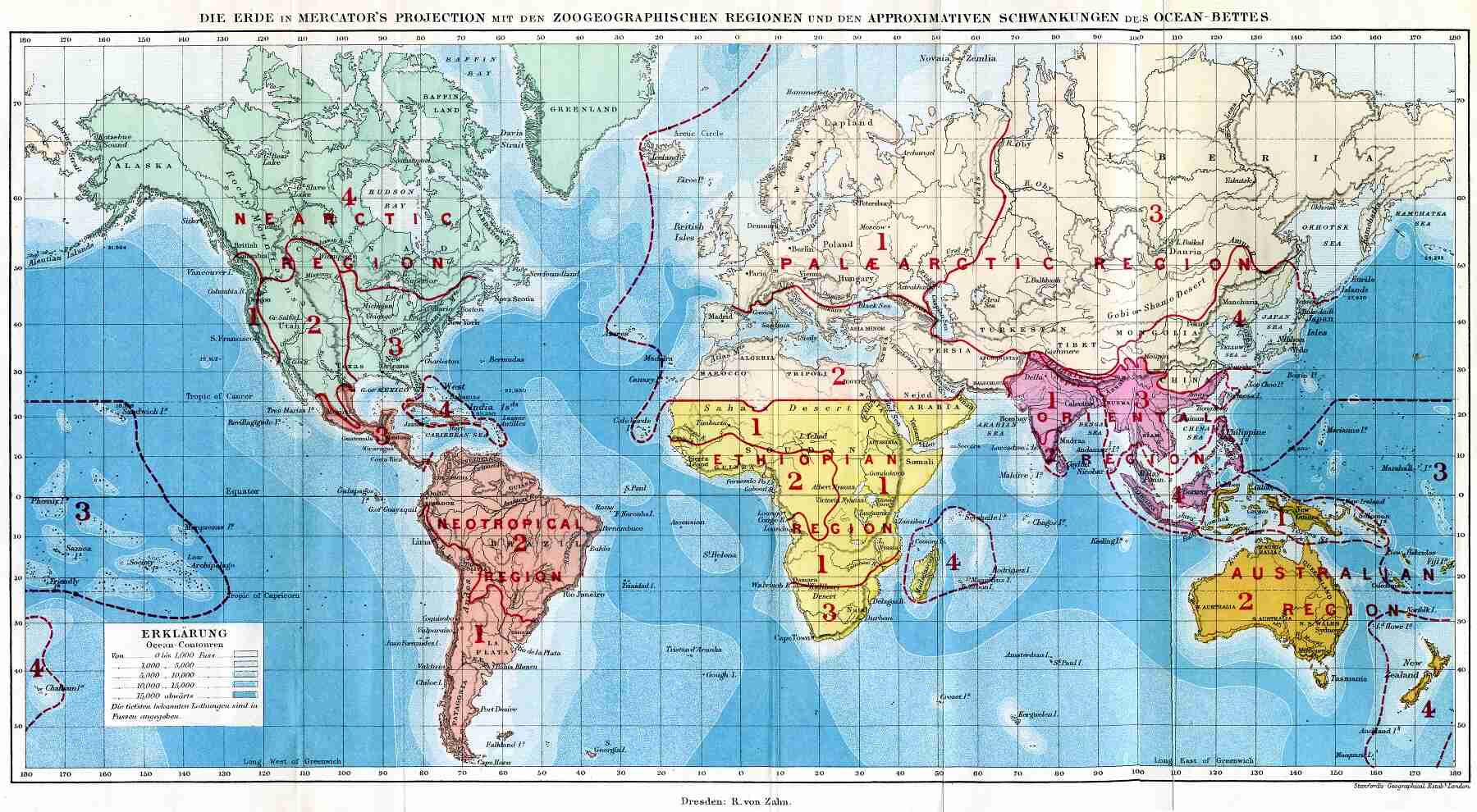
Biogeography is a fascinating field of study that explores the distribution of plant and animal species across the Earth’s surface. It delves into the intricate relationship between living organisms and their environment, shedding light on the factors that shape the biodiversity we see today. From the vast plains of Africa to the dense rainforests of South America, biogeography unveils the hidden stories behind the patterns of life on our planet.
In this article, we will uncover 20 surprising facts about biogeography that will not only amaze you but also deepen your understanding of how geography plays a crucial role in the formation and evolution of different ecosystems. From the discovery of unexpected species in remote locations to the remarkable connections between seemingly unrelated regions, biogeography allows us to connect the dots and unveil the intricate tapestry of life on Earth. So, let’s embark on this journey to uncover the hidden marvels of biogeography!
Key Takeaways:
- Biogeography studies how and why different species are distributed across the Earth, helping us predict invasive species and identify conservation priorities.
- Islands have high endemic species, and biogeography helps us understand the impacts of human activities on ecosystems, making it crucial for conservation efforts.
Biogeography studies the distribution of species across the Earth.
Biogeography is a field of study that examines how and why different species are distributed across the planet. It explores the patterns and processes that shape the biodiversity we see today.
The Wallace Line separates distinct biogeographical regions in Southeast Asia.
The Wallace Line, named after the naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace, marks the division between the Asian and Australian biogeographical regions. It is a significant boundary that influences the distribution of plant and animal species in the area.
Continental drift plays a major role in shaping biogeographical patterns.
The movement of Earth’s continents over millions of years has greatly impacted the distribution of species. It has resulted in the formation of land bridges, isolation of populations, and the emergence of unique ecosystems.
Islands often have a high number of endemic species.
Due to their isolated nature, islands tend to have a high number of endemic species – those that are found nowhere else in the world. This is because they have evolved independently and adapted to their specific island habitats.
Biogeography helps predict the spread of invasive species.
By understanding the patterns of species distribution, biogeographers can also identify areas vulnerable to the invasion of non-native species. This knowledge is crucial for implementing effective measures to control and manage invasive species.
The size of an island influences its species diversity.
Generally, larger islands have greater species diversity compared to smaller ones. This is because larger islands can support larger populations, provide more habitats, and offer a wider range of resources.
Biogeography is not limited to land-based habitats.
While terrestrial biogeography is well-known, the field also encompasses the study of marine and freshwater ecosystems. It examines the distribution of species in oceans, lakes, rivers, and other aquatic environments.
The Great Barrier Reef is home to a vast array of marine biodiversity.
Australia’s Great Barrier Reef is one of the most biodiverse regions on the planet, showcasing the intricate relationship between geography and the distribution of marine species.
Biogeography incorporates elements of ecology, geology, and evolutionary biology.
As a multidisciplinary field, biogeography draws upon various sciences to understand the complex interactions between organisms and their environments. It combines ecological principles with geological and evolutionary processes.
Islands can serve as natural laboratories for studying evolution.
Isolated islands provide unique opportunities to study the process of evolution. They often have a limited number of species, which allows for in-depth observations of speciation and adaptation.
Biogeography can help identify conservation priorities.
By mapping out the distribution of endangered species and identifying key habitats, biogeography plays a crucial role in setting conservation priorities and establishing protected areas.
The concept of biomes is central to biogeography.
Biomes are large-scale ecological areas characterized by their distinctive climate, vegetation, and animal life. Biogeography helps us understand the factors that shape and define different biomes around the world.
The movement of ice ages impacted species distribution.
During periods of glaciation, large ice sheets covered vast areas, causing species to retreat or move to more temperate regions. As the climate changed, species gradually migrated back into previously glaciated areas.
Biogeography can explain the distribution of certain diseases.
By studying the geographic distribution of diseases, researchers can better understand how diseases are spread and identify patterns and risk factors that contribute to their occurrence.
The Amazon Rainforest is a biogeographical hotspot.
The Amazon Rainforest is known for its exceptional biodiversity, housing countless unique species. Its complex and diverse biogeography makes it a globally significant region for conservation efforts.
Biogeography explores the movement of species over time.
Biogeographers investigate the migration and dispersal of species throughout history, uncovering how organisms have colonized new habitats and adapted to changing environments.
Biogeography can inform climate change research.
Understanding how species have responded to past climate changes helps scientists predict how they may respond to future environmental shifts. Biogeography provides valuable insights into the impacts of climate change on ecosystems.
The theory of island biogeography was developed by Robert MacArthur and E.O. Wilson.
The theory of island biogeography explores the factors that influence the number of species present on islands. It was developed to explain the patterns of species richness observed on different types of islands.
Biogeography can reveal the historical connections between different regions.
By studying the distribution of closely related species across different areas, biogeographers can uncover the historical connections between regions and trace the movement of ancestral populations.
Biogeography helps us understand the impacts of human activities on ecosystems.
Human activities, such as habitat destruction and climate change, have significant consequences for biodiversity. Biogeography provides a framework for assessing the impact of these activities and developing conservation strategies.
Conclusion
Biogeography is a fascinating field of study that reveals the intricate connections between living organisms and the Earth’s geographic features. Through the exploration of various biogeographical phenomena, we gain insight into the distribution, migration, and evolution of species across different habitats.
From the discovery of ancient fossils in unexpected locations to the extraordinary journeys undertaken by migratory birds, biogeography continuously surprises us with its complexity and beauty. By examining the historical and ecological factors that shape biodiversity patterns, we can better understand the delicate balance of life on our planet.
As we delve deeper into the study of biogeography, its significance in areas such as conservation, climate change research, and the understanding of our own origins becomes increasingly apparent. By unlocking the secrets of biogeography, we unlock a greater understanding of the world around us.
FAQs
1. What is biogeography?
Biogeography is the scientific study of the distribution of living organisms and their interactions with their environment across different geographic regions.
2. Why is biogeography important?
Biogeography helps us understand the patterns of biodiversity, species migration, and ecosystem functioning. It has implications in areas such as conservation, ecology, evolution, and even human health.
3. What are the main subfields of biogeography?
The main subfields of biogeography include historical biogeography, which studies the past distribution of species, ecological biogeography, which focuses on the present distribution and interactions of species, and conservation biogeography, which aims to protect and manage biodiversity.
4. How does biogeography contribute to conservation efforts?
By understanding the distribution patterns of species, biogeographers can help identify areas of high biodiversity and prioritize them for conservation efforts. They also play a crucial role in assessing the impact of habitat loss and climate change on species’ survival.
5. Can biogeography help us understand the effects of climate change?
Yes, biogeography helps us study how species respond and adapt to changes in their environment. By analyzing how different species have migrated or gone extinct in response to past climate shifts, scientists can make predictions about the future impacts of climate change on biodiversity.
6. How does biogeography help us understand human evolution?
Biogeography provides important insights into the origins and dispersal patterns of early human ancestors. By studying the distribution of hominin fossils and comparing them to other primates, scientists can infer how our early ancestors migrated and adapted to different environments.
7. What are some notable examples of biogeographical phenomena?
Notable examples include the Galapagos Islands, which inspired Darwin’s theory of evolution, and the Wallace Line, which separates distinct fauna between Indonesia and Australia. The migration of wildebeest in the Serengeti and the unique biodiversity found in rainforests and coral reefs are also fascinating biogeographical phenomena.
8. How does biogeography contribute to agricultural practices?
Biogeography helps farmers understand why certain crops thrive in specific regions and aids in the development of more efficient and sustainable farming practices. It also helps predict and control the spread of invasive species that can harm agricultural productivity.
9. Is biogeography limited to studying Earth’s ecosystems?
No, biogeography extends beyond Earth. Astrobiogeography examines the possibility of life on other planets and moons within our solar system, while exobiogeography explores the potential for life in distant galaxies.
10. How can I get involved in biogeography?
There are various ways to get involved in biogeography. You can pursue a degree or career in the field, participate in citizen science projects, contribute to biodiversity surveys, or simply stay informed about the latest research and conservation efforts.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.

