Intermolecular forces might sound like a complex topic, but they play a crucial role in our everyday lives. These forces are the invisible glue holding molecules together, affecting everything from the boiling point of water to the texture of ice cream. Understanding intermolecular forces helps explain why oil and water don't mix, why some substances evaporate quickly, and why others remain solid at room temperature. In this blog post, we'll dive into 36 fascinating facts about these forces, breaking down the science in a way that's easy to grasp. Get ready to see the world of molecules in a whole new light!
Understanding Intermolecular Forces
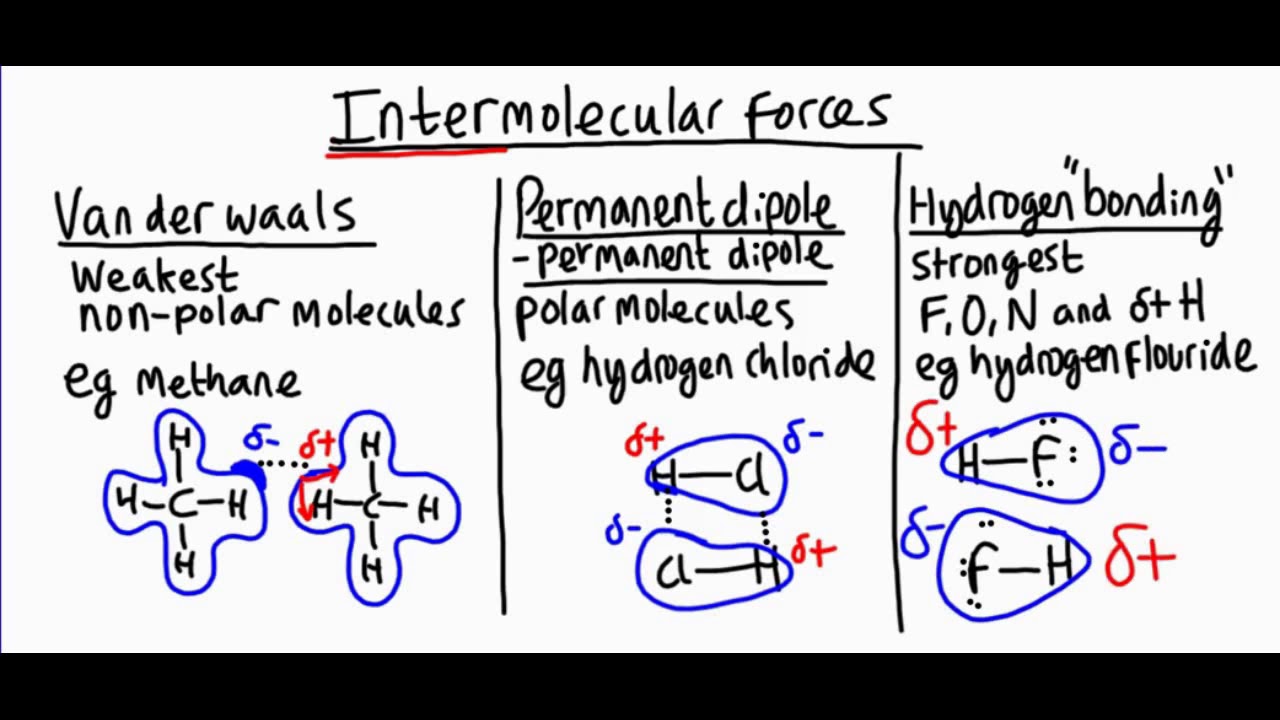
Intermolecular forces are the forces that hold molecules together. These forces are crucial in determining the physical properties of substances. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about these forces.
-
Intermolecular forces are weaker than intramolecular forces. Intramolecular forces, like covalent bonds, hold atoms together within a molecule. Intermolecular forces, on the other hand, are the attractions between molecules.
-
There are three main types of intermolecular forces. These include London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonds.
-
London dispersion forces are the weakest intermolecular forces. They arise due to temporary dipoles created when electrons move around a molecule.
-
All molecules experience London dispersion forces. Even nonpolar molecules, which lack permanent dipoles, exhibit these forces.
-
The strength of London dispersion forces increases with molecular size. Larger molecules have more electrons, leading to stronger temporary dipoles.
-
Dipole-dipole interactions occur between polar molecules. These forces arise from the attraction between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another.
-
Hydrogen bonds are a special type of dipole-dipole interaction. They occur when hydrogen is bonded to highly electronegative atoms like nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine.
-
Hydrogen bonds are stronger than regular dipole-dipole interactions. This is due to the high electronegativity of the atoms involved and the small size of hydrogen.
-
Water's high boiling point is due to hydrogen bonding. The strong hydrogen bonds between water molecules require significant energy to break.
-
Intermolecular forces affect melting and boiling points. Substances with stronger intermolecular forces have higher melting and boiling points.
The Role of Intermolecular Forces in Everyday Life
Intermolecular forces play a significant role in various everyday phenomena. They influence everything from the state of matter to the behavior of liquids and gases.
-
Surface tension in water is due to hydrogen bonding. The cohesive forces between water molecules create a "skin" on the surface.
-
Capillary action is influenced by intermolecular forces. This phenomenon allows liquids to flow in narrow spaces without external forces.
-
Intermolecular forces affect solubility. Polar substances dissolve in polar solvents, and nonpolar substances dissolve in nonpolar solvents due to similar intermolecular forces.
-
Viscosity is related to intermolecular forces. Substances with strong intermolecular forces tend to be more viscous.
-
Intermolecular forces are responsible for the formation of liquids and solids. Without these forces, all substances would exist as gases.
-
The unique properties of ice are due to hydrogen bonding. Ice is less dense than liquid water because hydrogen bonds create an open hexagonal structure.
-
Intermolecular forces influence evaporation rates. Substances with weaker intermolecular forces evaporate more quickly.
-
Intermolecular forces play a role in the formation of solutions. Solvent and solute molecules interact through these forces to form a homogeneous mixture.
-
The smell of substances is related to intermolecular forces. Volatile compounds with weaker intermolecular forces can easily vaporize and reach our noses.
-
Intermolecular forces affect the boiling points of liquids. Stronger forces result in higher boiling points, while weaker forces lead to lower boiling points.
Intermolecular Forces in Biological Systems
Intermolecular forces are crucial in biological systems, affecting the structure and function of biomolecules.
-
Hydrogen bonds stabilize the structure of DNA. The double helix is held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs.
-
Proteins rely on intermolecular forces for their structure. Hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, and van der Waals forces help maintain protein shape.
-
Cell membranes are influenced by intermolecular forces. The lipid bilayer is held together by hydrophobic interactions and van der Waals forces.
-
Enzyme-substrate interactions involve intermolecular forces. These forces help enzymes bind to their substrates and catalyze reactions.
-
Intermolecular forces play a role in drug design. Understanding these forces helps scientists create drugs that can effectively bind to their targets.
-
Hormones interact with receptors through intermolecular forces. These interactions trigger various biological responses.
-
Intermolecular forces affect the solubility of biomolecules. Polar biomolecules dissolve in water, while nonpolar biomolecules dissolve in lipids.
-
Hydrogen bonds are crucial for the function of nucleic acids. They help maintain the structure of RNA and DNA.
-
Intermolecular forces influence the folding of proteins. Proper folding is essential for protein function.
-
The stability of cell structures depends on intermolecular forces. These forces help maintain the integrity of cellular components.
Advanced Concepts in Intermolecular Forces
For those interested in deeper knowledge, here are some advanced concepts related to intermolecular forces.
-
Van der Waals forces encompass London dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions. These forces are named after Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals.
-
Intermolecular forces can be quantified using potential energy curves. These curves show the energy changes as molecules approach each other.
-
The Lennard-Jones potential describes intermolecular forces mathematically. It accounts for both attractive and repulsive forces between molecules.
-
Intermolecular forces play a role in phase transitions. Changes in temperature and pressure can alter the strength of these forces, leading to phase changes.
-
Supercritical fluids exhibit unique intermolecular interactions. These fluids have properties of both liquids and gases, influenced by intermolecular forces.
-
Intermolecular forces are essential in nanotechnology. Understanding these forces helps scientists manipulate materials at the nanoscale.
The Final Word on Intermolecular Forces
Intermolecular forces play a crucial role in determining the physical properties of substances. From boiling points to solubility, these forces dictate how molecules interact with each other. Understanding dispersion forces, dipole-dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonding can help explain why water is liquid at room temperature while oxygen is a gas. These forces also influence the viscosity and surface tension of liquids, impacting everything from how we cook to how we manufacture products. By grasping the basics of intermolecular forces, you gain insight into the behavior of materials in everyday life. Whether you're a student, a professional, or just curious, knowing these facts can make science more relatable and practical. So next time you see water boiling or oil not mixing with water, you'll know the invisible forces at play.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
