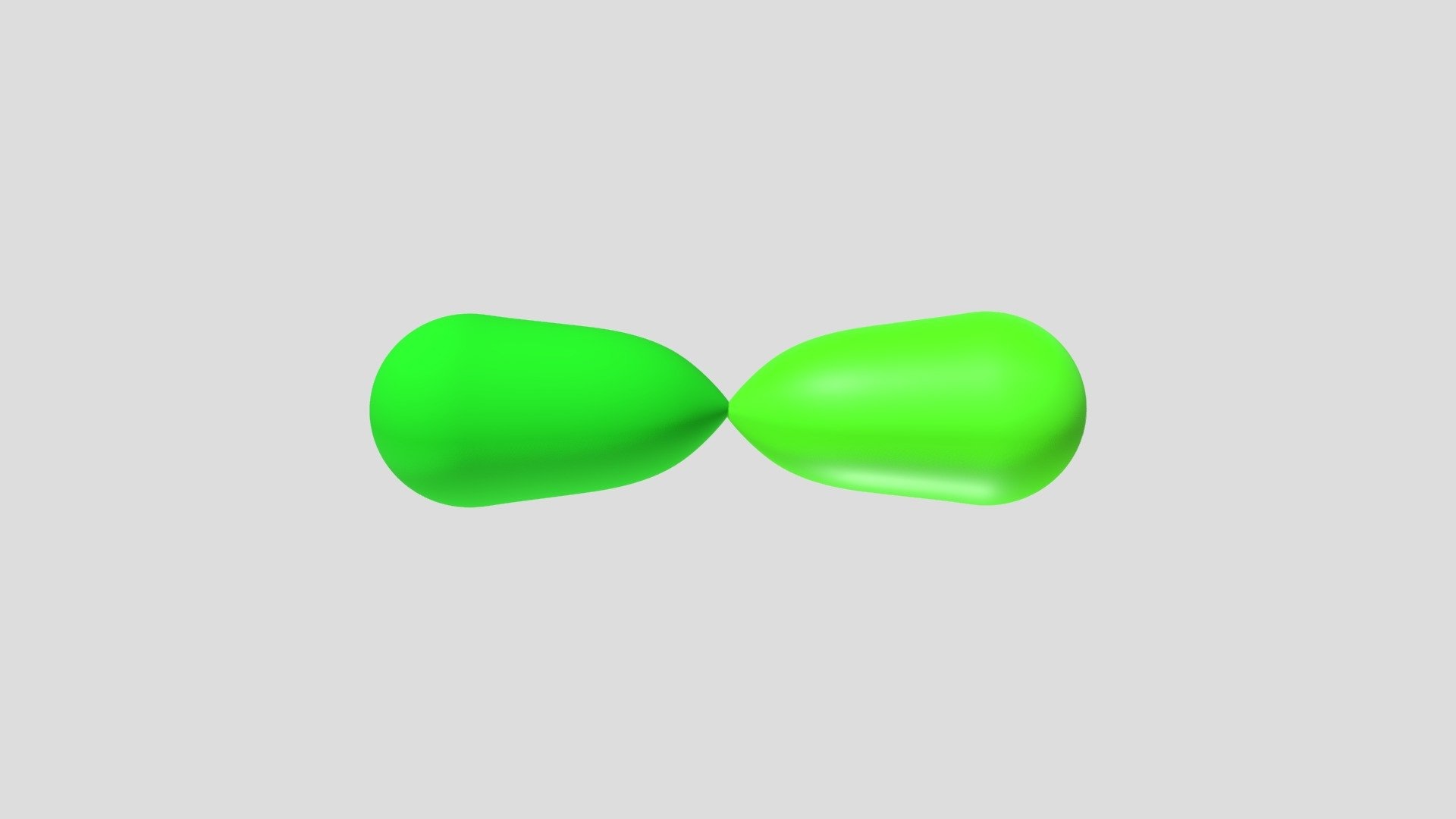
What is sp hybridization? sp hybridization is a concept in chemistry where one s orbital and one p orbital mix to form two equivalent hybrid orbitals. This type of hybridization is crucial for understanding the geometry of molecules like acetylene (C2H2) and carbon dioxide (CO2). In sp hybridization, the resulting orbitals are linear, with a bond angle of 180 degrees. This linear arrangement allows for the formation of strong sigma bonds, which are essential for the stability of certain molecules. Understanding sp hybridization helps explain the bonding and structure of molecules, making it a fundamental topic in chemistry.
What is sp Hybridization?
sp hybridization is a concept in chemistry that explains the formation of certain types of chemical bonds. It involves the mixing of one s orbital and one p orbital to create two equivalent sp hybrid orbitals. These orbitals are oriented 180 degrees apart, leading to linear molecular geometry.
- Linear Geometry: sp hybridization results in a linear shape, meaning the bond angle between the two hybrid orbitals is 180 degrees.
- Two Hybrid Orbitals: Only two hybrid orbitals are formed in sp hybridization, each containing one electron.
- Involves s and p Orbitals: Specifically, one s orbital and one p orbital mix to form sp hybrid orbitals.
- Occurs in Triple Bonds: Commonly seen in molecules with triple bonds, such as acetylene (C2H2).
- Single Bonds: Also occurs in molecules with single bonds, like beryllium chloride (BeCl2).
Examples of sp Hybridization
Understanding sp hybridization becomes easier with examples. Here are some common molecules where sp hybridization is observed.
- Acetylene (C2H2): Each carbon atom in acetylene uses sp hybrid orbitals to form a triple bond with the other carbon.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): The carbon atom in CO2 uses sp hybrid orbitals to form double bonds with two oxygen atoms.
- Beryllium Chloride (BeCl2): Beryllium in BeCl2 uses sp hybrid orbitals to form single bonds with two chlorine atoms.
- Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN): The carbon atom in HCN uses sp hybrid orbitals to form a triple bond with nitrogen and a single bond with hydrogen.
Characteristics of sp Hybrid Orbitals
sp hybrid orbitals have unique characteristics that differentiate them from other types of hybrid orbitals.
- Equal Energy: The two sp hybrid orbitals have the same energy level.
- Directional: These orbitals are highly directional, pointing in opposite directions.
- Symmetrical: The shape of sp hybrid orbitals is symmetrical around the nucleus.
- Strong Bonds: Bonds formed using sp hybrid orbitals are generally stronger due to better overlap.
- Electron Density: The electron density in sp hybrid orbitals is concentrated along the bond axis.
Importance in Molecular Geometry
sp hybridization plays a crucial role in determining the geometry of molecules.
- Linear Shape: Molecules with sp hybridization exhibit a linear shape.
- Bond Angles: The bond angles in sp hybridized molecules are always 180 degrees.
- Predicting Shapes: Helps in predicting the shapes of molecules in chemical reactions.
- Molecular Symmetry: Contributes to the overall symmetry of the molecule.
- Reactivity: Influences the reactivity of molecules by affecting bond strengths.
sp Hybridization in Organic Chemistry
In organic chemistry, sp hybridization is a fundamental concept that helps explain the structure and reactivity of various organic molecules.
- Alkynes: All alkynes exhibit sp hybridization at the carbon atoms involved in the triple bond.
- Nitriles: Carbon atoms in nitriles (R-CN) are sp hybridized.
- Carbenes: Some carbenes (R2C:) can exhibit sp hybridization.
- Allenes: Central carbon atoms in allenes (C=C=C) are sp hybridized.
- Isocyanides: Carbon atoms in isocyanides (R-NC) are sp hybridized.
sp Hybridization and Bond Strength
The type of hybridization can affect the strength and length of bonds in a molecule.
- Shorter Bonds: Bonds involving sp hybrid orbitals are generally shorter.
- Stronger Bonds: These bonds are also stronger compared to those involving sp2 or sp3 hybrid orbitals.
- Bond Dissociation Energy: Higher bond dissociation energy is observed in sp hybridized bonds.
- Triple Bonds: Triple bonds are stronger and shorter due to sp hybridization.
- Bond Length: The bond length in sp hybridized molecules is typically shorter than in sp2 or sp3 hybridized molecules.
Applications of sp Hybridization
Understanding sp hybridization has practical applications in various fields of science and technology.
- Material Science: Helps in designing materials with specific properties.
- Pharmaceuticals: Important in drug design and understanding molecular interactions.
- Nanotechnology: Used in the development of nanomaterials.
- Chemical Synthesis: Crucial for designing synthetic pathways in organic chemistry.
The Essence of sp Hybridization
sp hybridization is a fascinating concept in chemistry. It explains how atoms form bonds in molecules like acetylene. This hybridization involves the mixing of one s orbital and one p orbital, creating two sp hybrid orbitals. These orbitals form linear structures, making molecules more stable and predictable.
Understanding sp hybridization helps in predicting molecular shapes and bond angles. It’s crucial for grasping the behavior of molecules in reactions. This knowledge is not just for chemists; it’s useful in fields like materials science, pharmacology, and environmental science.
By mastering sp hybridization, you gain a deeper insight into the molecular world. It’s a key piece of the puzzle in understanding how molecules interact and react. So, keep exploring and learning about these fundamental concepts. They’re the building blocks of much of the science that shapes our world.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
