Gabriel synthesis is a fascinating chemical reaction used to create primary amines from potassium phthalimide and alkyl halides. Did you know that this method, named after the German chemist Siegmund Gabriel, has been a cornerstone in organic chemistry since the late 19th century? Why is it so important? Because it offers a straightforward way to produce amines, which are essential in pharmaceuticals, dyes, and polymers. Imagine the impact on medicine and industry without this reaction! Want to know more? Stick around as we dive into 30 intriguing facts about Gabriel synthesis, from its historical roots to modern applications.
What is Gabriel Synthesis?
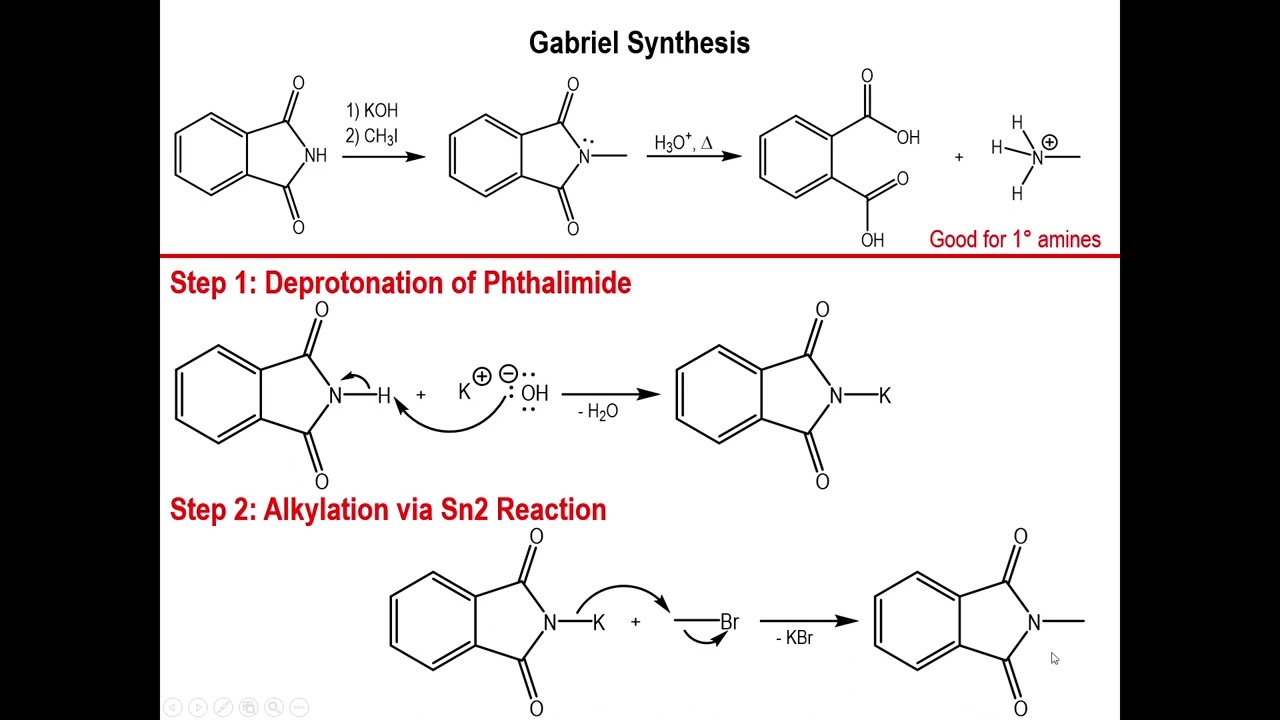
Gabriel synthesis is a chemical reaction used to transform primary alkyl halides into primary amines. This method is named after the German chemist Siegmund Gabriel. It's a reliable way to create amines, which are essential in many fields, including pharmaceuticals and agriculture.
-
Invented by Siegmund Gabriel: The reaction was first reported by Siegmund Gabriel in 1887. He was a pioneer in organic chemistry.
-
Uses Phthalimide: The reaction involves phthalimide, a compound derived from phthalic acid. Phthalimide acts as a nucleophile in this process.
-
Primary Amines: Gabriel synthesis specifically produces primary amines, which have one alkyl or aryl group attached to the nitrogen atom.
How Does Gabriel Synthesis Work?
Understanding the mechanism of Gabriel synthesis helps in appreciating its utility and efficiency. The process involves several steps, each crucial for the successful formation of primary amines.
-
Formation of Potassium Phthalimide: The first step involves treating phthalimide with potassium hydroxide to form potassium phthalimide.
-
Nucleophilic Substitution: Potassium phthalimide then reacts with an alkyl halide through nucleophilic substitution, forming N-alkylphthalimide.
-
Hydrolysis: The final step involves hydrolyzing N-alkylphthalimide to release the primary amine and phthalic acid.
Applications of Gabriel Synthesis
Gabriel synthesis is not just a laboratory curiosity; it has practical applications in various industries. Its ability to produce primary amines makes it invaluable.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Many drugs contain primary amines, making Gabriel synthesis crucial in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
-
Agriculture: Primary amines are used in the production of pesticides and herbicides.
-
Dyes and Pigments: The synthesis of certain dyes and pigments also relies on primary amines.
Advantages of Gabriel Synthesis
Gabriel synthesis offers several benefits that make it a preferred method for producing primary amines. These advantages highlight its efficiency and reliability.
-
Selectivity: The reaction is highly selective for primary amines, reducing the risk of unwanted by-products.
-
Mild Conditions: The reaction can be carried out under relatively mild conditions, making it safer and more practical.
-
High Yield: Gabriel synthesis often results in high yields of the desired product, making it economically viable.
Limitations of Gabriel Synthesis
Despite its advantages, Gabriel synthesis has some limitations. Understanding these can help in choosing the right method for amine production.
-
Not Suitable for Secondary or Tertiary Amines: The method is specific to primary amines and cannot be used to produce secondary or tertiary amines.
-
Limited to Alkyl Halides: The reaction requires alkyl halides, limiting its applicability to compounds containing these groups.
-
Hydrolysis Step: The hydrolysis step can sometimes be challenging, requiring specific conditions to proceed efficiently.
Variations of Gabriel Synthesis
Over the years, chemists have developed variations of the original Gabriel synthesis to overcome some of its limitations and expand its utility.
-
Gabriel-Colman Rearrangement: This variation involves the rearrangement of N-alkylphthalimides to produce different amines.
-
Gabriel-Malonic Ester Synthesis: This method uses malonic esters to produce amino acids, expanding the scope of Gabriel synthesis.
-
Microwave-Assisted Gabriel Synthesis: Using microwave irradiation can speed up the reaction and improve yields.
Interesting Facts About Gabriel Synthesis
Gabriel synthesis has a rich history and some fascinating aspects that make it a topic of interest beyond its practical applications.
-
Named After Its Inventor: Unlike many reactions named after their discoverers, Gabriel synthesis is directly named after Siegmund Gabriel, honoring his contribution.
-
Over a Century Old: The reaction has been in use for over 130 years, showcasing its enduring relevance in chemistry.
-
Educational Tool: Gabriel synthesis is often taught in organic chemistry courses due to its straightforward mechanism and practical importance.
Real-World Examples of Gabriel Synthesis
Gabriel synthesis is not just a theoretical concept; it has been used in various real-world applications, demonstrating its practical value.
-
Antibiotic Production: Some antibiotics are synthesized using Gabriel synthesis, highlighting its importance in medicine.
-
Herbicide Manufacturing: Certain herbicides are produced using primary amines obtained through Gabriel synthesis.
-
Synthetic Fibers: The production of some synthetic fibers involves primary amines, making Gabriel synthesis a key step in their manufacture.
Environmental Impact of Gabriel Synthesis
Like all chemical reactions, Gabriel synthesis has an environmental footprint. Understanding its impact can help in developing greener alternatives.
-
Waste Generation: The reaction produces phthalic acid as a by-product, which needs to be managed properly.
-
Solvent Use: The reaction often requires organic solvents, which can have environmental implications.
-
Energy Consumption: Although the reaction can be carried out under mild conditions, it still requires energy input, contributing to its overall environmental impact.
Future of Gabriel Synthesis
The future of Gabriel synthesis looks promising, with ongoing research aimed at improving its efficiency and expanding its applications.
-
Green Chemistry: Efforts are being made to develop greener versions of Gabriel synthesis, reducing its environmental impact.
-
New Applications: Researchers are exploring new applications for primary amines, potentially increasing the demand for Gabriel synthesis.
-
Technological Advancements: Advances in technology, such as microwave-assisted synthesis, are making Gabriel synthesis faster and more efficient.
Final Thoughts on Gabriel Synthesis
Gabriel synthesis is a fascinating method for creating primary amines. It's been around since the late 19th century, thanks to Siegmund Gabriel. This technique is especially useful because it avoids the over-alkylation problem common in other methods. By using phthalimide as a starting material, chemists can efficiently produce primary amines with fewer side reactions.
Understanding this process is crucial for anyone interested in organic chemistry. It’s not just about making amines; it’s about doing so in a way that’s both efficient and reliable. This method has stood the test of time, proving its value in both academic and industrial settings.
So, whether you're a student, a professional chemist, or just someone curious about chemistry, Gabriel synthesis offers a glimpse into the ingenuity and precision that define this field. Keep exploring, keep learning, and who knows what you might discover next!
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
