What is Xenon? Xenon is a colorless, odorless gas found in the Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Why is Xenon important? This noble gas plays a crucial role in various fields, from lighting to medical imaging. Where can you find Xenon? It's often extracted from the air through a process called fractional distillation. How is Xenon used? Xenon is used in high-intensity lamps, ion propulsion systems for spacecraft, and even in anesthesia. Is Xenon safe? Generally, yes, but it can be dangerous in high concentrations. Why should you care about Xenon? Its unique properties make it invaluable in scientific research and technology. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 28 fascinating facts about this intriguing element!
What is Xenon?
Xenon is a fascinating element with many unique properties and uses. This noble gas, found in the Earth's atmosphere, has a variety of applications in science, technology, and medicine. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about xenon.
-
Xenon is a Noble Gas
Xenon belongs to the noble gases group in the periodic table. These gases are known for their lack of reactivity due to having a full valence electron shell. -
Discovered in 1898
Xenon was discovered by Scottish chemist William Ramsay and English chemist Morris Travers in 1898. They found it while studying the residue left after evaporating liquid air. -
Named After the Greek Word for "Stranger"
The name "xenon" comes from the Greek word "xenos," meaning stranger. This name reflects its rarity and mysterious nature. -
Colorless and Odorless
Xenon is a colorless, odorless gas under standard conditions. It remains invisible to the naked eye. -
Heavy Noble Gas
Xenon is one of the heaviest noble gases, with an atomic number of 54 and an atomic weight of approximately 131.29.
Uses of Xenon
Xenon has a wide range of applications, from lighting to medical imaging. Here are some of the most interesting uses of this versatile element.
-
Used in Flash Lamps
Xenon is commonly used in flash lamps for photography. These lamps produce intense, short bursts of light, perfect for capturing high-speed images. -
Xenon Headlights
Many modern vehicles use xenon headlights. These lights are brighter and more energy-efficient than traditional halogen bulbs. -
Anesthetic Properties
Xenon has anesthetic properties and is sometimes used in medical anesthesia. It is preferred for its minimal side effects and rapid recovery times. -
Space Propulsion
Xenon is used as a propellant in ion thrusters for spacecraft. Its high atomic mass makes it an efficient choice for generating thrust in the vacuum of space. -
Medical Imaging
Xenon gas is used in medical imaging, particularly in lung imaging. It helps create clear images of the respiratory system.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Xenon's physical and chemical properties make it unique among the elements. Here are some key characteristics.
-
High Density
Xenon has a high density compared to other gases. This property makes it useful in various scientific applications. -
Low Boiling Point
Xenon has a boiling point of -108.1 degrees Celsius (-162.6 degrees Fahrenheit). This low boiling point is typical of noble gases. -
Forms Compounds
Unlike most noble gases, xenon can form compounds with other elements. Xenon hexafluoroplatinate was the first noble gas compound discovered. -
Inert but Reactive
While generally inert, xenon can react under extreme conditions. It forms compounds with fluorine and oxygen, among others. -
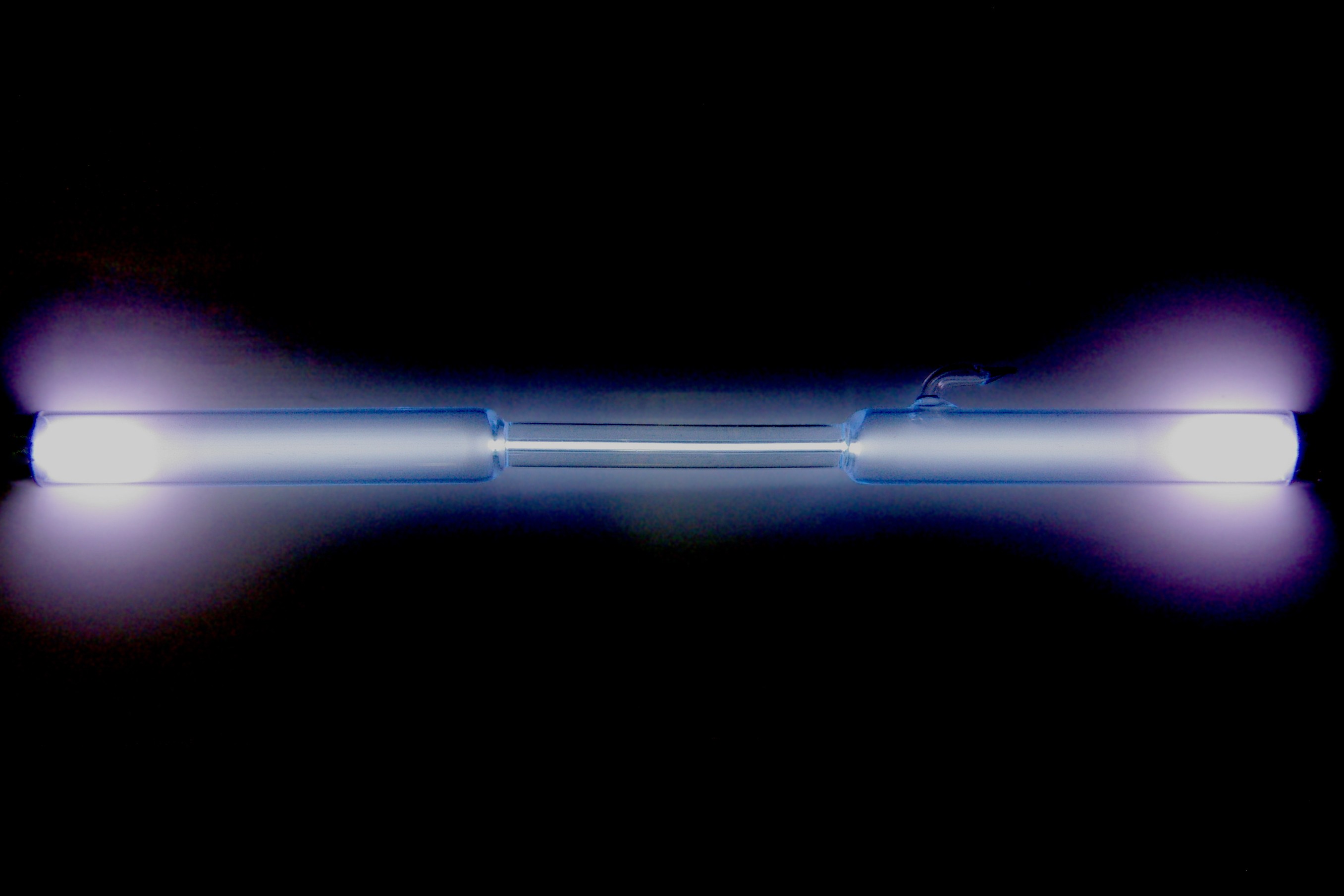
Emits Blue Light
When electrically excited, xenon emits a beautiful blue light. This property is utilized in various lighting applications.
Interesting Facts About Xenon
Beyond its practical uses, xenon has some fascinating trivia associated with it. Here are a few more intriguing facts.
-
Rare in Earth's Atmosphere
Xenon is extremely rare in the Earth's atmosphere, making up only about 0.0000087% by volume. -
Used in Plasma TVs
Plasma TVs use xenon gas to produce images. The gas is ionized to create plasma, which then emits light. -
Xenon in Lasers
Xenon is used in excimer lasers, which are employed in eye surgery and semiconductor manufacturing. -
Detecting Neutrinos
Xenon is used in experiments to detect neutrinos, elusive particles that are difficult to observe. -
Nuclear Reactor Coolant
Xenon can be used as a coolant in nuclear reactors due to its high thermal conductivity.
Fun Facts About Xenon
Xenon isn't just about serious science; it has some fun and quirky aspects too. Check out these fun facts.
-
Xenon in Fiction
Xenon often appears in science fiction. It's portrayed as a futuristic element with various advanced uses. -
Xenon in the Atmosphere of Mars
Scientists have detected xenon in the atmosphere of Mars, providing clues about the planet's history. -
Xenon and the Aurora Borealis
Xenon contributes to the colors seen in the aurora borealis. Its presence helps create the stunning light displays. -
Xenon in Deep-Sea Diving
Deep-sea divers sometimes use xenon in their breathing mixtures to prevent nitrogen narcosis. -
Xenon in Clocks
Xenon is used in some atomic clocks, which are incredibly accurate timekeeping devices. -
Xenon in Superconductors
Xenon can be used in the production of superconductors, materials that conduct electricity without resistance. -
Xenon in the Human Body
Small amounts of xenon are present in the human body, though its role is not well understood. -
Xenon and the Big Bang
Xenon isotopes provide valuable information about the early universe and the Big Bang.
The Final Word on Xenon
Xenon isn't just another element on the periodic table. It's a noble gas with some pretty cool uses. From lighting up movie projectors to powering spacecraft, xenon has found its place in both everyday life and advanced technology. Its unique properties make it valuable in medical imaging and anesthesia. Plus, it's a key player in scientific research. Understanding xenon gives us a glimpse into the complex world of chemistry and physics. So next time you see a bright light or hear about space missions, remember that xenon might be behind it. This versatile element continues to surprise and impress, proving that even the rarest gases can have a big impact.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
