Oncogenes are a captivating and essential topic in the field of biology. These genes play a crucial role in the development of cancer, making them a subject of intense research and investigation. Understanding oncogenes is instrumental in unravelling the complex mechanisms behind the formation and progression of various types of cancer. In this article, we will delve into 19 fascinating facts about oncogenes that will broaden your knowledge and give you a deeper understanding of their significance in cancer biology. From their discovery to their impact on cellular processes, these facts showcase the intricate nature of oncogenes and their implications for both scientific research and potential therapeutic interventions. So, let’s dive into the intriguing world of oncogenes and unravel the mysteries surrounding them.
Key Takeaways:
- Oncogenes are like troublemaking genes that can turn normal cells into cancerous ones. They can be activated by mutations, viruses, and lifestyle factors, but targeted therapies offer hope for cancer treatment.
- Understanding oncogenes is crucial for developing new cancer treatments. Their role in promoting uncontrolled cell growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis provides valuable insights for innovative therapies in precision medicine.
Oncogenes play a crucial role in cancer development.
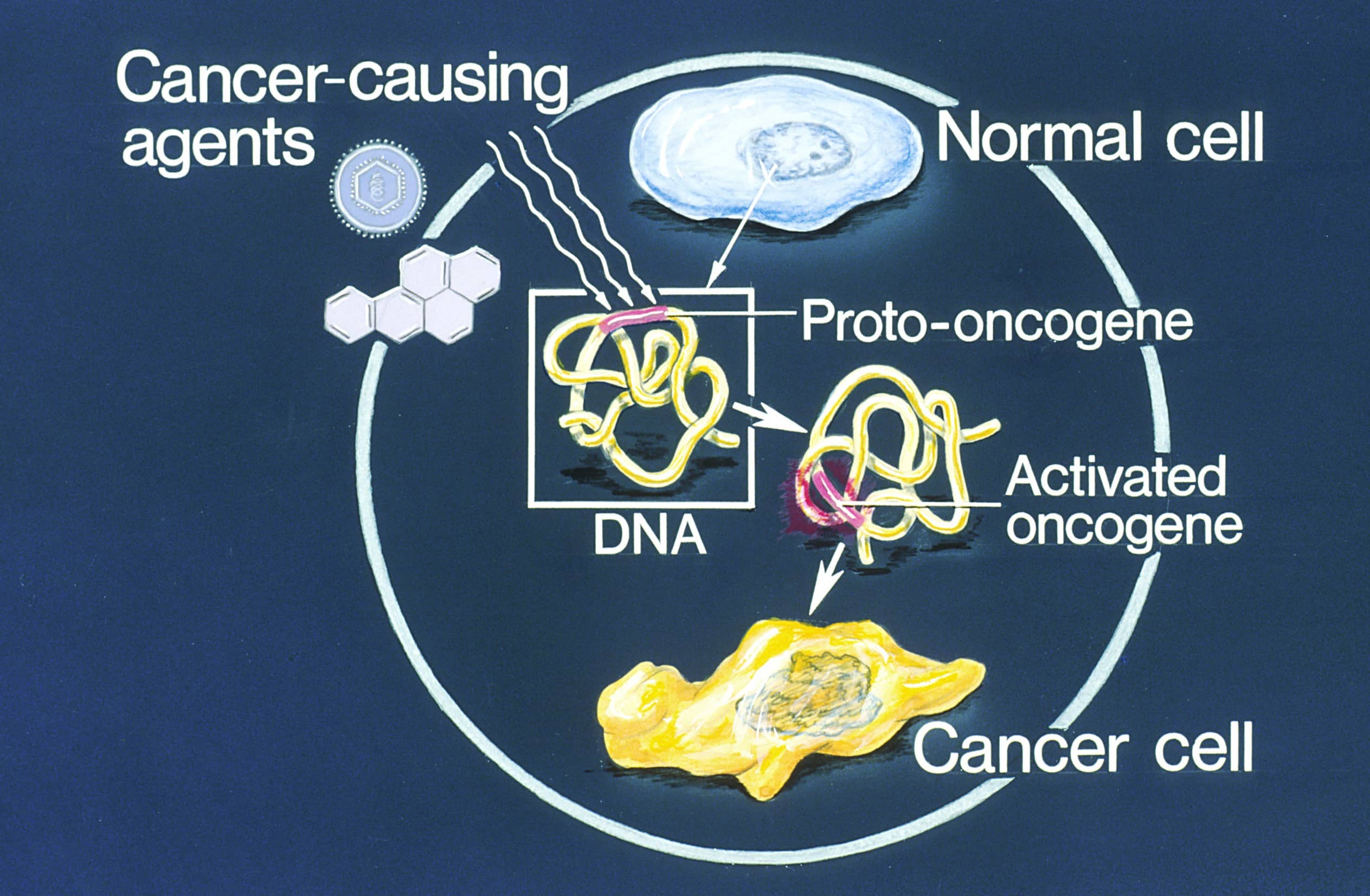
Oncogenes are specific genes that have the potential to transform normal cells into cancerous ones. Their activation or overexpression can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and division, ultimately contributing to the development of cancer.
There are several types of oncogenes.
Scientists have identified various types of oncogenes that are involved in different cellular processes. Some examples include proto-oncogenes, viral oncogenes, and mutated oncogenes.
Oncogenes can be activated by mutations.
Mutations in oncogenes can result in their activation, leading to the disruption of normal cell growth and division. These mutations can be caused by environmental factors, exposure to certain chemicals, or inherited genetic abnormalities.
Activation of oncogenes can be triggered by viruses.
Some viruses, such as human papillomavirus (HPV) and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), have been linked to the activation of oncogenes. These viruses can insert their genetic material into the host cell’s DNA, altering the function of oncogenes and promoting cancer development.
Oncogenes can promote angiogenesis.
Angiogenesis is the process of forming new blood vessels, and oncogenes can stimulate this process. Increased angiogenesis provides tumors with the necessary nutrients and oxygen for their growth and metastasis.
Certain lifestyle factors can influence oncogene activity.
Factors such as tobacco smoke, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and exposure to UV radiation can influence the activity of oncogenes, increasing the risk of cancer development.
Oncogenes can affect cell signaling pathways.
Oncogenes can disrupt normal cell signaling pathways, leading to the uncontrolled growth and division of cells. This can result in the formation of tumors and the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
Some oncogenes are associated with specific types of cancer.
Certain oncogenes have been found to be strongly associated with specific types of cancer. For example, the HER2 oncogene is frequently amplified in breast cancer, while the BCR-ABL oncogene is commonly found in chronic myeloid leukemia.
Oncogenes can be targeted for cancer treatment.
Targeted therapies that aim to inhibit the activity of specific oncogenes have shown promising results in cancer treatment. These therapies can help suppress the growth and progression of tumors, improving patient outcomes.
Epigenetic modifications can influence oncogene expression.
Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modifications, can affect the expression of oncogenes. Abnormal epigenetic changes can lead to the activation or silencing of oncogenes, contributing to cancer development.
Oncogenes can be inherited.
Some oncogenes can be passed down through generations. Inherited mutations in these genes can increase an individual’s susceptibility to certain types of cancer.
Mutations in tumor suppressor genes can lead to oncogene activation.
Tumor suppressor genes help regulate cell growth and division. Mutations in these genes can disrupt their normal function, leading to the activation of oncogenes and the development of cancer.
Activated oncogenes can drive uncontrolled cell division.
Oncogenes can override the normal mechanisms that control cell division, leading to the uncontrolled proliferation of cancer cells. This accelerated cell division contributes to tumor growth.
Oncogenes can influence cell survival and apoptosis.
Some oncogenes can promote cell survival and inhibit programmed cell death, or apoptosis. This ability to evade cell death mechanisms allows cancer cells to survive and proliferate.
Some oncogenes have prognostic significance.
The presence or activity of certain oncogenes can provide valuable prognostic information in cancer patients. High levels of certain oncogenes may indicate a more aggressive cancer and a poorer prognosis.
Interactions between oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes are crucial in cancer development.
Imbalances between oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes play a critical role in the initiation and progression of cancer. An intact and balanced interplay between these genes is essential for maintaining proper cellular homeostasis.
Oncogenes can be used as therapeutic targets in precision medicine.
The identification of specific oncogenes and their associated molecular pathways has paved the way for targeted therapies in precision medicine. These therapies aim to inhibit the activity of oncogenes, specifically tailored to the individual patient’s cancer.
Some oncogenes can promote metastasis.
Metastasis is the spread of cancer cells from the primary tumor to other parts of the body. Certain oncogenes can enhance the ability of cancer cells to invade surrounding tissues and travel to distant sites, contributing to the metastatic process.
Understanding oncogenes helps in the development of novel cancer treatments.
Advancements in our understanding of oncogenes and their role in cancer development have been instrumental in the development of new and innovative cancer therapies. These treatments hold the potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden of cancer worldwide.
Conclusion
Understanding oncogenes is vital for comprehending the development and progression of cancer. These genes play a significant role in the transformation of normal cells into cancerous cells. Through various mutations and alterations, oncogenes can drive uncontrolled cell growth, evade cell death mechanisms, and promote tumor formation.
Despite their association with cancer, oncogenes have also revealed several intriguing aspects of cellular biology. Their discovery has revolutionized the field of cancer research, leading to the development of targeted therapies and personalized medicine.
By unraveling the complexities of oncogenes, scientists are inching closer to finding more effective treatments and preventive measures for cancer. The ongoing research in this area promises to bring about significant breakthroughs that will ultimately improve the lives of millions of people affected by cancer.
FAQs
1. What are oncogenes?
Oncogenes are specific genes that have the potential to cause cancer when they become altered or mutated. They can promote uncontrolled cell growth, inhibit normal cell death mechanisms, and contribute to the development and progression of tumors.
2. How do oncogenes differ from tumor suppressor genes?
Oncogenes promote cell growth, while tumor suppressor genes regulate cell division and inhibit the formation of tumors. Alterations or mutations in oncogenes result in their activation, while mutations in tumor suppressor genes lead to their inactivation.
3. Can oncogenes be inherited?
While some genetic predispositions to cancer can be inherited, most oncogenes are acquired through environmental factors, such as exposure to carcinogens or viruses, or through random mutations that occur during a person’s lifetime.
4. Are all cancers caused by oncogenes?
No, not all cancers are caused by oncogenes. Cancer is a complex disease that can involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. While oncogenes can play a significant role in the development of certain cancers, other factors, such as tumor suppressor gene mutations, epigenetic changes, and immune system dysfunction, also contribute to cancer formation.
5. Can oncogenes be targeted for cancer treatment?
Yes, oncogenes can be targeted for cancer treatment. The development of targeted therapies, such as kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies, has paved the way for precision medicine approaches that specifically block the activity of oncogenes or their downstream pathways.
6. Are all oncogenes the same in different types of cancer?
No, different types of cancer can have different oncogenes driving their development. For example, the BRAF oncogene is commonly found in melanoma, while the HER2 oncogene is frequently associated with breast cancer. The specific oncogenes involved in a particular cancer type depend on the underlying genetic and molecular alterations.
Oncogenes' captivating role in cancer development sparks curiosity about cellular processes. Exploring cell cycle regulation reveals astonishing facts that deepen our understanding of cancer biology. Unraveling the complexities of oncogenes and cell cycle control opens doors to groundbreaking discoveries in cancer research. Dive into the fascinating world of cellular mechanisms and their impact on cancer progression.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
